|
Vertical Refresh
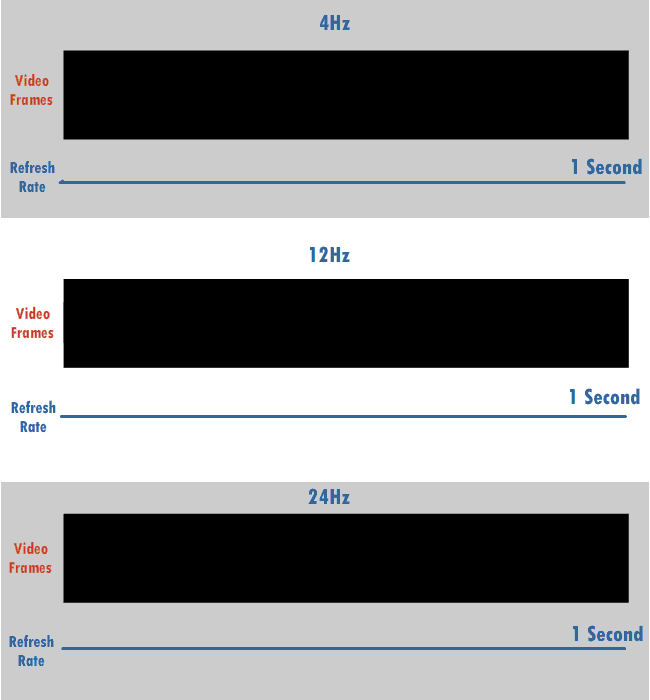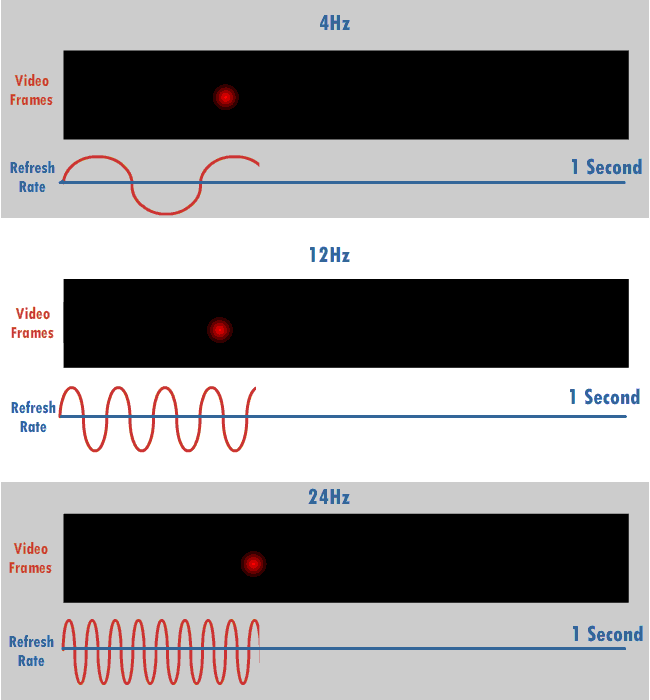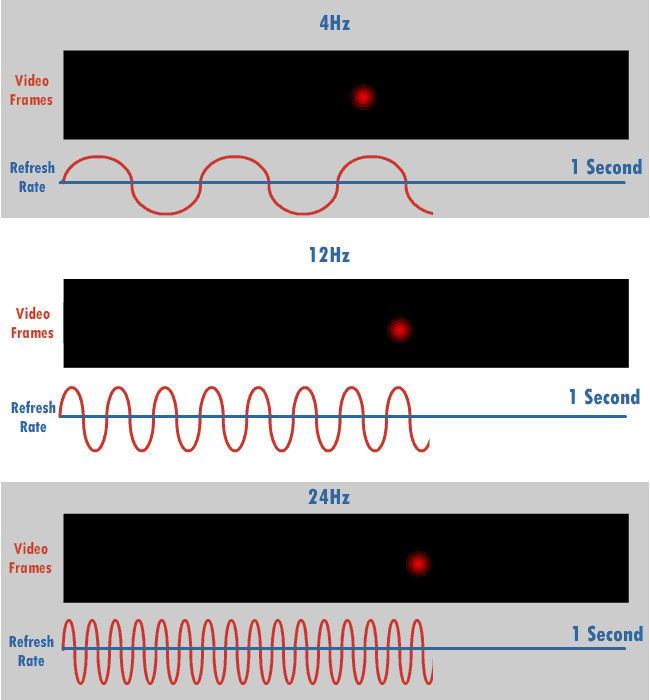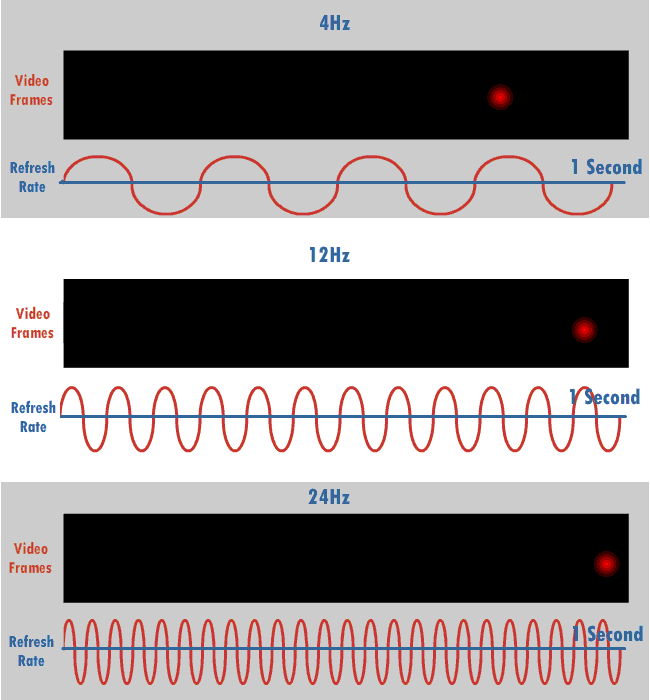
The refresh rate, also known as vertical refresh rate, vertical scan rate or vertical frequency in reference to terminology originating with the cathode-ray tubes (CRTs), is the number of times per second that a Raster scan, raster-based display device displays a new image. This is independent from frame rate, which describes how many images are stored or generated every second by the device driving the display. On CRT displays, higher refresh rates produce less flicker (screen), flickering, thereby reducing eye strain. In other technologies such as liquid-crystal displays, the refresh rate affects only how often the image can potentially be updated. Non-raster displays may not have a characteristic refresh rate. Vector displays, for instance, do not trace the entire screen, only the actual lines comprising the displayed image, so refresh speed may differ by the size and complexity of the image data. For computer programs or telemetry, the term is sometimes applied to how frequentl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cathode-ray Tube
A cathode-ray tube (CRT) is a vacuum tube containing one or more electron guns, which emit electron beams that are manipulated to display images on a phosphorescent screen. The images may represent electrical waveforms on an oscilloscope, a Film frame, frame of video on an Analog television, analog television set (TV), Digital imaging, digital raster graphics on a computer monitor, or other phenomena like radar targets. A CRT in a TV is commonly called a picture tube. CRTs have also been Williams tube, used as memory devices, in which case the screen is not intended to be visible to an observer. The term ''cathode ray'' was used to describe electron beams when they were first discovered, before it was understood that what was emitted from the cathode was a beam of electrons. In CRT TVs and computer monitors, the entire front area of the tube is scanned repeatedly and systematically in a fixed pattern called a raster scan, raster. In color devices, an image is produced by con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Screen Tearing
Screen tearing is a visual artifact in video display where a display device shows information from multiple frames in a single screen draw. The artifact occurs when the video feed to the device is not synchronized with the display's refresh rate. That can be caused by non-matching refresh rates, and the tear line then moves as the phase difference changes (with speed proportional to the difference of frame rates). It can also occur simply from a lack of synchronization between two equal frame rates, and the tear line is then at a fixed location that corresponds to the phase difference. During video motion, screen tearing creates a torn look as the edges of objects (such as a wall or a tree) fail to line up. Tearing can occur with most common display technologies and video cards and is most noticeable in horizontally-moving visuals, such as in slow camera pans in a movie or classic side-scrolling video games. Screen tearing is less noticeable when more than two frames finish r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
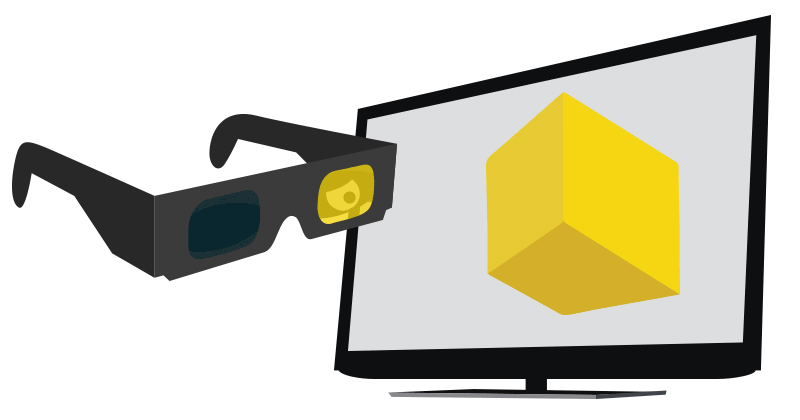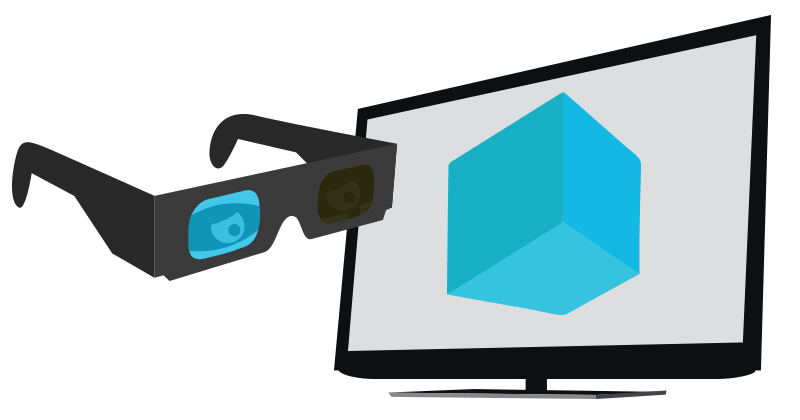
Shutter Glasses
An active shutter 3D system (a.k.a. alternate frame sequencing, alternate image, AI, alternating field, field sequential or eclipse method) is a technique for displaying stereoscopic 3D images. It works by only presenting the image intended for the left eye while blocking the right eye's view, then presenting the right-eye image while blocking the left eye, and repeating this so rapidly that the interruptions do not interfere with the perceived fusion of the two images into a single 3D image. Modern active shutter 3D systems generally use liquid crystal shutter glasses (also called "LC shutter glasses" or "active shutter glasses"). Each eye's glass contains a liquid crystal layer which has the property of becoming opaque when voltage is applied, being otherwise transparent. The glasses are controlled by a timing signal that allows the glasses to alternately block one eye, and then the other, in synchronization with the refresh rate of the screen. The timing synchronization to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
G-Sync
G-Sync is a proprietary adaptive sync technology developed by Nvidia aimed primarily at eliminating screen tearing and the need for software alternatives such as Vsync. G-Sync eliminates screen tearing by allowing a video display's refresh rate to adapt to the frame rate of the outputting device (graphics card/integrated graphics) rather than the outputting device adapting to the display, which could traditionally be refreshed halfway through the process of a frame being output by the device, resulting in screen tearing, or two or more frames being shown at once. In order for a device to use G-Sync, it must contain a proprietary G-Sync module sold by Nvidia. AMD has released a similar technology for displays, called FreeSync, which has the same function as G-Sync yet is royalty-free. Nvidia built a special collision avoidance feature to avoid the eventuality of a new frame being ready while a duplicate is being drawn on screen (something that could generate lag and/or stut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FreeSync
FreeSync is an adaptive synchronization technology that allows LCD and OLED displays to support a variable refresh rate aimed at avoiding tearing and reducing stuttering caused by misalignment between the screen's refresh rate and the content's frame rate. FreeSync was developed by AMD and first announced in 2014 to compete against Nvidia's proprietary G-Sync. It is royalty-free, free to use, and has no performance penalty. Overview FreeSync dynamically adapts the display refresh rate to variable frame rates which result from irregular GPU load when rendering complex gaming content as well as the lower 23.97/24/29.97/30 Hz used by fixed video content. This helps remove stuttering delays caused by the video interface having to finish the current frame and screen tearing when starting a new frame in the middle of transmission (with vertical sync off). The range of refresh rates supported by the standard is based on the capabilities reported by the display. FreeSync can be e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Video Card
A graphics card (also called a video card, display card, graphics accelerator, graphics adapter, VGA card/VGA, video adapter, display adapter, or colloquially GPU) is a computer expansion card that generates a feed of graphics output to a display device such as a computer monitor, monitor. Graphics cards are sometimes called ''discrete'' or ''dedicated'' graphics cards to emphasize their distinction to an graphics processing unit#Integrated graphics processing unit, integrated graphics processor on the motherboard or the central processing unit (CPU). A graphics processing unit (GPU) that performs the necessary computations is the main component in a graphics card, but the acronym "GPU" is sometimes also used to refer to the graphics card as a whole erroneously. Most graphics cards are not limited to simple display output. The graphics processing unit can be used for additional processing, which reduces the load from the CPU. Additionally, computing platforms such as OpenCL and C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Windows 7
Windows 7 is a major release of the Windows NT operating system developed by Microsoft. It was Software release life cycle#Release to manufacturing (RTM), released to manufacturing on July 22, 2009, and became generally available on October 22, 2009. It is the successor to Windows Vista, released nearly three years earlier. Windows 7's Windows Server, server counterpart, Windows Server 2008 R2, was released at the same time. It sold over 630 million copies before it was succeeded by Windows 8 in October 2012. Extended support ended on January 14, 2020, over 10 years after the release of Windows 7, and the operating system ceased receiving further updates. A paid support program was available for enterprises, providing security updates for Windows 7 for up to three years since the official end of life. Windows 7 was intended to be an incremental upgrade to Windows Vista, addressing the previous OS's poor reception while maintaining hardware and software compatibility as well as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Windows Vista
Windows Vista is a major release of the Windows NT operating system developed by Microsoft. It was the direct successor to Windows XP, released five years earlier, which was then the longest time span between successive releases of Microsoft Windows. It was Software release life cycle#Release to manufacturing (RTM), released to manufacturing on November 8, 2006, and over the following two months, it was released in stages to business customers, original equipment manufacturers (OEMs), and retail channels. On January 30, 2007, it was released internationally and was made available for purchase and download from the Windows Marketplace; it is the first release of Windows to be made available through a digital distribution platform. Development of Windows Vista began in 2001 under the codename "Longhorn"; originally envisioned as a minor successor to Windows XP, it feature creep, gradually included numerous new features from the then-next major release of Windows codenamed "Blackc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |