|
William Mundy (composer)
William Mundy (c. 1529–1591) was a Renaissance English composer of sacred music and father of composer John Mundy. Over four hundred years after his death, William Mundy's music is still performed and recorded. Life Mundy was the son of Thomas Mundy, a musician and sexton of the London church St Mary-at-Hill. William Mundy married Mary Alcock and had two sons, John Mundy, an organist and composer, and Stephen Mundy, a gentleman of the household to James I and Charles I. In 1543, William Mundy was head chorister of Westminster Abbey, until his voice broke. He was appointed deputy to St Martin, Ludgate in 1547, and from 1548 to 1558 Mundy served as Parish Clerk for the church of St Mary-at-Hill in London (his father Thomas' employer). Mundy was appointed Vicar choral to the Chapel Royal in 1559, and as a Gentleman of the Chapel in 1564, and remained in that position for twenty-seven years until his death around early October 1591.Most sources cite 1591 as William Mundy year o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hampton Court Palace, Chapel, By Charles Wild, 1819 - Royal Coll 922125 313698 ORI 2
Hampton may refer to: Places Australia * Hampton bioregion, an IBRA biogeographic region in Western Australia * Hampton, New South Wales *Hampton, Queensland, a town in the Toowoomba Region * Hampton, Victoria Canada * Hampton, New Brunswick *Hampton Parish, New Brunswick * Hampton, Nova Scotia * Hampton, Ontario *Hampton, Prince Edward Island United Kingdom *Hampton, Cheshire, former civil parish *Hampton, Herne Bay, Kent **Hampton-on-Sea, Herne Bay, Kent (drowned settlement at the above location) * Hampton, London, London Borough of Richmond upon Thames * Hampton, Peterborough in Cambridgeshire * Hampton Loade, Shropshire * Hampton Lucy, Warwickshire *Hampton, Worcestershire * Hampton in Arden in Solihull, West Midlands * Hampton-on-the-Hill, Warwickshire United States * Hampton, Arkansas * Hampton, Connecticut * Hampton, Florida * Hampton, Georgia * Hampton, Illinois * Hampton, Iowa * Hampton, Kentucky * Hampton, Maryland * Hampton, Minnesota * Hampton, Missouri * Hampton, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
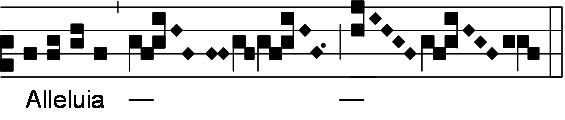
Alleluia
Alleluia (derived from the Hebrew ''Hallelujah'', meaning "Praise Yahweh") is a Latin phrase in Christianity used to give praise to God. In Christian worship, Alleluia is used as a liturgical chant in which that word is combined with verses of scripture, usually from the Psalms. This chant is commonly used before the proclamation of the Gospel. In Western Christianity, congregations commonly cease using the word "Alleluia" during the period of Lent but restore it into their services at Easter. The form of praise "Alleluia" is used by Christians to thank and glorify God; it finds itself present in many prayers and hymns, especially those related to Eastertide, such as ''Jesus Christ Is Risen Today''. History The Hebrew word ''Hallelujah'' as an expression of praise to God was preserved, untranslated, by the Early Christians as a superlative expression of thanksgiving, joy, and triumph. Thus it appears in the ancient Greek Liturgy of St. James, which is still used to this day by t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Verse Anthem
In religious music, the verse anthem is a type of choral music, or song, distinct from the motet or 'full' anthem (i.e. for full choir). In the 'verse' anthem the music alternates between sections for a solo voice or voices (called the 'verse') and the full choir. The organ provided accompaniment in liturgical settings, but viols took the accompaniment outside of the church. In the 'verses', solo voices were expected to ornament their parts for expressive effect. The 'full choir' sections providing contrast in volume and texture. The verse anthems were a major part of the English Reformation due to the use of the vernacular. In addition to this, the use of soloists allowed the text to be expressed more clearly. For the choirmaster they were useful too: the choir only had to learn a small part of the anthem, leaving the hardest passages to a soloist to learn on their own, reducing rehearsal time. Verse anthems developed and were very popular during the early 17th to the middle of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elizabethan Era
The Elizabethan era is the epoch in the Tudor period of the history of England during the reign of Queen Elizabeth I (1558–1603). Historians often depict it as the golden age in English history. The symbol of Britannia (a female personification of Great Britain) was first used in 1572, and often thereafter, to mark the Elizabethan age as a renaissance that inspired national pride through classical ideals, international expansion, and naval triumph over Spain. This "golden age" represented the apogee of the English Renaissance and saw the flowering of poetry, music and literature. The era is most famous for its theatre, as William Shakespeare and many others composed plays that broke free of England's past style of theatre. It was an age of exploration and expansion abroad, while back at home, the Protestant Reformation became more acceptable to the people, most certainly after the Spanish Armada was repelled. It was also the end of the period when England was a sepa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psalm 98
Psalm 98 is the 98th psalm of the Book of Psalms, beginning in English in the King James Version: "O sing unto the Lord a new song; for he hath done marvellous things". The Book of Psalms starts the third section of the Hebrew Bible, and, as such, is a book of the Christian Old Testament. In Latin, it is known as ''Cantate Domino''. In the slightly different numbering system in the Greek Septuagint version of the Bible, and in the Latin Vulgate, this psalm is Psalm 97. The psalm is a hymn psalm, one of the Royal Psalms, praising God as the King of His people. Like Psalms 33 and 96, it calls for the singing of "a new song". The psalm forms a regular part of Jewish, Catholic, Lutheran, Anglican and other Protestant liturgies. It has inspired hymns such as "Joy to the World" and "Nun singt ein neues Lied dem Herren", and has often been set to music, including by Claudio Monteverdi, Marc-Antoine Charpentier, Dieterich Buxtehude and Antonín Dvořák who set it in Czech in his '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psalm 119
Psalm 119 is the 119th psalm of the Book of Psalms, beginning in the English of the King James Version: "Blessed are the undefiled in the way, who walk in the law of the Lord". The Book of Psalms is in the third section of the Hebrew Bible, the ''Khetuvim'', and a book of the Christian Old Testament. The psalm, which is anonymous, is referred to in Hebrew by its opening words, "''Ashrei temimei derech''" ("happy are those whose way is perfect"). In Latin, it is known as "Beati inmaculati in via qui ambulant in lege Domini". The psalm is a hymn psalm and an acrostic poem, in which each set of eight verses begins with a letter of the Hebrew alphabet. The theme of the verses is the prayer of one who delights in and lives by the Torah, the sacred law. Psalms 1, 19 and this psalm may be referred to as "the psalms of the Law". Kirkpatrick, A.Cambridge Bible for Schools and Collegeson Psalm 119, accessed 29 May 2022 In the slightly different numbering system used in the Greek Septua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psalm 51
Psalm 51, one of the penitential psalms, is the 51st psalm of the Book of Psalms, beginning in English in the King James Version: "Have mercy upon me, O God". In the slightly different numbering system used in the Greek Septuagint and Latin Vulgate translations of the Bible, this psalm is Psalm 50. In Latin, it is known as Miserere, ( grc, ἐλέησόν με ὁ θεός, eléēsón me ho theós) in grc, Ἥ Ἐλεήμων, Hḗ Eleḗmōn), especially in musical settings. The introduction in the text says that it was composed by David as a confession to God after he sinned with Bathsheba. The psalm forms a regular part of Jewish, Catholic, Eastern Orthodox and Protestant liturgies. Background and themes Psalm 51 is based on the incident recorded in 2 Samuel, chapters 11–12. David's confession is regarded as a model for repentance in both Judaism and Christianity. The Midrash Tehillim states that one who acknowledges that he has sinned and is fearful and pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psalms
The Book of Psalms ( or ; he, תְּהִלִּים, , lit. "praises"), also known as the Psalms, or the Psalter, is the first book of the ("Writings"), the third section of the Tanakh, and a book of the Old Testament. The title is derived from the Greek translation, (), meaning "instrumental music" and, by extension, "the words accompanying the music". The book is an anthology of individual Hebrew religious hymns, with 150 in the Jewish and Western Christian tradition and more in the Eastern Christian churches. Many are linked to the name of David, but modern mainstream scholarship rejects his authorship, instead attributing the composition of the psalms to various authors writing between the 9th and 5th centuries BC. In the Quran, the Arabic word ‘Zabur’ is used for the Psalms of David in the Hebrew Bible. Structure Benedictions The Book of Psalms is divided into five sections, each closing with a doxology (i.e., a benediction). These divisions were probably introdu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Musical Setting
A musical setting is a musical composition that is written on the basis of a literary work. The literary work is said to be ''set'', or adapted, to music. Musical settings include choral music and other vocal music. A musical setting is made to particular words, such as poems. By contrast, a musical arrangement is a musical reconceptualization of a previously composed work, rather than a brand new piece of music. An arrangement often refers to a change in medium or style and can be instrumental, not necessarily vocal music. Texts commonly used in choral settings include the mass and the requiem in Western Christianity, and the Divine Liturgy of St. John Chrysostom and the All-night vigil in Eastern Christianity. Examples include Mozart's Great Mass, and Leontovych's Liturgy of St. John Chrysostom. A poem that has been set to music is known as an art song or Lied (German variant). Composers known for their art songs include Franz Schubert and Robert Schumann. Some notable settin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anthems
An anthem is a musical composition of celebration, usually used as a symbol for a distinct group, particularly the national anthems of countries. Originally, and in music theory and religious contexts, it also refers more particularly to short sacred choral work (still frequently seen in Sacred Harp and other types of shape note singing) and still more particularly to a specific form of liturgical music. In this sense, its use began ca. 1550 in English-speaking churches; it uses English language words, in contrast to the originally Roman Catholic 'motet' which sets a Latin text. Etymology ''Anthem'' is derived from the Greek (''antíphōna'') via Old English . Both words originally referred to antiphons, a call-and-response style of singing. The adjectival form is "anthemic". History Anthems were originally a form of liturgical music. In the Church of England, the rubric appoints them to follow the third collect at morning and evening prayer. Several anthems are includ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Motets
In Western classical music, a motet is mainly a vocal musical composition, of highly diverse form and style, from high medieval music to the present. The motet was one of the pre-eminent polyphonic forms of Renaissance music. According to Margaret Bent, "a piece of music in several parts with words" is as precise a definition of the motet as will serve from the 13th to the late 16th century and beyond.Margaret Bent,The Late-Medieval Motet in ''Companion to Medieval & Renaissance Music'', edited by Tess Knighton and David Fallows, 114–19 (Berkeley, California: University of California Press, 1992): 114. . The late 13th-century theorist Johannes de Grocheo believed that the motet was "not to be celebrated in the presence of common people, because they do not notice its subtlety, nor are they delighted in hearing it, but in the presence of the educated and of those who are seeking out subtleties in the arts". Etymology In the early 20th century, it was generally believed the name ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Service (music)
In Anglican church music, a service is a musical setting of certain parts of the liturgy, generally for choir with or without organ accompaniment. Liturgical services Morning Prayer *Venite (Psalm 95 — rarely set after the Restoration) *Te Deum or Benedicite * Benedictus (Luke I, 68) or Jubilate (Psalm 100) Evening Prayer *Magnificat or (rarely) Cantate Domino (Psalm 98) *Nunc dimittis or (rarely) Deus misereatur ( Psalm 67) Holy Communion *Responses to the Commandments *Nicene Creed *Sanctus *Agnus Dei *Kyrie Eleison * Gloria in Excelsis This follows the ''Book of Common Prayer''. Modern Anglican liturgy has largely reverted to the order of the Roman Catholic Mass. Unlike masses written in the Catholic tradition, however, masses by Anglican composers may choose to omit the Credo, which, in Anglican churches, is often recited rather than sung. Also, rather than setting the traditional Latin and Greek liturgy, several Anglican-composed masses use an English translation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |