|
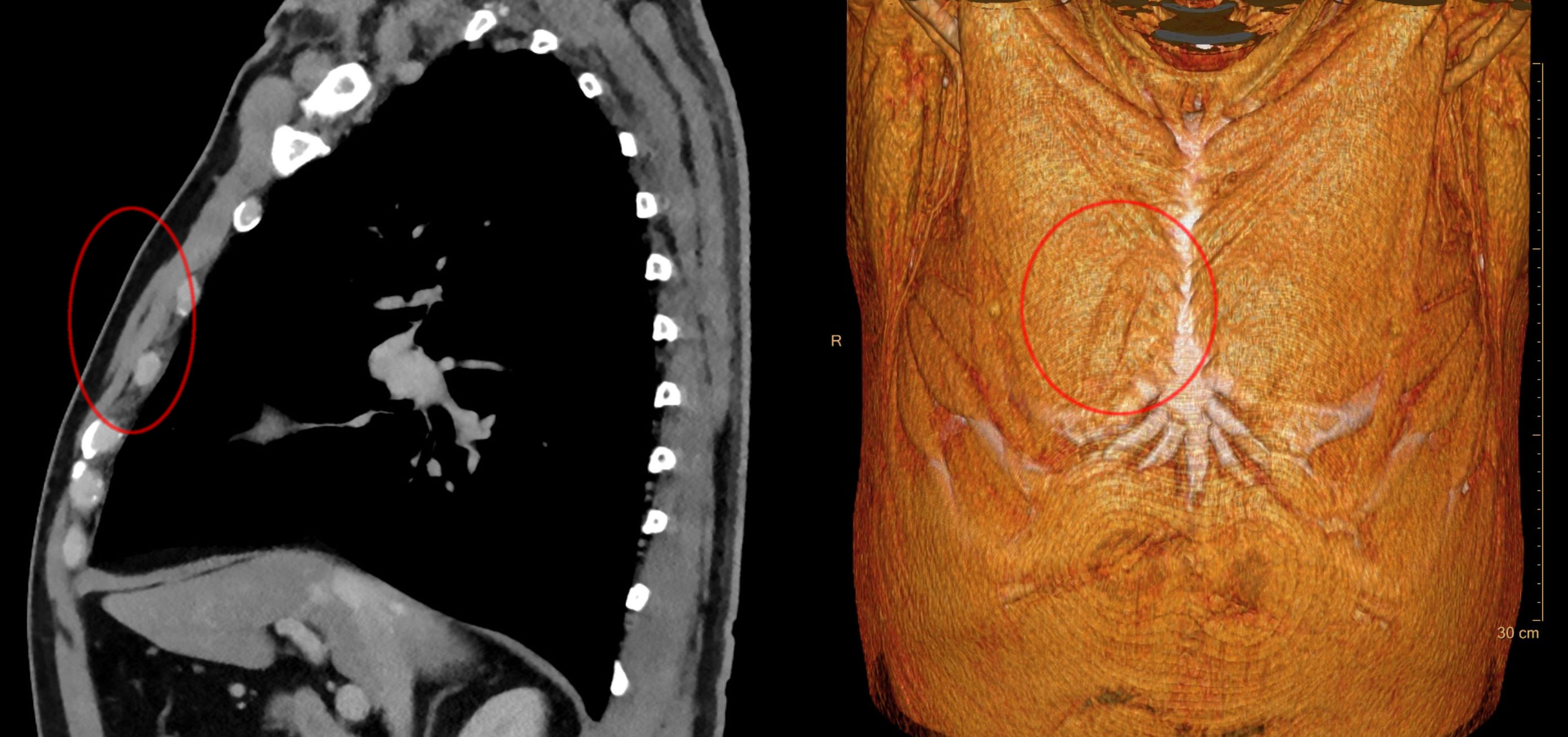
Sternalis Muscle
The rectus sternalis muscle is an anatomical variation that lies in front of the sternal end of the pectoralis major parallel to the margin of the sternum. The sternalis muscle may be a variation of the pectoralis major or of the rectus abdominis. Structure The sternalis is a muscle that runs along the anterior aspect of the body of the sternum. It lies superficially and parallel to the sternum. Its origin and insertion are variable. The sternalis muscle often originates from the upper part of the sternum and can display varying insertions such as the pectoral fascia, lower ribs, costal cartilages, rectus sheath, aponeurosis of the abdominal external oblique muscle. It may be present unilaterally or bilaterally. There is still a great deal of disagreement about its innervation and its embryonic origin. In a review, it was reported that the muscle was innervated by the external or internal thoracic nerves in 55% of the cases, by the intercostal nerves in 43% of the cases, whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sternum
The sternum (: sternums or sterna) or breastbone is a long flat bone located in the central part of the chest. It connects to the ribs via cartilage and forms the front of the rib cage, thus helping to protect the heart, lungs, and major blood vessels from injury. Shaped roughly like a necktie, it is one of the largest and longest flat bones of the body. Its three regions are the manubrium, the body, and the xiphoid process. The word ''sternum'' originates from Ancient Greek στέρνον (''stérnon'') 'chest'. Structure The sternum is a narrow, flat bone, forming the middle portion of the front of the chest. The top of the sternum supports the clavicles (collarbones) and its edges join with the costal cartilages of the first two pairs of ribs. The inner surface of the sternum is also the attachment of the sternopericardial ligaments. Its top is also connected to the sternocleidomastoid muscle. The sternum consists of three main parts, listed from the top: * Man ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proprioception
Proprioception ( ) is the sense of self-movement, force, and body position. Proprioception is mediated by proprioceptors, a type of sensory receptor, located within muscles, tendons, and joints. Most animals possess multiple subtypes of proprioceptors, which detect distinct kinesthetic parameters, such as joint position, movement, and load. Although all mobile animals possess proprioceptors, the structure of the sensory organs can vary across species. Proprioceptive signals are transmitted to the central nervous system, where they are integrated with information from other Sensory nervous system, sensory systems, such as Visual perception, the visual system and the vestibular system, to create an overall representation of body position, movement, and acceleration. In many animals, sensory feedback from proprioceptors is essential for stabilizing body posture and coordinating body movement. System overview In vertebrates, limb movement and velocity (muscle length and the rate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1640 In Science
The year 1640 in science and technology involved some significant events. Botany * John Parkinson publishes ''Theatrum Botanicum:The Theater of Plants, or, An Herbal of a Large Extent''. Mathematics * The 16-year-old Blaise Pascal demonstrates the properties of the ''hexagrammum mysticum'' in his ''Essai pour les coniques'' which he sends to Mersenne. * October 18 – Fermat states his " little theorem" in a letter to Frénicle de Bessy: if ''p'' is a prime number, then for any integer ''a'', ''a'' ''p'' − ''a'' will be divisible by ''p''. * December 25 – Fermat claims a proof of the theorem on sums of two squares in a letter to Mersenne ("Fermat's Christmas Theorem"): an odd prime ''p'' is expressible as the sum of two squares. Technology * The micrometer is developed. * A form of bayonet is invented; in later years it will gradually replace the pike. * The reticle telescope is developed and initiates the birth of sharpshooting. Births * April 1 � ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muscles Of The Torso
Muscle is a soft tissue, one of the four basic types of animal tissue. There are three types of muscle tissue in vertebrates: skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle. Muscle tissue gives skeletal muscles the ability to contract. Muscle tissue contains special contractile proteins called actin and myosin which interact to cause movement. Among many other muscle proteins, present are two regulatory proteins, troponin and tropomyosin. Muscle is formed during embryonic development, in a process known as myogenesis. Skeletal muscle tissue is striated consisting of elongated, multinucleate muscle cells called muscle fibers, and is responsible for movements of the body. Other tissues in skeletal muscle include tendons and perimysium. Smooth and cardiac muscle contract involuntarily, without conscious intervention. These muscle types may be activated both through the interaction of the central nervous system as well as by innervation from peripheral plexus or endocrin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Accessory Muscle
An accessory muscle is a relatively rare anatomical variation where duplication of a muscle may appear anywhere in the muscular system. Treatment is not indicated unless the accessory muscle interferes with normal function. Examples Examples are the accessory soleus muscle in the calf or ankle, the extensor digitorum brevis manus in the hand and epitrochleoanconeus muscle of the upper arm. Additional examples in the hand include Flexor carpi radialis brevis which can compress the anterior interosseous nerve. Also see palmaris profundus muscle. On the extensor side: extensor digitorum brevis manus,extensor carpi radialis intermedius extensor medii proprius muscle Accessory muscles of the anterior thoracic wall include the sternalis muscle, the axillary arch (Langer's), variations of pectoralis major such as the ''pectoralis minimus'', ''pectoralis quartus'', and ''pectoralis intermedius'', the ''chondrocoracoideus'' and ''chondrofascialis''. The whole pectoral region is subject ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anatomical Variations
An anatomical variation, anatomical variant, or anatomical variability is a presentation of body structure with morphological features different from those that are typically described in the majority of individuals. Anatomical variations are categorized into three types including morphometric (size or shape), consistency (present or absent), and spatial (proximal/distal or right/left). Variations are seen as normal in the sense that they are found consistently among different individuals, are mostly without symptoms, and are termed anatomical variations rather than abnormalities. Anatomical variations are mainly caused by genetics and may vary considerably between different populations. The rate of variation considerably differs between single organs, particularly in muscles. Knowledge of anatomical variations is important in order to distinguish them from pathological conditions. A very early paper published in 1898, presented anatomic variations to have a wide range and signi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latissimus Dorsi
The latissimus dorsi () is a large, flat muscle on the back that stretches to the sides, behind the arm, and is partly covered by the trapezius on the back near the midline. The word latissimus dorsi (plural: ''latissimi dorsi'') comes from Latin and means "broadest [muscle] of the back", from "latissimus" () and "dorsum" (). The pair of muscles are commonly known as "lats", especially among bodybuilders. The latissimus dorsi is responsible for Extension (kinesiology), extension, adduction, transverse extension also known as horizontal abduction (or horizontal extension), flexion from an extended position, and (medial) internal rotation of the shoulder joint. It also has a synergistic role in extension and Anatomical terms of motion, lateral flexion of the lumbar spine. Due to bypassing the scapulothoracic joints and attaching directly to the spine, the actions the latissimi dorsi have on moving the arms can also influence the movement of the scapulae, such as their downward ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reconstructive Surgery
Reconstructive surgery is surgery performed to restore normal appearance and function to body parts malformed by a disease or medical condition. Description Reconstructive surgery is a term with training, clinical, and reimbursement implications. It has historically been referred to as synonymous with plastic surgery. In regard to training, plastic surgery is a recognized medical specialty and a surgeon can be a "board-certified" plastic surgeon by the American Board of Plastic Surgery. However, reconstructive surgery is not a specialty and there are no board-certified reconstructive surgeons. More accurately, reconstructive surgery should be contrasted with cosmetic surgery. Reconstructive surgery is performed to # Improve/restore to normal function. # Restore to a normal appearance of "abnormal" or "malformed" body parts caused by the disease or condition and/or # Improve the patient's quality of life. Separately, the patient must be healthy enough so that the benefits o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
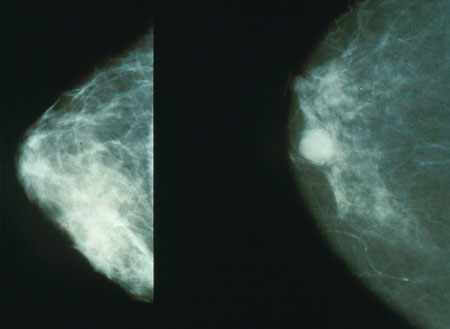
Mammography
Mammography (also called mastography; DICOM modality: MG) is the process of using low-energy X-rays (usually around 30 kVp) to examine the human breast for diagnosis and screening. The goal of mammography is the early detection of breast cancer, typically through detection of characteristic masses, microcalcifications, asymmetries, and distortions. As with all X-rays, mammograms use doses of ionizing radiation to create images. These images are then analyzed for abnormal findings. It is usual to employ lower-energy X-rays, typically Mo (K-shell X-ray energies of 17.5 and 19.6 keV) and Rh (20.2 and 22.7 keV) than those used for radiography of bones. Mammography may be 2D or 3D ( tomosynthesis), depending on the available equipment or purpose of the examination. Ultrasound, ductography, positron emission mammography (PEM), and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are adjuncts to mammography. Ultrasound is typically used for further evaluation of masses found on mammography or palp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrocardiography
Electrocardiography is the process of producing an electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG), a recording of the heart's electrical activity through repeated cardiac cycles. It is an electrogram of the heart which is a graph of voltage versus time of the electrical activity of the heart using electrodes placed on the skin. These electrodes detect the small electrical changes that are a consequence of cardiac muscle depolarization followed by repolarization during each cardiac cycle (heartbeat). Changes in the normal ECG pattern occur in numerous cardiac abnormalities, including: * Cardiac rhythmicity, Cardiac rhythm disturbances, such as atrial fibrillation and ventricular tachycardia; * Inadequate coronary artery blood flow, such as myocardial ischemia and myocardial infarction; * and electrolyte disturbances, such as hypokalemia. Traditionally, "ECG" usually means a 12-lead ECG taken while lying down as discussed below. However, other devices can record the electrical activity of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asymmetry
Asymmetry is the absence of, or a violation of, symmetry (the property of an object being invariant to a transformation, such as reflection). Symmetry is an important property of both physical and abstract systems and it may be displayed in precise terms or in more aesthetic terms. The absence of or violation of symmetry that are either expected or desired can have important consequences for a system. In organisms Due to how cell (biology), cells divide in organisms, asymmetry in organisms is fairly usual in at least one dimension, with Symmetry in biology, biological symmetry also being common in at least one dimension. Louis Pasteur proposed that biological molecules are asymmetric because the cosmic [i.e. physical] forces that preside over their formation are themselves asymmetric. While at his time, and even now, the symmetry of physical processes are highlighted, it is known that there are fundamental physical asymmetries, starting with time. Asymmetry in biology Asy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |