|
Rectus
"Rectus" is the Latin word meaning "straight" and is used in English to refer to multiple topics in the sciences, including: In molecular chemistry the ''R'' in the ''R'' & ''S'' isomerism stands for "rectus" In grammar "casus rectus" is a formal term for nominative case In mathematics sine is also known as "sinus rectus" In the classification of the animal kingdom it is the systematic taxonomic name of several species, ''e.g.'' campylobacter rectus & syllitus rectus In anatomy it is used to refer to a rectus muscle, primarily ''e.g.'' the "rectus abdominis muscle"; in anatomy it can also refer to: *Inferior rectus muscle *Superior rectus muscle *Lateral rectus muscle *Medial rectus muscle * Musculus rectus thoracis *Rectus capitis lateralis muscle *Rectus femoris muscle The rectus femoris muscle is one of the four quadriceps muscles of the human body. The others are the vastus medialis, the vastus intermedius (deep to the rectus femoris), and the vastus lateralis. All fou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Superior Rectus Muscle
The superior rectus muscle is a muscle in the orbit. It is one of the extraocular muscles. It is innervated by the superior division of the oculomotor nerve (III). In the primary position (looking straight ahead), its primary function is elevation, although it also contributes to intorsion and adduction. It is associated with a number of medical conditions, and may be weak, paralysed, overreactive, or even congenitally absent in some people. Structure The superior rectus muscle originates from the annulus of Zinn. It inserts into the anterosuperior surface of the eye. This insertion has a width of around 11 mm. It is around 8 mm from the corneal limbus. Nerve supply The superior rectus muscle is supplied by the superior division of the ipsilateral oculomotor nerve (III). Each superior rectus muscle is innervated by contralateral oculomotor nucleus in the mesencephalon. Relations The superior rectus muscle is related to the other extraocular muscles, particularly to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Rectus Abdominis Muscle
The rectus abdominis muscle, () also known as the "abdominal muscle" or simply better known as the "abs", is a pair of segmented skeletal muscle on the ventral aspect of a person's abdomen. The paired muscle is separated at the midline by a band of dense connective tissue called the linea alba, and the connective tissue defining each lateral margin of the rectus abdominus is the linea semilunaris. The muscle extends from the pubic symphysis, pubic crest and pubic tubercle inferiorly, to the xiphoid process and costal cartilages of the 5th–7th ribs superiorly. The rectus abdominis muscle is contained in the rectus sheath, which consists of the aponeuroses of the lateral abdominal muscles. Each rectus abdominus is traversed by bands of connective tissue called the tendinous intersections, which interrupt it into distinct muscle bellies. Structure The rectus abdominis is a very long flat muscle, which extends along the whole length of the front of the abdomen, and is s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Lateral Rectus Muscle
The lateral rectus muscle is a muscle on the lateral side of the eye in the orbit. It is one of six extraocular muscles that control the movements of the eye. The lateral rectus muscle is responsible for lateral movement of the eyeball, specifically abduction. Abduction describes the movement of the eye away from the midline (i.a. nose), allowing the eyeball to move horizontally in the lateral direction, bringing the pupil away from the midline of the body. Structure The lateral rectus muscle originates at the lateral part of the common tendinous ring, also known as the annular tendon. The common tendinous ring is a tendinous ring that surrounds the optic nerve and serves as the origin for five of the seven extraocular muscles, excluding the inferior oblique muscle. The lateral rectus muscle inserts into the temporal side of the eyeball. This insertion is around 7 mm from the corneal limbus. It has a width of around 10 mm. Nerve supply The lateral rectus is the only musc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Inferior Rectus Muscle
The inferior rectus muscle is a muscle in the orbit near the eye. It is one of the four recti muscles in the group of extraocular muscles. It originates from the common tendinous ring, and inserts into the anteroinferior surface of the eye. It depresses the eye (downwards). Structure The inferior rectus muscle originates from the common tendinous ring (annulus of Zinn). It inserts into the anteroinferior surface of the eye. This insertion has a width of around 10.5 mm. It is around 7 mm from the corneal limbus. Blood supply The inferior rectus muscle is supplied by an inferior muscular branch of the ophthalmic artery. It may also be supplied by a branch of the infraorbital artery. It is drained by the corresponding veins: the inferior muscular branch of the ophthalmic vein, and sometimes a branch of the infraorbital vein. Nerve supply The inferior rectus muscle is supplied by the inferior division of the oculomotor nerve (III). Development The inferior rectus muscle deve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Medial Rectus Muscle
The medial rectus muscle is a muscle in the orbit near the eye. It is one of the extraocular muscles. It originates from the common tendinous ring, and inserts into the anteromedial surface of the eye. It is supplied by the inferior division of the oculomotor nerve (III). It rotates the eye medially (adduction). Structure The medial rectus muscle shares an origin with several other extrinsic eye muscles, the common tendinous ring. It inserts into the anteromedial surface of the eye. This insertion has a width of around 11 mm. Nerve supply The medial rectus muscle is supplied by the inferior division of the oculomotor nerve (III). A branch of it enters the muscle around two fifths along its length. It usually divides into 2 smaller branches, occasionally 3. These further subdivide, becoming smaller down the length of the muscle until they become imperceptible to standard staining around 17 mm from the insertion of the muscle. Relations The insertion of the medial rectus mu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Rectus Muscle (other)
"Rectus" is the Latin word meaning "straight" and is used in English to refer to multiple topics in the sciences, including: In molecular chemistry the ''R'' in the ''R'' & ''S'' isomerism stands for "rectus" In grammar "casus rectus" is a formal term for nominative case In mathematics sine is also known as "sinus rectus" In the classification of the animal kingdom it is the systematic taxonomic name of several species, ''e.g.'' campylobacter rectus & syllitus rectus In anatomy it is used to refer to a rectus muscle, primarily ''e.g.'' the "rectus abdominis muscle"; in anatomy it can also refer to: *Inferior rectus muscle *Superior rectus muscle *Lateral rectus muscle *Medial rectus muscle * Musculus rectus thoracis *Rectus capitis lateralis muscle *Rectus femoris muscle The rectus femoris muscle is one of the four quadriceps muscles of the human body. The others are the vastus medialis, the vastus intermedius (deep to the rectus femoris), and the vastus lateralis. All fou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Campylobacter Rectus
''Campylobacter rectus'' is a species of ''Campylobacter''. It is implicated as a pathogen in chronic periodontitis, which can induce bone loss. This motile bacillus is a Gram negative, facultative anaerobe. ''C. rectus'' is associated with hypertension together with '' Prevotella melaninogenica'' and ''Veillonella parvula''. It was first described and characterized as ''Wolinella recta'' in 1981 after the bacterium was isolated from human patients with gingivitis, periodontitis, and periodontosis. The species name was changed to ''Campylobacter rectus'' in 1991 after phylogenetic analyses grouped it closely with other members of rRNA Group I ''Campylobacter''. Physiology ''C. rectus'' is gram negative, rod-shaped, and anaerobic, although growth in 5% oxygen is possible for some strains. It can use hydrogen and formate for energy, but does not metabolize carbohydrates, and can reduce nitrite. ''C. rectus'' is susceptible to multiple classes of antibiotics. The bacterium is su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
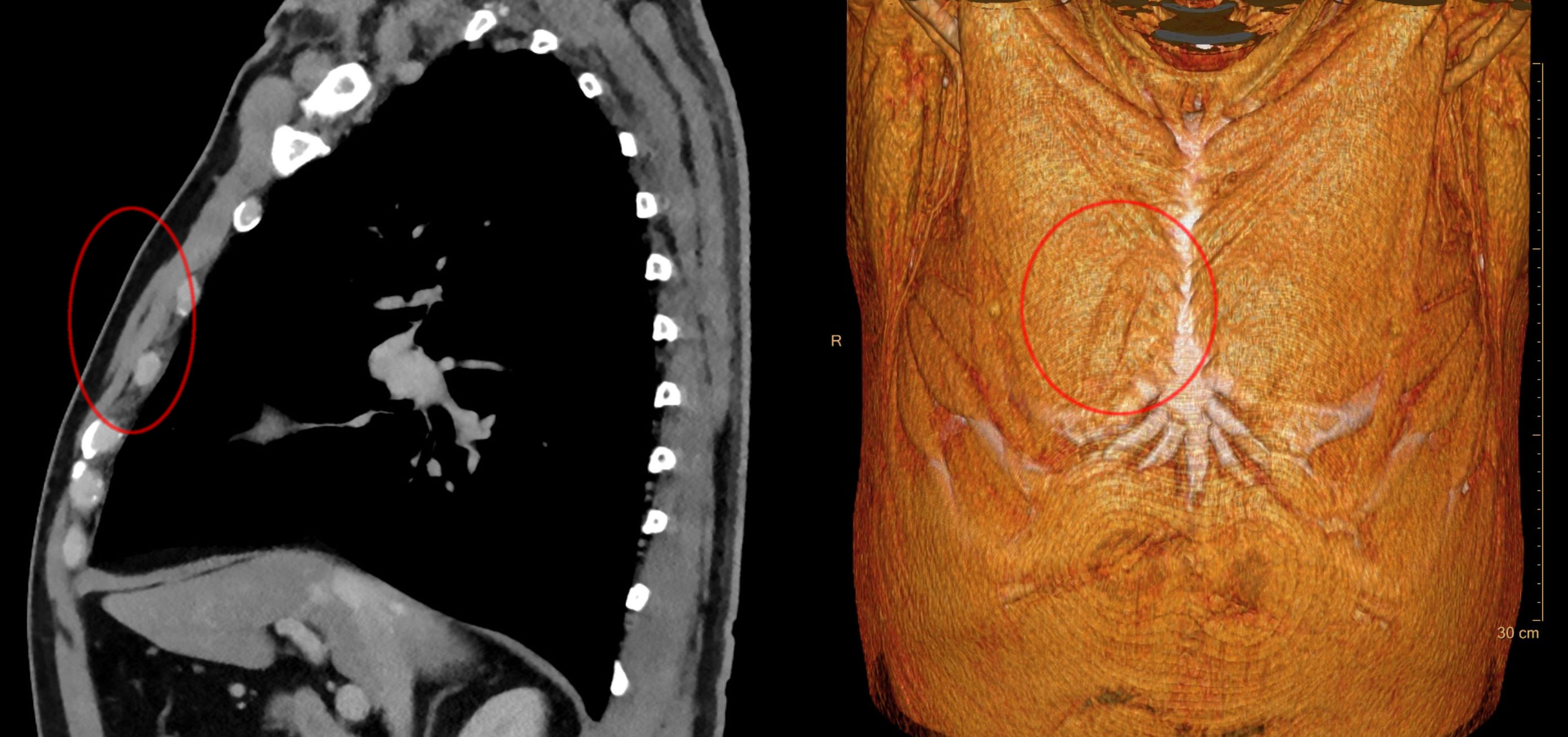 |
Sternalis Muscle
The rectus sternalis muscle is an anatomical variation that lies in front of the sternal end of the pectoralis major parallel to the margin of the sternum. The sternalis muscle may be a variation of the pectoralis major or of the rectus abdominis. Structure The sternalis is a muscle that runs along the anterior aspect of the body of the sternum. It lies superficially and parallel to the sternum. Its origin and insertion are variable. The sternalis muscle often originates from the upper part of the sternum and can display varying insertions such as the pectoral fascia, lower ribs, costal cartilages, rectus sheath, aponeurosis of the abdominal external oblique muscle. It may be present unilaterally or bilaterally. There is still a great deal of disagreement about its innervation and its embryonic origin. In a review, it was reported that the muscle was innervated by the external or internal thoracic nerves in 55% of the cases, by the intercostal nerves in 43% of the cases, whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
Rectus Capitis Lateralis Muscle
The rectus capitis lateralis, a short, flat muscle, arises from the upper surface of the transverse process of the atlas, and is inserted into the under surface of the jugular process of the occipital bone. Additional images File:Rectus capitis lateralis muscle - animation01.gif, Position of rectus capitis lateralis muscle (shown in red). Animation. File:Rectus capitis lateralis muscle - animation05.gif, Close up. Skull has been removed (except occipital bone). File:Rectus capitis lateralis muscle03.png, Lateral view. Still image. File:Gray129.png, Occipital bone. Outer surface. File:Gray187.png, Base of skull. Inferior surface. See also * Atlanto-occipital joint * Rectus capitis posterior major muscle * Rectus capitis posterior minor muscle The rectus capitis posterior minor (or rectus capitis posticus minor) is a muscle in the upper back part of the neck. It is one of the suboccipital muscles. Its inferior attachment is at the posterior arch of atlas; its superior at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
 |
Absolute Configuration
In chemistry, absolute configuration refers to the spatial arrangement of atoms within a molecular entity (or Functional group, group) that is chirality (chemistry), chiral, and its resultant stereochemical description. Absolute configuration is typically relevant in organic molecules where carbon is bonded to four different substituents. This type of construction creates two possible enantiomers. Absolute configuration uses a set of rules to describe the relative positions of each bond around the chiral center atom. The most common labeling method uses the descriptors ''R'' or ''S'' and is based on the Cahn–Ingold–Prelog priority rules. ''R'' and ''S'' refer to and , Latin for right and left, respectively. Chiral molecules can differ in their chemical properties, but are identical in their physical properties, which can make distinguishing enantiomers challenging. Absolute configurations for a chiral molecule (in pure form) are most often obtained by X-ray crystallography, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
Syllitus Rectus
''Syllitus'' is a genus of long-horned beetles in the family Cerambycidae. There are more than 40 described species in ''Syllitus''. Species These 47 species belong to the genus ''Syllitus'': * ''Syllitus acanthias'' McKeown, 1937 * ''Syllitus adonarensis'' Jordan, 1894 * ''Syllitus albipennis'' Pascoe, 1869 * ''Syllitus araucariae'' McKeown, 1938 * ''Syllitus argillaceus'' McKeown, 1937 * ''Syllitus bellulus'' McKeown, 1942 * ''Syllitus beltrani'' Cerda, 1968 * ''Syllitus bicolor'' (Schwarzer, 1924) * ''Syllitus bipunctatus'' Waterhouse, 1877 * ''Syllitus brimblecombei'' McKeown, 1938 * ''Syllitus buloloensis'' Gressitt, 1959 * ''Syllitus cassiniae'' McKeown, 1938 * ''Syllitus centocrus'' McKeown, 1938 * ''Syllitus cylindricus'' Germain, 1899 * ''Syllitus deustus'' (Newman, 1841) * ''Syllitus divergens'' McKeown, 1937 * ''Syllitus dubius'' McKeown, 1938 * ''Syllitus elguetai'' Cerda, 1991 * ''Syllitus froggatti'' McKeown, 1937 * ''Syllitus fulvipennis'' Gahan, 1893 * ''Syllitus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |