Process variable on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In
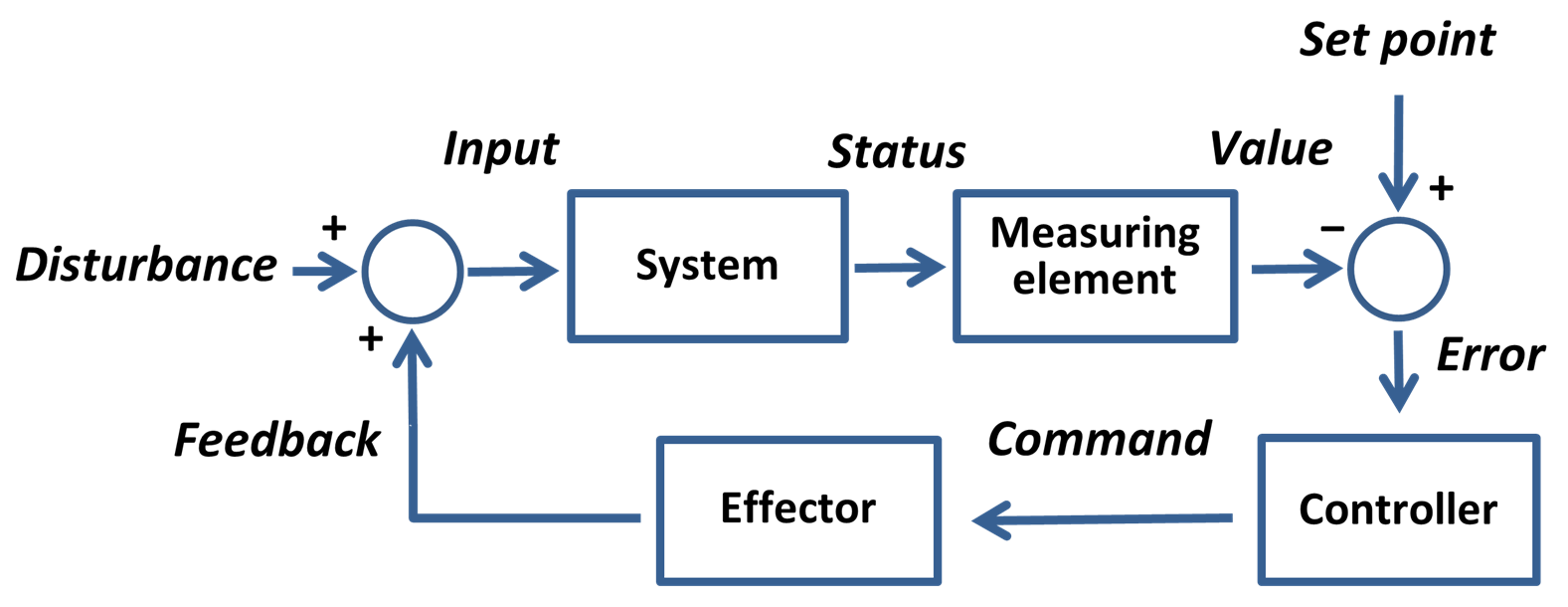 Measurement of process variables is essential in
Measurement of process variables is essential in
control theory
Control theory is a field of mathematics that deals with the control of dynamical systems in engineered processes and machines. The objective is to develop a model or algorithm governing the application of system inputs to drive the system to a ...
, a process variable (PV; also process value or process parameter) is the current measured value of a particular part of a process which is being monitored or controlled. An example of this would be the temperature of a furnace. The current temperature is the process variable, while the desired temperature is known as the set-point (SP).
Control system use
 Measurement of process variables is essential in
Measurement of process variables is essential in control system
A control system manages, commands, directs, or regulates the behavior of other devices or systems using control loops. It can range from a single home heating controller using a thermostat controlling a domestic boiler to large industrial ...
s to controlling a process. The value of the process variable is continuously monitored so that control may be exerted.
Four commonly measured variables that affect chemical and physical processes are: pressure
Pressure (symbol: ''p'' or ''P'') is the force applied perpendicular to the surface of an object per unit area over which that force is distributed. Gauge pressure (also spelled ''gage'' pressure)The preferred spelling varies by country a ...
, temperature
Temperature is a physical quantity that expresses quantitatively the perceptions of hotness and coldness. Temperature is measured with a thermometer.
Thermometers are calibrated in various temperature scales that historically have relied on ...
, level and flow. but there are in fact a large number of measurement quantities which for international purposes use the International System of Units (SI)
The SP-PV error is used to exert control on a process so that the value of PV equals the value of the SP. A classic use of this is in the
PID controller
A proportional–integral–derivative controller (PID controller or three-term controller) is a control loop mechanism employing feedback that is widely used in industrial control systems and a variety of other applications requiring continuou ...
.
References
Control theory {{Tech-stub