|
Xiao Riben
''Xiao Riben'' () is a derogatory Chinese slang term for the Japanese people or a person of Japanese descent. Literally translated, it means "little Japan" or "little Japanese". It is often used with " guizi" or ghost/devil, such as "xiao Riben guizi", or "little Japanese devil". Usage This is a derogatory term used in China against Japan from the beginning of the Second Sino-Japanese War until today. See also * Jap ''Jap'' is an English abbreviation of the word " Japanese". In the United States, some Japanese Americans have come to find the term offensive because of the internment they suffered during World War II. Before the attack on Pearl Harbor, ''Jap ... * Guizi * Gweilo * Hinomoto Oniko * Shina References {{Reflist Anti–East Asian slurs China–Japan relations Anti-Japanese sentiment in China Chinese words and phrases ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
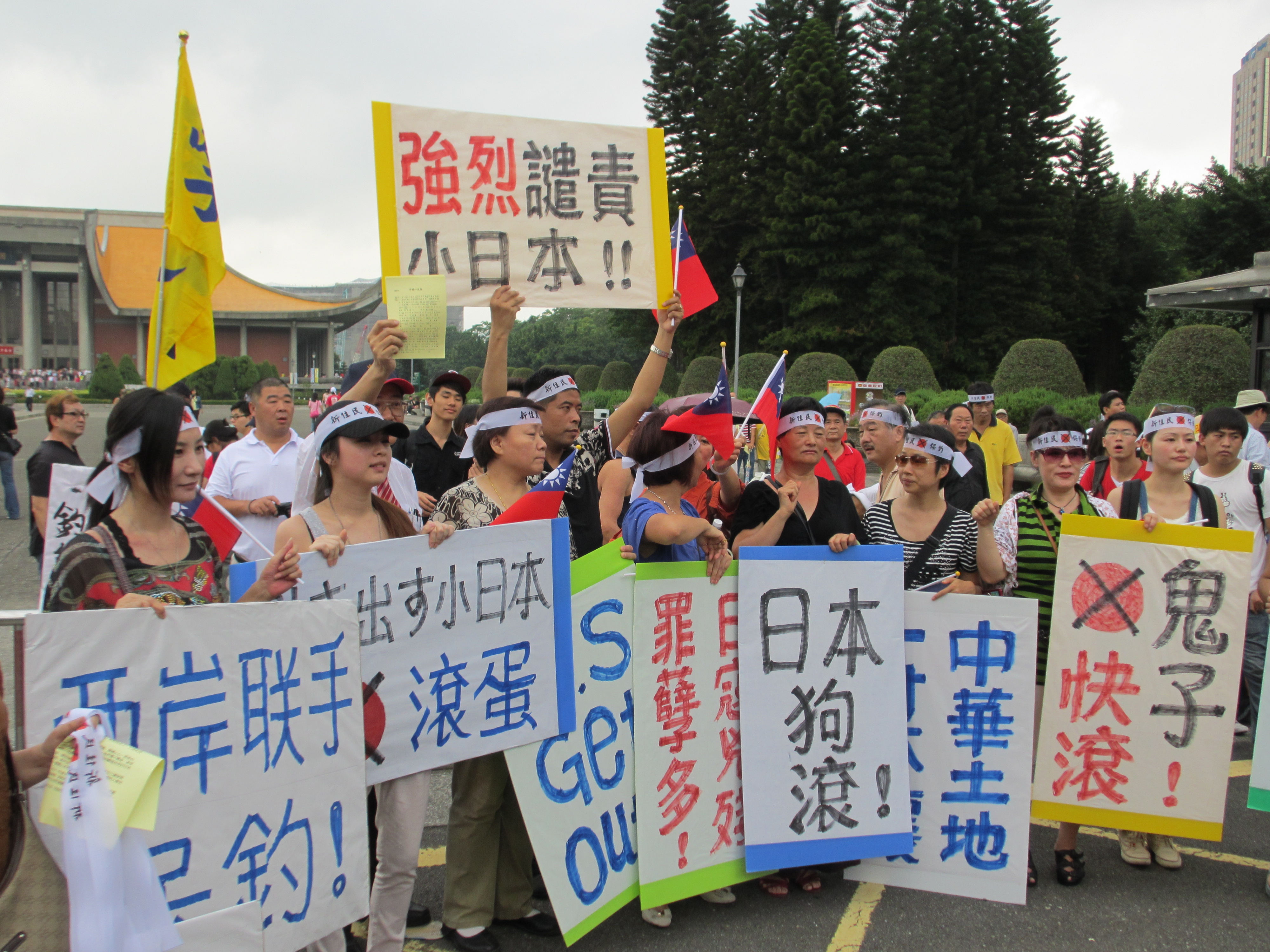
2012 Anti-Japan Demonstrations7
1 (one, unit, unity) is a number, Numeral (linguistics), numeral, and glyph. It is the first and smallest Positive number, positive integer of the infinite sequence of natural numbers. This fundamental property has led to its unique uses in other fields, ranging from science to sports, where it commonly denotes the first, leading, or top thing in a group. 1 is the unit (measurement), unit of counting or measurement, a determiner for singular nouns, and a gender-neutral pronoun. Historically, the representation of 1 evolved from ancient Sumerian and Babylonian symbols to the modern Arabic numeral. In mathematics, 1 is the multiplicative identity, meaning that any number multiplied by 1 equals the same number. 1 is by convention not considered a prime number. In Digital electronics, digital technology, 1 represents the "on" state in binary code, the foundation of computing. Philosophically, 1 symbolizes the ultimate reality or source of existence in various traditions. In math ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2012 China Anti-Japanese Demonstrations In Beijing
1 (one, unit, unity) is a number, numeral, and glyph. It is the first and smallest positive integer of the infinite sequence of natural numbers. This fundamental property has led to its unique uses in other fields, ranging from science to sports, where it commonly denotes the first, leading, or top thing in a group. 1 is the unit of counting or measurement, a determiner for singular nouns, and a gender-neutral pronoun. Historically, the representation of 1 evolved from ancient Sumerian and Babylonian symbols to the modern Arabic numeral. In mathematics, 1 is the multiplicative identity, meaning that any number multiplied by 1 equals the same number. 1 is by convention not considered a prime number. In digital technology, 1 represents the "on" state in binary code, the foundation of computing. Philosophically, 1 symbolizes the ultimate reality or source of existence in various traditions. In mathematics The number 1 is the first natural number after 0. Each natural number, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
小日本
''Xiao Riben'' () is a derogatory Chinese slang term for the Japanese people or a person of Japanese descent. Literally translated, it means "little Japan" or "little Japanese". It is often used with "guizi" or ghost/devil, such as "xiao Riben guizi", or "little Japanese devil". Usage This is a derogatory term used in China against Japan from the beginning of the Second Sino-Japanese War until today. See also * Jap * Guizi * Gweilo * Hinomoto Oniko is a Japanese moe character created in 2010 which originated from the Breaking News (VIP) Board on 2channel, and has since become an internet meme within various forums and imageboards in Japan. The character is a moe anthropomorphism of the p ... * Shina References {{Reflist Anti–East Asian slurs China–Japan relations Anti-Japanese sentiment in China Chinese words and phrases ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Language
Chinese ( or ) is a group of languages spoken natively by the ethnic Han Chinese majority and List of ethnic groups in China, many minority ethnic groups in China, as well as by various communities of the Chinese diaspora. Approximately 1.39 billion people, or 17% of the global population, speak a variety of Chinese as their first language. Chinese languages form the Sinitic languages, Sinitic branch of the Sino-Tibetan language family. The spoken varieties of Chinese are usually considered by native speakers to be dialects of a single language. However, their lack of mutual intelligibility means they are sometimes considered to be separate languages in a Language family, family. Investigation of the historical relationships among the varieties of Chinese is ongoing. Currently, most classifications posit 7 to 13 main regional groups based on phonetic developments from Middle Chinese, of which the most spoken by far is Mandarin Chinese, Mandarin with 66%, or around 800&nb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese People
are an East Asian ethnic group native to the Japanese archipelago. Japanese people constitute 97.4% of the population of the country of Japan. Worldwide, approximately 125 million people are of Japanese descent, making them list of contemporary ethnic groups, one of the largest ethnic groups. Approximately 120.8 million Japanese people are residents of Japan, and there are approximately 4 million members of the Japanese diaspora, known as . In some contexts, the term "Japanese people" may be used to refer specifically to the Yamato people, who are primarily from the historically principal islands of Honshu, Kyushu and Shikoku and constitute by far the largest group. In other contexts, the term may include other groups native to the Japanese archipelago, including Ryukyuan people, who share connections with the Yamato but are often regarded as distinct, and Ainu people. In recent decades, there has also been an increase in the number of people with both Japanese and non-Japanes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guizi
''Guizi'' ( zh, c=鬼子, p=guǐzi, l=devil) is a pejorative Chinese slang term referring to foreigners, with a history of xenophobic connotations. History Starting with the arrival of European sailors in the sixteenth century, foreigners were often perceived in China as "uncivilized tribes given to mayhem and destruction". In the southern parts of China, the term '' gweilo'' () was used; this term remains popular today in the Cantonese-speaking regions of China. In northern parts, the term 'western devil' ( ) was used. Use The character ''gui'' () can have negative connotations itself without the ''zi'' () suffix. For example, when it was attached to the Westerners in the term ''yang guizi'' ( 'overseas devils') during the Boxer Rebellion, to the Japanese military in the term ''guizi bing'' ( 'devil soldiers') during the Second Sino-Japanese War, and to the Korean collaborators with the term ''er guizi'' ( 'second-rank devil'). It can also be used as an adjective to expres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Sino-Japanese War
The Second Sino-Japanese War was fought between the Republic of China (1912–1949), Republic of China and the Empire of Japan between 1937 and 1945, following a period of war localized to Manchuria that started in 1931. It is considered part of World War II, and often regarded as the beginning of World WarII in Asia. It was the largest Asian war in the 20th century and has been described as The Asian Holocaust, in reference to the scale of Japanese war crimes against Chinese civilians. It is known in China as the War of Resistance against Japanese Aggression. On 18 September 1931, the Japanese staged the Mukden incident, a false flag event fabricated to justify their Japanese invasion of Manchuria, invasion of Manchuria and establishment of the puppet state of Manchukuo. This is sometimes marked as the beginning of the war. From 1931 to 1937, China and Japan engaged in skirmishes, including January 28 incident, in Shanghai and in Northern China. Chinese Nationalist and C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guizi
''Guizi'' ( zh, c=鬼子, p=guǐzi, l=devil) is a pejorative Chinese slang term referring to foreigners, with a history of xenophobic connotations. History Starting with the arrival of European sailors in the sixteenth century, foreigners were often perceived in China as "uncivilized tribes given to mayhem and destruction". In the southern parts of China, the term '' gweilo'' () was used; this term remains popular today in the Cantonese-speaking regions of China. In northern parts, the term 'western devil' ( ) was used. Use The character ''gui'' () can have negative connotations itself without the ''zi'' () suffix. For example, when it was attached to the Westerners in the term ''yang guizi'' ( 'overseas devils') during the Boxer Rebellion, to the Japanese military in the term ''guizi bing'' ( 'devil soldiers') during the Second Sino-Japanese War, and to the Korean collaborators with the term ''er guizi'' ( 'second-rank devil'). It can also be used as an adjective to expres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gweilo
''Gweilo'' or (, pronounced ) is a common Cantonese slang term for Westerners. The term can be literally translated as "ghost man" and has a history of racially deprecatory and pejorative use, though its modern usage is often in a general and non-derogatory context. The appropriateness of the term and whether it constitutes as an offensive ethnic slur are disputed among both Cantonese speakers and Westerners. Etymology and history ''Gwái'' (, ''gui'' in Mandarin) means "ghost" or "devil", and ''lóu'' () means "man" or "guy". The literal translation of ''gwáilóu'' would thus be "ghost man" or "devil man". It is sometimes translated into English as "foreign devil". In many Sinitic languages, "鬼" gwai and its local equivalents can be a derogatory term used as a curse or an insult. The term ''鬼'' gwai has also been used to describe other ethnic groups, for example, a 17th-century writer from Canton, , wrote that Africans "look like ghosts", and ''gwáinòuh'' () was onc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hinomoto Oniko
is a Japanese moe character created in 2010 which originated from the Breaking News (VIP) Board on 2channel, and has since become an internet meme within various forums and imageboards in Japan. The character is a moe anthropomorphism of the phrase "日本鬼子", a commonly used Chinese ethnic slur against people of Japanese descent. Backgrounds The character was originally conceived by users on a 2ch board as a satire of the aforementioned Chinese racial term. In China, the term Riben guizi "日本鬼子" () is a phrase used since World War II, and still used today, as a disparaging epithet against the Japanese. Japanese netizens chose to transform the normally racist and offensive phrase into a character which could be depicted as "cute" or ''moe'', in an expression that the negative connotations behind the slur can be reversed. The creation of the character in 2010 follows the escalation of the Senkaku Islands dispute as a result of the fishing trawler collision incident ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shina (word)
''Shina'' is a largely archaic name for China. Its use in Japanese originally had a neutral connotation, but the word came to be perceived as derogatory by Chinese people during the course of the First and Second Sino-Japanese Wars. As a result, it fell into disuse after World War II and is now viewed as offensive, with the standard Japanese name for China being replaced by . During the 2019–2020 Hong Kong protests, the word was used as a form of protest against the Chinese government but also as a xenophobic remark against mainland Chinese. Origins and early usage The Sanskrit word (), meaning "China", was transcribed into various forms including (), (), () and (). Thus, the term ''Shina'' was initially created as a transliteration of , and this term was in turn brought to Japan with the spread of Chinese Buddhism. Some scholars believe that the Sanskrit , like Middle Persian and Latin , is derived from the name of the state of Qin, which founded a dynasty (, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |