|
National Renewable Energy Laboratory
The National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) in the US specializes in the research and development of renewable energy, energy efficiency, energy systems integration, and sustainable transportation. NREL is a federally funded research and development center sponsored by the Department of Energy and operated by the Alliance for Sustainable Energy, a joint venture between MRIGlobal and Battelle. Located in Golden, Colorado, NREL is home to the National Center for Photovoltaics, the National Bioenergy Center, and the National Wind Technology Center. History Establishment During the 1973 oil crisis, soaring energy prices caused gasoline shortages and contributed significantly to inflation. US President Gerald Ford openly recognized the need for greater energy independence at the September 1974 World Energy Conference in Detroit. A month later, the Solar Energy Research, Development and Demonstration Act of 1974 was signed. Section 10 of the bill explicitly outlined ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Photovoltaic Energy Research, Development, And Demonstration Act Of 1978
Solar Photovoltaic Energy Research, Development, and Demonstration Act of 1978 is a United States statute authorizing the research and development of photovoltaic systems utilizing solar irradiance or sunlight as a source for electricity generation. The Act of Congress promotes energy conservation by the displacement of conventional energy systems dependent upon alternative fuel and fossil fuel resources. The H.R. 12874 legislation was passed by the 95th U.S. Congressional session and enacted into law by the 39th President of the United States Jimmy Carter on November 4, 1978. Provisions of the Act Title 42 United States Code Chapter 71 and Subchapter III was compiled as fourteen code of law sections based on U.S. Congressional findings regarding potential benefits of solar power and declaration of a renewable energy policy. :42 U.S.C. § 5581 - ''Congressional findings and declaration of policy'' :42 U.S.C. § 5582 - ''Definitions'' :42 U.S.C. § 5583 - ''Establishment and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photovoltaics
Photovoltaics (PV) is the conversion of light into electricity using semiconducting materials that exhibit the photovoltaic effect, a phenomenon studied in physics, photochemistry, and electrochemistry. The photovoltaic effect is commercially used for electricity generation and as photosensors. A photovoltaic system employs solar modules, each comprising a number of solar cells, which generate electrical power. PV installations may be ground-mounted, rooftop-mounted, wall-mounted or floating. The mount may be fixed or use a solar tracker to follow the sun across the sky. Photovoltaic technology helps to mitigate climate change because it emits much less carbon dioxide than fossil fuels. Solar PV has specific advantages as an energy source: once installed, its operation does not generate any pollution or any greenhouse gas emissions; it shows scalability in respect of power needs and silicon has large availability in the Earth's crust, although other materials required ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydro Power
Hydropower (from Ancient Greek -, "water"), also known as water power or water energy, is the use of falling or fast-running water to produce electricity or to power machines. This is achieved by converting the gravitational potential or kinetic energy of a water source to produce power. Hydropower is a method of sustainable energy production. Hydropower is now used principally for hydroelectric power generation, and is also applied as one half of an energy storage system known as pumped-storage hydroelectricity. Hydropower is an attractive alternative to fossil fuels as it does not directly produce carbon dioxide or other atmospheric pollutants and it provides a relatively consistent source of power. Nonetheless, it has economic, sociological, and environmental downsides and requires a sufficiently energetic source of water, such as a river or elevated lake. International institutions such as the World Bank view hydropower as a low-carbon means for economic development. Si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geothermal Energy
Geothermal energy is thermal energy extracted from the crust (geology), crust. It combines energy from the formation of the planet and from radioactive decay. Geothermal energy has been exploited as a source of heat and/or electric power for millennia. Geothermal heating, using water from hot springs, for example, has been used for bathing since Paleolithic times and for space heating since Roman times. Geothermal power (generation of electricity from geothermal energy), has been used since the 20th century. Unlike wind and solar energy, geothermal plants produce power at a constant rate, without regard to weather conditions. Geothermal resources are theoretically more than adequate to supply humanity's energy needs. Most extraction occurs in areas near tectonic plate boundaries. The cost of generating geothermal power decreased by 25% during the 1980s and 1990s. Technological advances continued to reduce costs and thereby expand the amount of viable resources. In 2021, the US ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fuel Cell
A fuel cell is an electrochemical cell that converts the chemical energy of a fuel (often hydrogen fuel, hydrogen) and an oxidizing agent (often oxygen) into electricity through a pair of redox reactions. Fuel cells are different from most battery (electricity), batteries in requiring a continuous source of fuel and oxygen (usually from air) to sustain the chemical reaction, whereas in a battery the chemical energy usually comes from substances that are already present in the battery. Fuel cells can produce electricity continuously for as long as fuel and oxygen are supplied. The first fuel cells were invented by Sir William Robert Grove, William Grove in 1838. The first commercial use of fuel cells came almost a century later following the invention of the hydrogen–oxygen fuel cell by Francis Thomas Bacon in 1932. The alkaline fuel cell, also known as the Bacon fuel cell after its inventor, has been used in NASA space programs since the mid-1960s to generate power for sate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen Technologies
Hydrogen technologies are technologies that relate to the production and use of hydrogen as a part hydrogen economy. Hydrogen technologies are applicable for many uses. Some hydrogen technologies are carbon neutral and could have a role in preventing climate change and a possible future hydrogen economy. Hydrogen is a chemical widely used in various applications including ammonia production, oil refining and energy. The most common methods for producing hydrogen on an industrial scale are: Steam reforming, oil reforming, coal gasification, water electrolysis. Hydrogen is not a primary energy source, because it is not naturally occurring as a fuel. It is, however, widely regarded as an ideal energy storage medium, due to the ease with which electricity can convert water into hydrogen and oxygen through electrolysis and can be converted back to electrical power using a fuel cell or hydrogen turbine. There are a wide number of different types of fuel and electrolysis ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
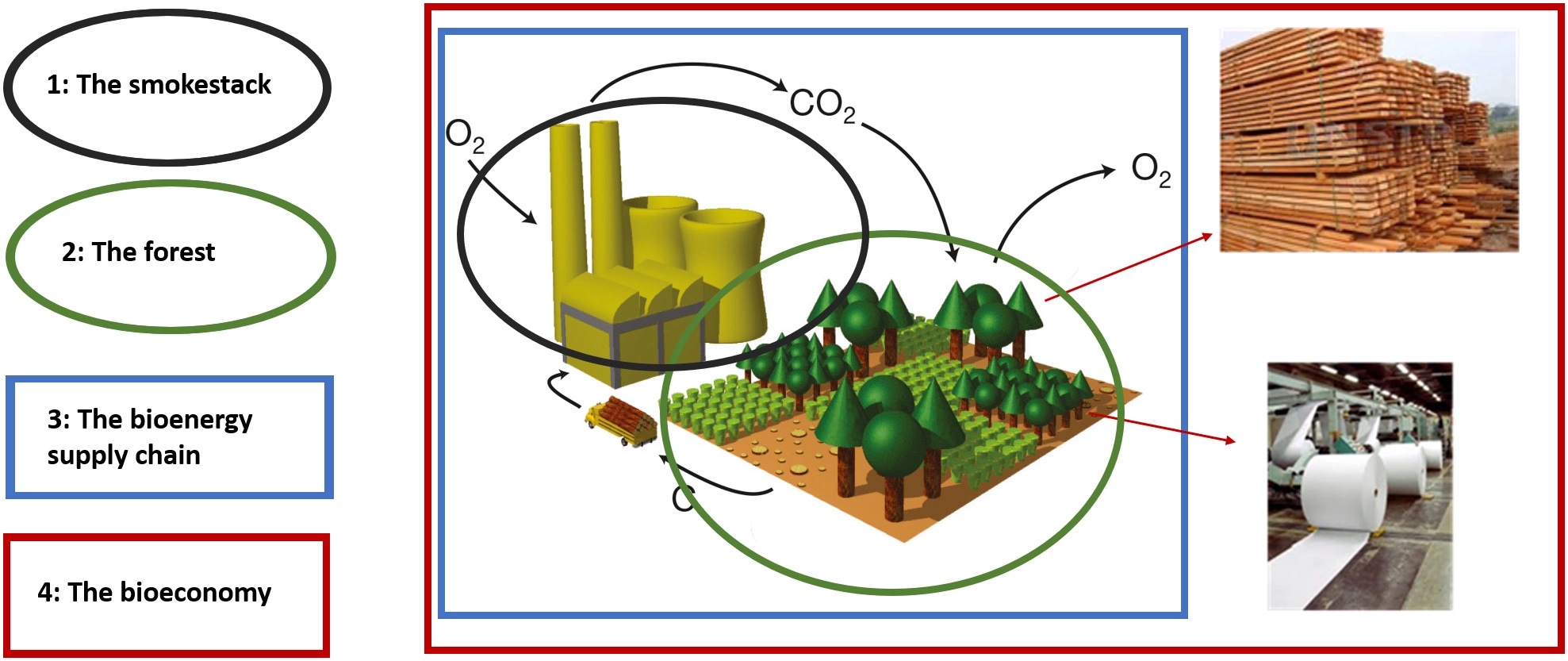
Bioenergy
Bioenergy is a type of renewable energy that is derived from plants and animal waste. The Biomass (energy), biomass that is used as input materials consists of recently living (but now dead) organisms, mainly plants. Thus, Fossil fuel, fossil fuels are not regarded as biomass under this definition. Types of biomass commonly used for bioenergy include wood, food crops such as corn, energy crops and waste from forests, yards, or farms. Bioenergy can help with climate change mitigation but in some cases the required biomass production can increase greenhouse gas emissions or lead to local biodiversity loss. The environmental impacts of biomass production can be problematic, depending on how the biomass is produced and harvested. But it still produces CO2; so long as the energy is derived from breaking chemical bonds. The International Energy Agency, IEA's Net Zero by 2050 scenario calls for traditional bioenergy to be phased out by 2030, with modern bioenergy's share increasing fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wind Power
Wind power is the use of wind energy to generate useful work. Historically, wind power was used by sails, windmills and windpumps, but today it is mostly used to generate electricity. This article deals only with wind power for electricity generation. Today, wind power is generated almost completely using wind turbines, generally grouped into wind farms and connected to the electrical grid. In 2024, wind supplied over 2,494 TWh of electricity, which was 8.1% of world electricity. With about 100 Gigawatt, GW added during 2021, mostly Wind power in China, in China and the Wind power in the United States, United States, global installed wind power capacity exceeded 800 GW. 30 countries generated more than a tenth of their electricity from wind power in 2024 and wind generation has nearly tripled since 2015. To help meet the Paris Agreement goals to Climate change mitigation, limit climate change, analysts say it should expand much faster – by over 1% of electricity generation p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Energy
Solar energy is the radiant energy from the Sun's sunlight, light and heat, which can be harnessed using a range of technologies such as solar electricity, solar thermal energy (including solar water heating) and solar architecture. It is an essential source of renewable energy, and its technologies are broadly characterized as either passive solar or active solar depending on how they capture and distribute solar energy or convert it into solar power. Active solar techniques include the use of photovoltaic systems, concentrated solar power, and solar water heating to harness the energy. Passive solar techniques include designing a building for better daylighting (architecture), daylighting, selecting materials with favorable thermal mass or light-dispersing properties, and organizing spaces that ventilation (architecture), naturally circulate air. In 2011, the International Energy Agency said that "the development of affordable, inexhaustible and clean solar energy technolo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
US Projected Cost Of Wind Power
US or Us most often refers to: * ''Us'' (pronoun), the objective case of the English first-person plural pronoun ''we'' * US, an abbreviation for the United States US, U.S., Us, us, or u.s. may also refer to: Arts and entertainment Albums * ''Us'' (Brother Ali album) or the title song, 2009 * ''Us'' (Empress Of album), 2018 * ''Us'' (Mull Historical Society album), 2003 * ''Us'' (Peter Gabriel album), 1992 * ''Us'' (EP), by Moon Jong-up, 2021 * ''Us'', by Maceo Parker, 1974 * ''Us'', mini-album by Peakboy, 2019 Songs * "Us" (James Bay song), 2018 * "Us" (Jennifer Lopez song), 2018 * "Us" (Regina Spektor song), 2004 * "Us" (Gracie Abrams song), 2024 * "Us", by Azealia Banks from '' Fantasea'', 2012 * "Us", by Celine Dion from ''Let's Talk About Love'', 1997 * "Us", by Gucci Mane from '' Delusions of Grandeur'', 2019 * "Us", by Spoon from '' Hot Thoughts'', 2017 Other media * US Festival, two 1980s California music festivals organized by Steve Wozniak * ''Us'' (1991 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dan Arvizu
Dan Arvizu is a mechanical engineer at the United States Department of Energy (DOE) National Laboratories, where he has taken on various roles over the course of more than 30 years. Arvizu is also an expert in energy materials, technology commercialization and process sciences. He is a leader in higher education that is determined to harness education, research, and outreach initiatives to promote economic development and social mobility. Since 2021, he has been a member of the President’s Council of Advisors on Science and Technology (PCAST). Career Arvizu was the first Hispanic to lead the DOE national laboratory, where he also was the former director and chief executive of the National Renewable Energy Laboratory, and currently director emeritus. He served as board chair to the National Science Board (NSB), where he was appointed the position by Presidents George W. Bush and Barack Obama. Arvizu is a member of the National Academy of Engineering The National Academy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |