|
Windscale
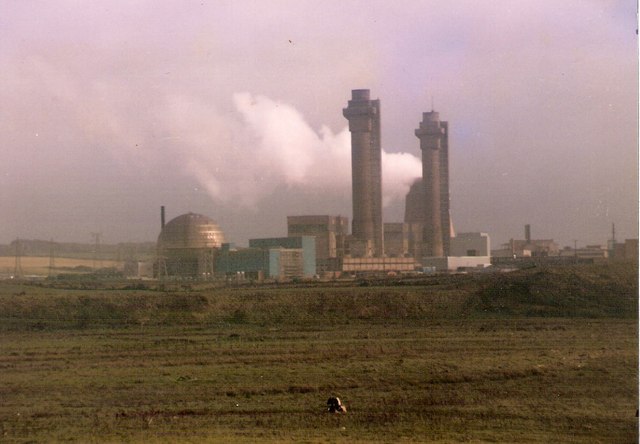
Sellafield, formerly known as Windscale, is a large multi-function nuclear site close to Seascale on the coast of Cumbria, England. As of August 2022, primary activities are nuclear waste processing and storage and nuclear decommissioning. Former activities included nuclear power generation from 1956 to 2003, and nuclear fuel reprocessing from 1952 to 2022. The licensed site covers an area of , and comprises more than 200 nuclear facilities and more than 1,000 buildings. It is Europe's largest nuclear site and has the most diverse range of nuclear facilities in the world on a single site. The site's workforce size varies, and before the COVID-19 pandemic was approximately 10,000 people. The UK's National Nuclear Laboratory has its Central Laboratory and headquarters on the site. Originally built as a Royal Ordnance Factory in 1942, the site briefly passed into the ownership of Courtaulds for rayon manufacture following World War II, but was re-acquired by the Ministry of Su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Windscale Fire
The Windscale fire of 10 October 1957 was the worst nuclear accident in the United Kingdom's history, and one of the worst in the world, ranked in severity at level 5 out of 7 on the International Nuclear Event Scale. The fire was in Unit 1 of the two-pile Windscale site on the north-west coast of England in Cumberland (now Sellafield). The two graphite-moderated reactors, referred to at the time as "piles", had been built as part of the British post-war atomic bomb project. Windscale Pile No. 1 was operational in October 1950, followed by Pile No. 2 in June 1951. The fire burned for three days and released radioactive fallout which spread across the UK and the rest of Europe. The radioactive isotope iodine-131, which may lead to cancer of the thyroid, was of particular concern at the time. It has since come to light that small but significant amounts of the highly dangerous radioactive isotope polonium-210 were also released. It is estimated that the radiation leak ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ROF Sellafield
Sellafield, formerly known as Windscale, is a large multi-function nuclear site close to Seascale on the coast of Cumbria, England. As of August 2022, primary activities are nuclear waste processing and storage and nuclear decommissioning. Former activities included nuclear power generation from 1956 to 2003, and nuclear fuel reprocessing from 1952 to 2022. The licensed site covers an area of , and comprises more than 200 nuclear facilities and more than 1,000 buildings. It is Europe's largest nuclear site and has the most diverse range of nuclear facilities in the world on a single site. The site's workforce size varies, and before the COVID-19 pandemic was approximately 10,000 people. The UK's National Nuclear Laboratory has its Central Laboratory and headquarters on the site. Originally built as a Royal Ordnance Factory in 1942, the site briefly passed into the ownership of Courtaulds for rayon manufacture following World War II, but was re-acquired by the Ministry of Su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Windscale Piles
The Windscale Piles were two air-cooled graphite-moderated reactor, graphite-moderated nuclear reactors on the Windscale nuclear site in Cumberland (now known as Sellafield, Sellafield site, Cumbria) on the north-west coast of England. The two reactors, referred to at the time as "piles", were built as part of the British post-war High Explosive Research, atomic bomb project and produced Weapons-grade nuclear material, weapons-grade plutonium for use in nuclear weapons. Windscale Pile No. 1 became operational in October 1950 followed by Pile No. 2 in June 1951. They were intended to last five years, but operated for seven until shut down following the Windscale fire on 10 October 1957. Nuclear decommissioning operations commenced in the 1980s and are estimated to last beyond 2040. Visible changes have been seen as the chimneys were slowly dismantled from top-down; Pile 2's chimney being reduced to the height of adjacent buildings in the early 2000s. However, the demolition of pi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Nuclear And Radiation Accidents By Death Toll
There have been several nuclear and radiation accidents involving fatalities, including nuclear power plant accidents, nuclear submarine accidents, and radiotherapy incidents. List of accidents Events with disputed fatality counts Chernobyl disaster Estimates of the total number of deaths potentially resulting from the Chernobyl disaster vary enormously: A UNSCEAR report proposes 45 total confirmed deaths from the accident . This number includes 2 non-radiation related fatalities from the accident itself, 28 fatalities from radiation doses in the immediate following months and 15 fatalities due to thyroid cancer likely caused by iodine-131 contamination; it does not include 19 additional individuals initially diagnosed with acute radiation syndrome who had also died , but who are not believed to have died due to radiation doses. The World Health Organization (WHO) suggested in 2006 that cancer deaths could reach 4,000 among the 600,000 most heavily exposed people, a group whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnox
Magnox is a type of nuclear power / production reactor that was designed to run on natural uranium with graphite as the moderator and carbon dioxide gas as the heat exchange coolant. It belongs to the wider class of gas-cooled reactors. The name comes from the magnesium-aluminium alloy (called magnesium non-oxidising), used to clad the fuel rods inside the reactor. Like most other generation I nuclear reactors, the magnox was designed with the dual purpose of producing electrical power and plutonium-239 for the nascent nuclear weapons programme in Britain. The name refers specifically to the United Kingdom design but is sometimes used generically to refer to any similar reactor. As with other plutonium-producing reactors, conserving neutrons is a key element of the design. In magnox, the neutrons are moderated in large blocks of graphite. The efficiency of graphite as a moderator allows the magnox to run using natural uranium fuel, in contrast with the more common commerc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Nuclear Event Scale
The International Nuclear and Radiological Event Scale (INES) was introduced in 1990 by the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) in order to enable prompt communication of safety significant information in case of nuclear accidents. The scale is intended to be logarithmic, similar to the moment magnitude scale that is used to describe the comparative magnitude of earthquakes. Each increasing level represents an accident approximately ten times as severe as the previous level. Compared to earthquakes, where the event intensity can be quantitatively evaluated, the level of severity of a human-made disaster, such as a nuclear accident, is more subject to interpretation. Because of this subjectivity, the INES level of an incident is assigned well after the fact. The scale is therefore intended to assist in disaster-aid deployment. Details A number of criteria and indicators are defined to assure coherent reporting of nuclear events by different official authorities. There ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Advanced Gas-cooled Reactor
The advanced gas-cooled reactor (AGR) is a type of nuclear reactor designed and operated in the United Kingdom. These are the generation II reactor, second generation of British gas-cooled reactors, using Nuclear graphite, graphite as the neutron moderator and carbon dioxide as coolant. They have been the backbone of the UK's nuclear power generation fleet since the 1980s. The AGR was developed from the Magnox reactor, the UK's first-generation reactor design. The first Magnox design had been optimised for generating plutonium, and for this reason it had features that were not the most economic for power generation. Primary among these was the requirement to run on natural uranium, which required a coolant with a low neutron cross section, in this case carbon dioxide, and an efficient neutron moderator, graphite. The Magnox design also ran relatively cool gas temperatures compared to other power-producing designs, which resulted in less efficient steam conditions. The AGR design r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calder Hall Nuclear Power Station
Calder Hall Nuclear Power Station is a former Magnox nuclear power station at Sellafield in Cumbria in North West England. Calder Hall was the first full-scale nuclear power station to enter operation in the West, and was the sister plant to the Chapelcross plant in Scotland. Both were commissioned and originally operated by the United Kingdom Atomic Energy Authority. The primary purpose of both plants was to produce weapons-grade plutonium for the UK's nuclear weapons programme, but they also generated electrical power for the National Grid. Decommissioning by Sellafield Ltd started in 2005. The site is partially demolished and is expected that only the reactor cores and associated radiation shielding will remain by 2027, when it will enter a period of extended care and maintenance using the "safestore" principle, before final demolition. Description It was decided by the UK Government to proceed with the civil nuclear power programme in 1952, and construction at Calder ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Power Generation
Nuclear power is the use of nuclear reactions to produce electricity. Nuclear power can be obtained from nuclear fission, nuclear decay and nuclear fusion reactions. Presently, the vast majority of electricity from nuclear power is produced by nuclear ''fission'' of uranium and plutonium in nuclear power plants. Nuclear ''decay'' processes are used in niche applications such as radioisotope thermoelectric generators in some space probes such as ''Voyager 2''. Reactors producing controlled ''fusion'' power have been operated since 1958 but have yet to generate net power and are not expected to be commercially available in the near future. The first nuclear power plant was built in the 1950s. The global installed nuclear capacity grew to 100GW in the late 1970s, and then expanded during the 1980s, reaching 300GW by 1990. The 1979 Three Mile Island accident in the United States and the 1986 Chernobyl disaster in the Soviet Union resulted in increased regulation and public opposi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermal Oxide Reprocessing Plant
The Thermal Oxide Reprocessing Plant, or THORP, is a nuclear fuel reprocessing plant at Sellafield in Cumbria, England. THORP is owned by the Nuclear Decommissioning Authority and operated by Sellafield Ltd, the site licensee. Spent nuclear fuel from nuclear reactors was reprocessed to separate the 96% uranium and the 1% plutonium from the 3% radioactive wastes, which are treated and stored at the plant. The uranium is then made available for customers to be manufactured into new fuel, and the plutonium incorporated into mixed oxide fuel. On 14 November 2018 it was announced that reprocessing operations had ended at THORP after earning £9bn in revenue. The receipt and storage facility (which makes up nearly half of THORP's physical footprint), will operate through to the 2070s to receive and store spent nuclear fuel from the UK's PWR and AGR fleet. The decommissioning is expected to start around 2075. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cumbria
Cumbria ( ) is a ceremonial county in North West England. It borders the Scottish council areas of Dumfries and Galloway and Scottish Borders to the north, Northumberland and County Durham to the east, North Yorkshire to the south-east, Lancashire to the south, and the Irish Sea to the west. Its largest settlement is the city of Carlisle. Cumbria is predominantly rural, with an area of and a population of 500,012; this makes it the third-largest ceremonial county in England by area but the eighth-smallest by population. Carlisle is located in the north; the towns of Workington and Whitehaven lie on the west coast, Barrow-in-Furness on the south coast, and Penrith, Cumbria, Penrith and Kendal in the east of the county. For local government purposes the county comprises two Unitary authorities of England, unitary authority areas, Westmorland and Furness and Cumberland (unitary authority), Cumberland. Cumbria was created in 1974 from the historic counties of Cumberland and Westmor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seascale
Seascale is a village and civil parish on the Irish Sea coast of Cumbria, England, historically within Cumberland. The parish had a population of 1,754 in 2011, barely decreasing by 0.4% in 2021. History The place-name indicates that it was inhabited by Norse settlers, probably before 1000 AD. It is derived from ''skali'', meaning in Norse a wooden hut or shelter. This could well date from the time of King Harold Fairhair, who vowed revenge on the many Norsemen who had settled in Ireland and the Isle of Man, causing them to flee across the sea to the Cumbrian coast some time after AD 885. Many other Norse place names are to be found, including Seascale How, ''Skala Haugr'', (the hill near the shelter), and Whitriggs, ''hvitihrgger'' (the white ridge). As the Norse penetrated inland other skalar were named, so Seascale was distinguished by reference to the sea. The earliest written reference to Seascale is in the period 1154–1181, when an Aldwin de Seascale was witness to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |