|
Cissoid Of Diocles
In geometry, the cissoid of Diocles (; named for Diocles (mathematician), Diocles) is a cubic plane curve notable for the property that it can be used to construct two Geometric mean, mean proportionals to a given ratio. In particular, it can be used to Doubling the cube, double a cube. It can be defined as the cissoid of a circle and a line tangent to it with respect to the point on the circle opposite to the point of tangency. In fact, the Family of curves, curve family of cissoids is named for this example and some authors refer to it simply as ''the'' cissoid. It has a single cusp (singularity), cusp at the pole, and is symmetric about the diameter of the circle which is the line of tangency of the cusp. The line is an asymptote. It is a member of the conchoid of de Sluze family of curves and in form it resembles a tractrix. Construction and equations Let the radius of be . By translation and rotation, we may take to be the origin and the center of the circle to be (''a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
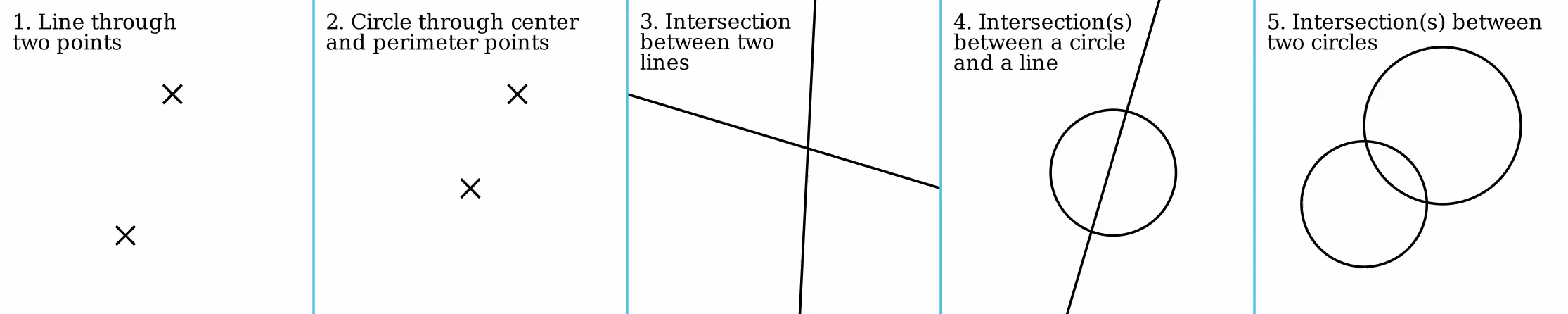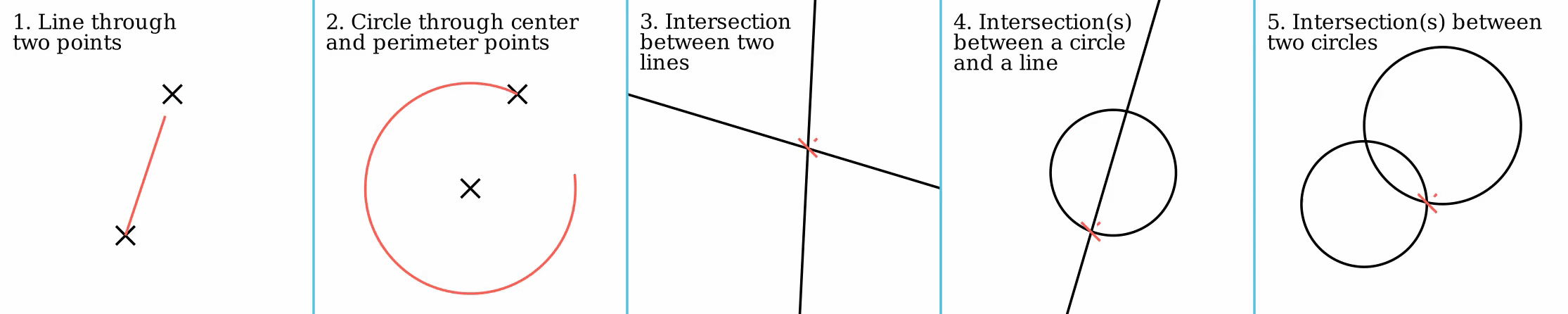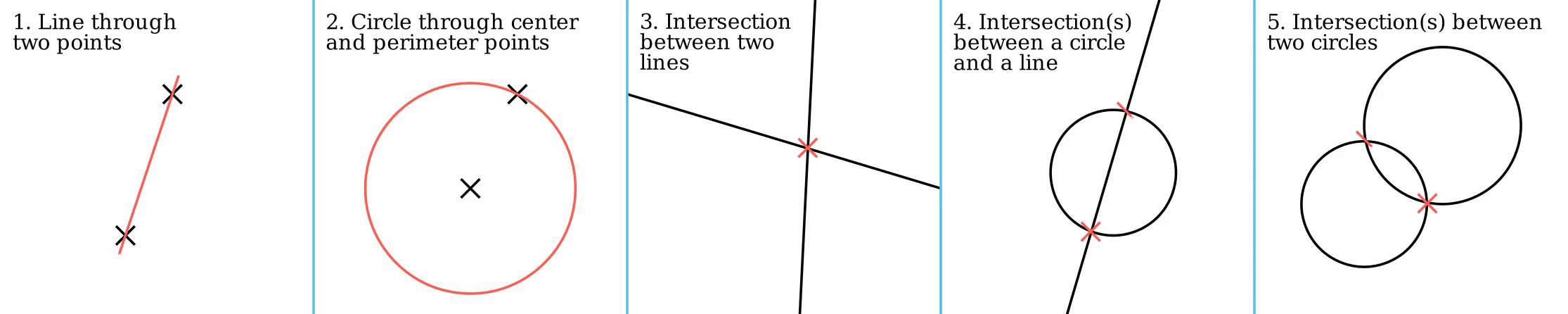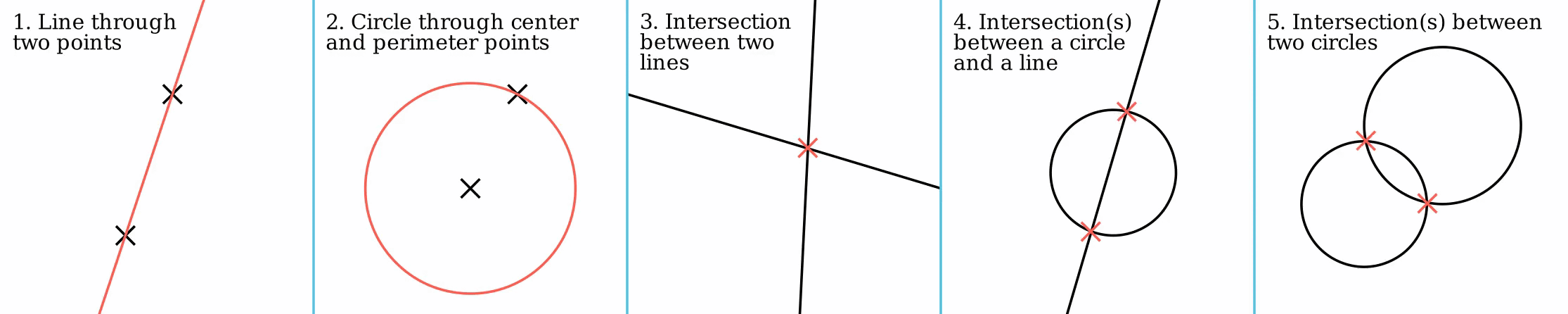
Straightedge And Compass Construction
In geometry, straightedge-and-compass construction – also known as ruler-and-compass construction, Euclidean construction, or classical construction – is the construction of lengths, angles, and other geometric figures using only an idealized ruler and a compass. The idealized ruler, known as a straightedge, is assumed to be infinite in length, have only one edge, and no markings on it. The compass is assumed to have no maximum or minimum radius, and is assumed to "collapse" when lifted from the page, so it may not be directly used to transfer distances. (This is an unimportant restriction since, using a multi-step procedure, a distance can be transferred even with a collapsing compass; see compass equivalence theorem. Note however that whilst a non-collapsing compass held against a straightedge might seem to be equivalent to marking it, the neusis construction is still impermissible and this is what unmarked really means: see Markable rulers below.) More formally, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pedal Curve
A pedal (from the Latin ''wikt:pes#Latin, pes'' ''pedis'', "foot") is a lever designed to be operated by foot and may refer to: Computers and other equipment * Footmouse, a foot-operated computer mouse * In medical transcription, a pedal is used to control playback of voice dictations Geometry * Pedal curve, a curve derived by construction from a given curve * Pedal triangle, a triangle obtained by projecting a point onto the sides of a triangle Music Albums * Pedals (Rival Schools album), ''Pedals'' (Rival Schools album) * Pedals (Speak album), ''Pedals'' (Speak album) Other music * Bass drum pedal, a pedal used to play a bass drum while leaving the drummer's hands free to play other drums with drum sticks, hands, etc. * Effects pedal, a pedal used commonly for electric guitars * Pedal keyboard, a musical keyboard operated by the player's feet * Pedal harp, a modern orchestral harp with pedals used to change the tuning of its strings * Pedal point, a type of nonchord t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synthetic Geometry
Synthetic geometry (sometimes referred to as axiomatic geometry or even pure geometry) is geometry without the use of coordinates. It relies on the axiomatic method for proving all results from a few basic properties initially called postulates, and at present called axioms. After the 17th-century introduction by René Descartes of the coordinate method, which was called analytic geometry, the term "synthetic geometry" was coined to refer to the older methods that were, before Descartes, the only known ones. According to Felix Klein Synthetic geometry is that which studies figures as such, without recourse to formulae, whereas analytic geometry consistently makes use of such formulae as can be written down after the adoption of an appropriate system of coordinates. The first systematic approach for synthetic geometry is Euclid's ''Elements''. However, it appeared at the end of the 19th century that Euclid's postulates were not sufficient for characterizing geometry. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Axiom
An axiom, postulate, or assumption is a statement that is taken to be true, to serve as a premise or starting point for further reasoning and arguments. The word comes from the Ancient Greek word (), meaning 'that which is thought worthy or fit' or 'that which commends itself as evident'. The precise definition varies across fields of study. In classic philosophy, an axiom is a statement that is so evident or well-established, that it is accepted without controversy or question. In modern logic, an axiom is a premise or starting point for reasoning. In mathematics, an ''axiom'' may be a " logical axiom" or a " non-logical axiom". Logical axioms are taken to be true within the system of logic they define and are often shown in symbolic form (e.g., (''A'' and ''B'') implies ''A''), while non-logical axioms are substantive assertions about the elements of the domain of a specific mathematical theory, for example ''a'' + 0 = ''a'' in integer arithmetic. N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
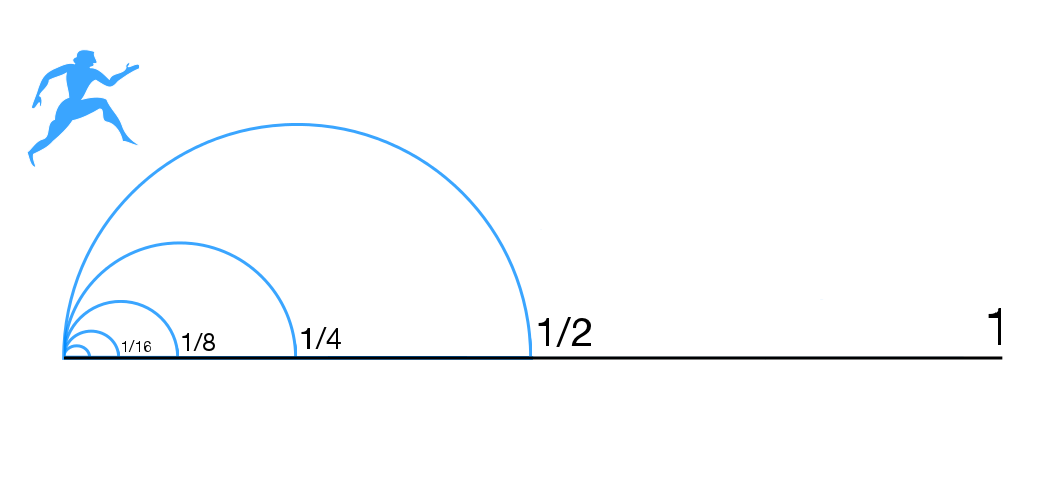
Zeno's Paradoxes
Zeno's paradoxes are a series of philosophical arguments presented by the ancient Greek philosopher Zeno of Elea (c. 490–430 BC), primarily known through the works of Plato, Aristotle, and later commentators like Simplicius of Cilicia. Zeno devised these paradoxes to support his teacher Parmenides's philosophy of monism, which posits that despite people's sensory experiences, reality is singular and unchanging. The paradoxes famously challenge the notions of plurality (the existence of many things), motion, space, and time by suggesting they lead to logical contradictions. Zeno's work, primarily known from second-hand accounts since his original texts are lost, comprises forty "paradoxes of plurality," which argue against the coherence of believing in multiple existences, and several arguments against motion and change. Of these, only a few are definitively known today, including the renowned "Achilles Paradox", which illustrates the problematic concept of infinite divisibi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cissoid 500points 220x220
In geometry, a cissoid () is a plane curve generated from two given curves , and a point (the pole). Let be a variable line passing through and intersecting at and at . Let be the point on so that \overline = \overline. (There are actually two such points but is chosen so that is in the same direction from as is from .) Then the locus of such points is defined to be the cissoid of the curves , relative to . Slightly different but essentially equivalent definitions are used by different authors. For example, may be defined to be the point so that \overline = \overline + \overline. This is equivalent to the other definition if is replaced by its reflection through . Or may be defined as the midpoint of and ; this produces the curve generated by the previous curve scaled by a factor of 1/2. Equations If and are given in polar coordinates by r=f_1(\theta) and r=f_2(\theta) respectively, then the equation r=f_2(\theta)-f_1(\theta) describes the cissoid of and r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compass And Straightedge Construction
In geometry, straightedge-and-compass construction – also known as ruler-and-compass construction, Euclidean construction, or classical construction – is the construction of lengths, angles, and other geometric figures using only an idealized ruler and a compass. The idealized ruler, known as a straightedge, is assumed to be infinite in length, have only one edge, and no markings on it. The compass is assumed to have no maximum or minimum radius, and is assumed to "collapse" when lifted from the page, so it may not be directly used to transfer distances. (This is an unimportant restriction since, using a multi-step procedure, a distance can be transferred even with a collapsing compass; see compass equivalence theorem. Note however that whilst a non-collapsing compass held against a straightedge might seem to be equivalent to marking it, the neusis construction is still impermissible and this is what unmarked really means: see Markable rulers below.) More formally, the o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volume
Volume is a measure of regions in three-dimensional space. It is often quantified numerically using SI derived units (such as the cubic metre and litre) or by various imperial or US customary units (such as the gallon, quart, cubic inch). The definition of length and height (cubed) is interrelated with volume. The volume of a container is generally understood to be the capacity of the container; i.e., the amount of fluid (gas or liquid) that the container could hold, rather than the amount of space the container itself displaces. By metonymy, the term "volume" sometimes is used to refer to the corresponding region (e.g., bounding volume). In ancient times, volume was measured using similar-shaped natural containers. Later on, standardized containers were used. Some simple three-dimensional shapes can have their volume easily calculated using arithmetic formulas. Volumes of more complicated shapes can be calculated with integral calculus if a formula exists for the shape ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doubling The Cube
Doubling the cube, also known as the Delian problem, is an ancient geometry, geometric problem. Given the Edge (geometry), edge of a cube, the problem requires the construction of the edge of a second cube whose volume is double that of the first. As with the related problems of squaring the circle and trisecting the angle, doubling the cube is now known to be impossible to construct by using only a compass and straightedge, but even in ancient times solutions were known that employed other methods. According to Eutocius, Archytas was the first to solve the problem of doubling the cube (the so-called Delian problem) with an ingenious geometric construction. The nonexistence of a compass-and-straightedge solution was finally proven by Pierre Wantzel in 1837. In algebraic terms, doubling a unit cube requires the construction of a line segment of length , where ; in other words, , the cube root of two. This is because a cube of side length 1 has a volume of , and a cube of twice tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cube
A cube or regular hexahedron is a three-dimensional space, three-dimensional solid object in geometry, which is bounded by six congruent square (geometry), square faces, a type of polyhedron. It has twelve congruent edges and eight vertices. It is a type of parallelepiped, with pairs of parallel opposite faces, and more specifically a rhombohedron, with congruent edges, and a rectangular cuboid, with right angles between pairs of intersecting faces and pairs of intersecting edges. It is an example of many classes of polyhedra: Platonic solid, regular polyhedron, parallelohedron, zonohedron, and plesiohedron. The dual polyhedron of a cube is the regular octahedron. The cube can be represented in many ways, one of which is the graph known as the cubical graph. It can be constructed by using the Cartesian product of graphs. The cube is the three-dimensional hypercube, a family of polytopes also including the two-dimensional square and four-dimensional tesseract. A cube with 1, unit s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |