|
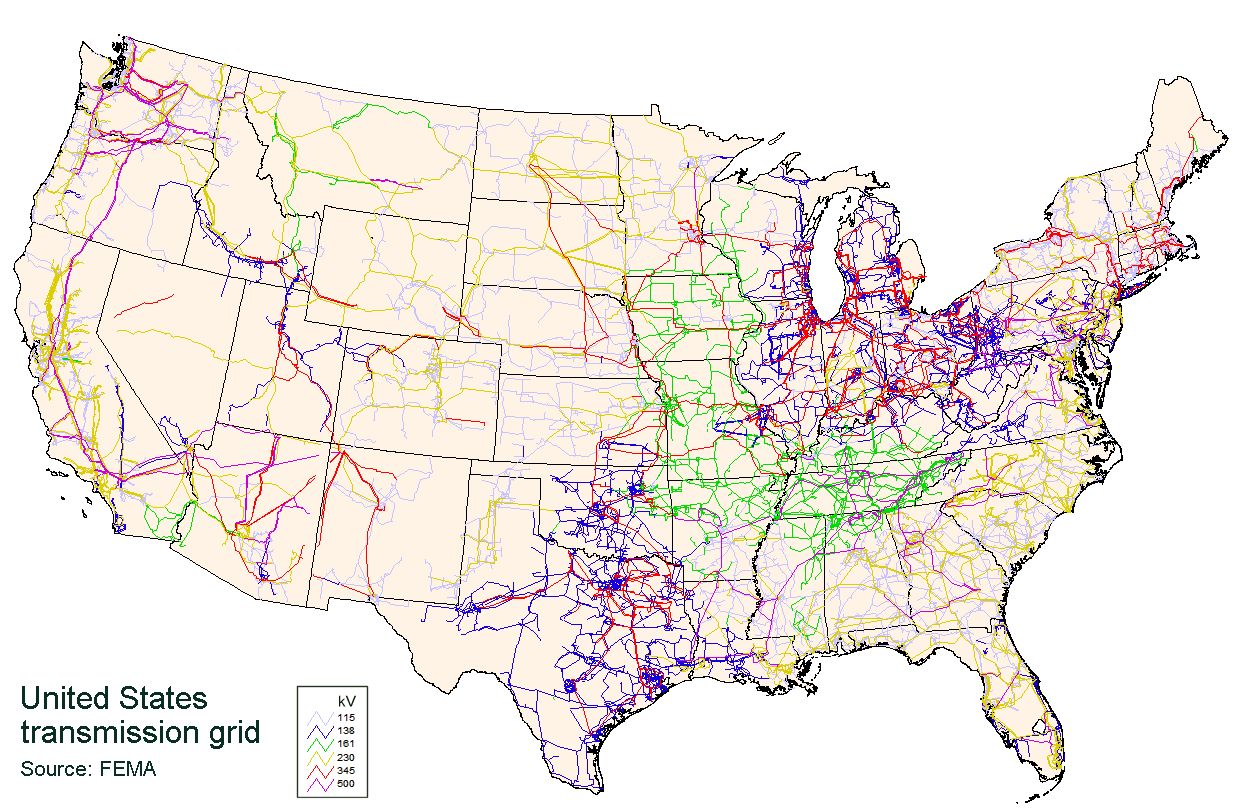
Wide-area Synchronous Grid
A wide area synchronous grid (also called an "interconnection" in North America) is a three-phase electric power grid that has regional scale or greater that operates at a synchronized utility frequency and is electrically tied together during normal system conditions. Also known as ''synchronous zones'', the most powerful is the Northern Chinese State Grid with 1,700 gigawatts (GW) of generation capacity, while the widest region served is that of the IPS/UPS system serving most countries of the former Soviet Union. Synchronous grids with ample capacity facilitate electricity trading across wide areas. In the CESA system in 2008, over 350,000 megawatt hours were sold per day on the European Energy Exchange (EEX). Neighbouring interconnections with the same frequency and standards can be synchronized and directly connected to form a larger interconnection, or they may share power without synchronization via high-voltage direct current power transmission lines (DC ties), sol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere, Northern and Western Hemisphere, Western hemispheres. North America is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Caribbean Sea, and to the south and west by the Pacific Ocean. The region includes Middle America (Americas), Middle America (comprising the Caribbean, Central America, and Mexico) and Northern America. North America covers an area of about , representing approximately 16.5% of Earth's land area and 4.8% of its total surface area. It is the third-largest continent by size after Asia and Africa, and the list of continents and continental subregions by population, fourth-largest continent by population after Asia, Africa, and Europe. , North America's population was estimated as over 592 million people in list of sovereign states and dependent territories in North America, 23 independent states, or about 7.5% of the world's popula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fukushima Daiichi
The is a disabled nuclear power plant located on a site in the towns of Ōkuma and Futaba in Fukushima Prefecture, Japan. The plant suffered major damage from the magnitude 9.1 earthquake and tsunami that hit Japan on March 11, 2011. The chain of events caused radiation leaks and permanently damaged several of its reactors, making them impossible to restart. The working reactors were not restarted after the events. First commissioned in 1971, the plant consists of six boiling water reactors. These light water reactors drove electrical generators with a combined power of 4.7 GWe, making Fukushima Daiichi one of the 15 largest nuclear power stations in the world. Fukushima was the first nuclear plant to be designed, constructed, and run in conjunction with General Electric and Tokyo Electric Power Company (TEPCO). The sister nuclear plant Fukushima Daini ( "number two"), to the south, is also run by TEPCO. It also suffered serious damage during the tsunami, at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serbia
, image_flag = Flag of Serbia.svg , national_motto = , image_coat = Coat of arms of Serbia.svg , national_anthem = () , image_map = , map_caption = Location of Serbia (green) and the claimed but uncontrolled territory of Kosovo (light green) in Europe (dark grey) , image_map2 = , capital = Belgrade , coordinates = , largest_city = capital , official_languages = Serbian language, Serbian , ethnic_groups = , ethnic_groups_year = 2022 , religion = , religion_year = 2022 , demonym = Serbs, Serbian , government_type = Unitary parliamentary republic , leader_title1 = President of Serbia, President , leader_name1 = Aleksandar Vučić , leader_title2 = Prime Minister of Serbia, Prime Minister , leader_name2 = Đuro Macut , leader_title3 = Pres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kosovo
Kosovo, officially the Republic of Kosovo, is a landlocked country in Southeast Europe with International recognition of Kosovo, partial diplomatic recognition. It is bordered by Albania to the southwest, Montenegro to the west, Serbia to the north and east, and North Macedonia to the southeast. It covers an area of and has a population of approximately 1.6 million. Kosovo has a varied terrain, with high plains along with rolling hills and List of mountains in Kosovo, mountains, some of which have an altitude over . Its climate is mainly Continental climate, continental with some Mediterranean climate, Mediterranean and Alpine climate, alpine influences. Kosovo's capital and List of cities and towns in Kosovo#List, most populous city is Pristina; other major cities and urban areas include Prizren, Ferizaj, Gjilan and Peja. Kosovo formed the core territory of the Dardani, an ancient Paleo-Balkanic languages, Paleo-Balkanic people attested in classical sources from the 4th cent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Short Circuit Ratio (electrical Grid)
In an electrical grid, the short circuit ratio (or SCR) is the ratio of: the short circuit apparent power (SCMVA) in the case of a line-line-line-ground (3LG) fault at the location in the grid where some generator is connected, to: the power rating of the generator itself (GMW). Since the power that can be delivered by the grid varies by location, frequently a location is indicated, for example, at the point of interconnection (POI): :SCR_ = \frac SCR is used to quantify the system strength of the grid (its ability to deal with changes in active and reactive power injection and consumption). On a simplified level, a high SCR indicates that the particular generator represents a small portion of the power available at the point of its connection to the grid, and therefore the generator problems cannot affect the grid in a significant way. SCMVA is defined as a product of the voltage before the 3LG fault and the current that would flow after the fault (this worst-case combina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Renewable Energy Laboratory
The National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) in the US specializes in the research and development of renewable energy, energy efficiency, energy systems integration, and sustainable transportation. NREL is a federally funded research and development center sponsored by the Department of Energy and operated by the Alliance for Sustainable Energy, a joint venture between MRIGlobal and Battelle. Located in Golden, Colorado, NREL is home to the National Center for Photovoltaics, the National Bioenergy Center, and the National Wind Technology Center. History Establishment During the 1973 oil crisis, soaring energy prices caused gasoline shortages and contributed significantly to inflation. US President Gerald Ford openly recognized the need for greater energy independence at the September 1974 World Energy Conference in Detroit. A month later, the Solar Energy Research, Development and Demonstration Act of 1974 was signed. Section 10 of the bill explicitly outlined ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synthetic Inertia
Inertial response is a property of large synchronous generators, which contain large synchronous rotating masses, and which acts to overcome any immediate imbalance between power supply and demand for electric power systems, typically the electrical grid. Due to the ever existing power imbalance between mechanical power supply and electric power demand the rotational frequency of the rotating masses in all synchronous generators in the grid either speed up and thus absorb the extra power in case of an excess power supply, or slow down and provide additional power in case of an excess power demand. This response in case of a synchronous generator is built-in into the design and happens without any external intervention or coordination, providing the automatic generation control and the grid operator with valuable time (few seconds) to rebalance the system The grid frequency is the combined result of the detailed motions of all individual synchronous rotors in the grid, which are m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interconnector
An interconnector (also known as a DC tie in the USA) is a structure which enables high-voltage DC electricity to flow between electrical grids, connecting separate AC networks, or linking synchronous grids. It may be formed of submarine power cables, underground power cables or overhead power lines. The longest interconnection as of July 2022 was the Hami - Zhengzhou delivering 8 GW of high voltage direct current power. The longest proposed connector is the , 3.6 GW Xlinks Morocco-UK Power Project. Economy Interconnectors allow the trading of electricity between territories. For example, the East–West Interconnector allows the trading of electricity between Great Britain and Ireland. A territory which generates more energy than it requires for its own activities can therefore sell surplus energy to a neighbouring territory. Interconnectors also provide increased resilience. Within the European Union there is a movement towards a single market for energy, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HVDC
A high-voltage direct current (HVDC) electric power transmission system uses direct current (DC) for electric power transmission, in contrast with the more common alternating current (AC) transmission systems. Most HVDC links use voltages between 100 kV and 800 kV. HVDC lines are commonly used for long-distance power transmission, since they require fewer conductors and incur less power loss than equivalent AC lines. HVDC also allows power transmission between AC transmission systems that are not Synchronization (alternating current), synchronized. Since the power flow through an HVDC link can be controlled independently of the phase angle between source and load, it can stabilize a network against disturbances due to rapid changes in power. HVDC also allows the transfer of power between grid systems running at different frequencies, such as 50 and 60 Hz. This improves the stability and economy of each grid, by allowing the exchange of power between previously inc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Automatic Generation Control
In an electric power system, automatic generation control (AGC) is a system for adjusting the power output of multiple generators at different power plants, in response to changes in the load. Since a power grid requires that generation and load closely balance moment by moment, frequent adjustments to the output of generators are necessary. The balance can be judged by measuring the system frequency; if it is increasing, more power is being generated than used, which causes all the machines in the system to accelerate. If the system frequency is decreasing, more load is on the system than the instantaneous generation can provide, which causes all generators to slow down. History Before the use of automatic generation control, one generating unit in a system would be designated as the regulating unit and would be manually adjusted to control the balance between generation and load to maintain system frequency at the desired value. The remaining units would be controlled with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Droop Speed Control
Droop speed control is a control mode used for AC electrical power generators, whereby the power output of a generator reduces as the line frequency increases. It is commonly used as the speed control mode of the governor of a prime mover driving a synchronous generator connected to an electrical grid. It works by controlling the rate of power produced by the prime mover according to the grid frequency. With droop speed control, when the grid is operating at maximum operating frequency, the prime mover's power is reduced to zero, and when the grid is at minimum operating frequency, the power is set to 100%, and intermediate values at other operating frequencies. This mode allows synchronous generators to run in parallel, so that loads are shared among generators with the same droop curve in proportion to their power rating. In practice, the droop curves that are used by generators on large electrical grids are not necessarily linear or the same, and may be adjusted by operators. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |