cathode-ray tube on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]


 A cathode-ray tube (CRT) is a
A cathode-ray tube (CRT) is a 



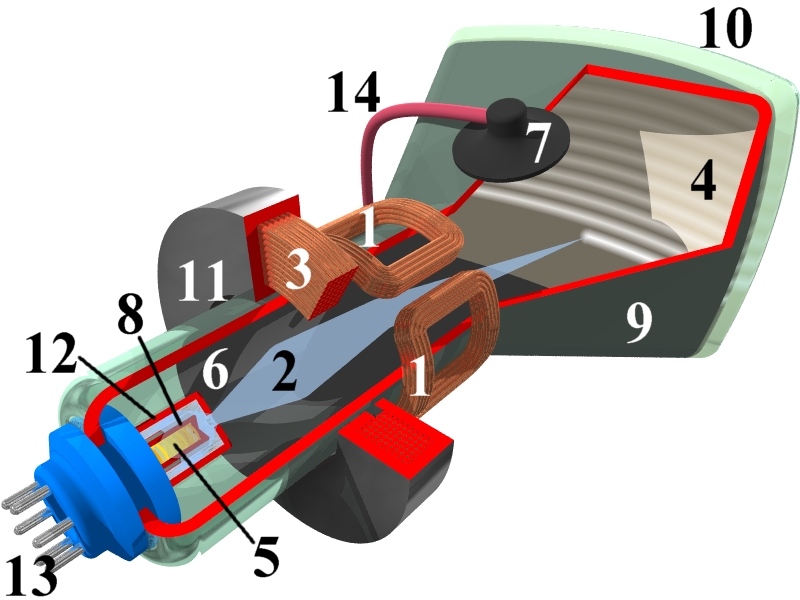
 A CRT is a glass envelope which is deep (i.e., long from front screen face to rear end), heavy, and fragile. The interior is evacuated to to or less, to facilitate the free flight of electrons from the gun(s) to the tube's face without scattering due to collisions with air molecules. As such, handling a CRT carries the risk of violent implosion that can hurl glass at great velocity. The face is typically made of thick lead glass or special barium-strontium glass to be shatter-resistant and to block most X-ray emissions. CRTs make up most of the weight of CRT TVs and computer monitors.
Since the mid-late 2000's, CRTs have been superseded by flat-panel display technologies such as
A CRT is a glass envelope which is deep (i.e., long from front screen face to rear end), heavy, and fragile. The interior is evacuated to to or less, to facilitate the free flight of electrons from the gun(s) to the tube's face without scattering due to collisions with air molecules. As such, handling a CRT carries the risk of violent implosion that can hurl glass at great velocity. The face is typically made of thick lead glass or special barium-strontium glass to be shatter-resistant and to block most X-ray emissions. CRTs make up most of the weight of CRT TVs and computer monitors.
Since the mid-late 2000's, CRTs have been superseded by flat-panel display technologies such as
 Cathode rays were discovered by Julius Plücker and
Cathode rays were discovered by Julius Plücker and


 A cathode-ray tube (CRT) is a
A cathode-ray tube (CRT) is a vacuum tube
A vacuum tube, electron tube, valve (British usage), or tube (North America), is a device that controls electric current flow in a high vacuum between electrodes to which an electric voltage, potential difference has been applied.
The type kn ...
containing one or more electron guns, which emit electron
The electron (, or in nuclear reactions) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary electric charge. Electrons belong to the first generation of the lepton particle family,
and are generally thought to be elementary partic ...
beams that are manipulated to display images on a phosphorescent screen. The images may represent electrical waveforms ( oscilloscope), pictures (television set
A television set or television receiver, more commonly called the television, TV, TV set, telly, tele, or tube, is a device that combines a tuner, display, and loudspeakers, for the purpose of viewing and hearing television broadcasts, or using ...
, computer monitor), radar
Radar is a detection system that uses radio waves to determine the distance ('' ranging''), angle, and radial velocity of objects relative to the site. It can be used to detect aircraft, ships, spacecraft, guided missiles, motor vehicles, w ...
targets, or other phenomena. A CRT on a television set is commonly called a picture tube. CRTs have also been used as memory devices, in which case the screen is not intended to be visible to an observer. The term '' cathode ray'' was used to describe electron beams when they were first discovered, before it was understood that what was emitted from the cathode was a beam of electrons.
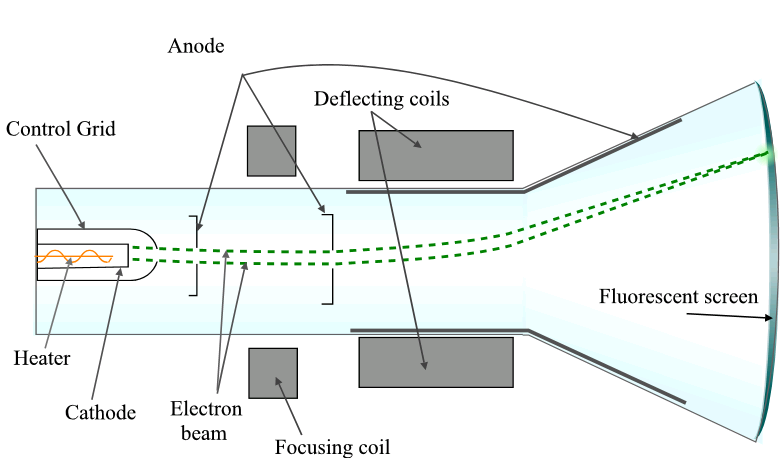
In CRT television sets and computer monitors, the entire front area of the tube is scanned repeatedly and systematically in a fixed pattern called a raster. In color devices, an image is produced by controlling the intensity of each of three electron beams, one for each additive primary color (red, green, and blue) with a video signal as a reference. In modern CRT monitors and televisions the beams are bent by magnetic deflection, using a deflection yoke
A deflection yoke is a kind of magnetic lens, used in cathode ray tubes to scan the electron beam both vertically and horizontally over the whole screen.
In a CRT television, the electron beam is moved in a raster scan on the screen. By adjusti ...
. Electrostatic deflection is commonly used in oscilloscopes.




 A CRT is a glass envelope which is deep (i.e., long from front screen face to rear end), heavy, and fragile. The interior is evacuated to to or less, to facilitate the free flight of electrons from the gun(s) to the tube's face without scattering due to collisions with air molecules. As such, handling a CRT carries the risk of violent implosion that can hurl glass at great velocity. The face is typically made of thick lead glass or special barium-strontium glass to be shatter-resistant and to block most X-ray emissions. CRTs make up most of the weight of CRT TVs and computer monitors.
Since the mid-late 2000's, CRTs have been superseded by flat-panel display technologies such as
A CRT is a glass envelope which is deep (i.e., long from front screen face to rear end), heavy, and fragile. The interior is evacuated to to or less, to facilitate the free flight of electrons from the gun(s) to the tube's face without scattering due to collisions with air molecules. As such, handling a CRT carries the risk of violent implosion that can hurl glass at great velocity. The face is typically made of thick lead glass or special barium-strontium glass to be shatter-resistant and to block most X-ray emissions. CRTs make up most of the weight of CRT TVs and computer monitors.
Since the mid-late 2000's, CRTs have been superseded by flat-panel display technologies such as LCD
A liquid-crystal display (LCD) is a flat-panel display or other electronically modulated optical device that uses the light-modulating properties of liquid crystals combined with polarizers. Liquid crystals do not emit light directly but in ...
, plasma display
A plasma display panel (PDP) is a type of flat panel display that uses small cells containing Plasma (physics), plasma: ionized gas that responds to electric fields. Plasma televisions were the first large (over 32 inches diagonal) flat panel displ ...
, and OLED
An organic light-emitting diode (OLED or organic LED), also known as organic electroluminescent (organic EL) diode, is a light-emitting diode (LED) in which the emissive electroluminescent layer is a film of organic compound that emits light ...
displays which are cheaper to manufacture and run, as well as significantly lighter and less bulky. Flat-panel displays can also be made in very large sizes whereas to was about the largest size of a CRT.
A CRT works by electrically heating a tungsten coil which in turn heats a cathode in the rear of the CRT, causing it to emit electrons which are modulated and focused by electrodes. The electrons are steered by deflection coils or plates, and an anode accelerates them towards the phosphor-coated screen, which generates light when hit by the electrons.
History
Discoveries
 Cathode rays were discovered by Julius Plücker and
Cathode rays were discovered by Julius Plücker and Johann Wilhelm Hittorf
Johann Wilhelm Hittorf (27 March 1824 – 28 November 1914) was a German physicist who was born in Bonn and died in Münster, Germany.
Hittorf was the first to compute the electricity-carrying capacity of charged atoms and molecules (ions), an ...
. Hittorf observed that some unknown rays were emitted from the cathode
A cathode is the electrode from which a conventional current leaves a polarized electrical device. This definition can be recalled by using the mnemonic ''CCD'' for ''Cathode Current Departs''. A conventional current describes the direction i ...
(negative electrode) which could cast shadows on the glowing wall of the tube, indicating the rays were traveling in straight lines. In 1890, Arthur Schuster demonstrated cathode rays could be deflected by electric fields, and William Crookes showed they could be deflected by magnetic fields. In 1897, J. J. Thomson succeeded in measuring the charge-mass-ratio of cathode rays, showing that they consisted of negatively charged particles smaller than atoms, the first " subatomic particles", which had already been named ''electron
The electron (, or in nuclear reactions) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary electric charge. Electrons belong to the first generation of the lepton particle family,
and are generally thought to be elementary partic ...
s'' by Irish physicist George Johnstone Stoney in 1891. The earliest version of the CRT was known as the "Braun tube", invented by the German physicist Ferdinand Braun in 1897.
It was a cold-cathode diode, a modification of the Crookes tube
A Crookes tube (also Crookes–Hittorf tube) is an early experimental electrical discharge tube, with partial vacuum, invented by English physicist William Crookes and others around 1869-1875, in which cathode rays, streams of electrons, were ...
with a phosphor-coated screen. Braun was the first to conceive the use of a CRT as a display device.
In 1908, Alan Archibald Campbell-Swinton, fellow of the Royal Society
The Royal Society, formally The Royal Society of London for Improving Natural Knowledge, is a learned society and the United Kingdom's national academy of sciences. The society fulfils a number of roles: promoting science and its benefits, r ...
(UK), published a letter in the scientific journal ''Nature
Nature, in the broadest sense, is the physical world or universe. "Nature" can refer to the phenomena of the physical world, and also to life in general. The study of nature is a large, if not the only, part of science. Although humans ar ...
'', in which he described how "distant electric vision" could be achieved by using a cathode-ray tube (or "Braun" tube) as both a transmitting and receiving device.
He expanded on his vision in a speech given in London in 1911 and reported in ''The Times
''The Times'' is a British daily national newspaper based in London. It began in 1785 under the title ''The Daily Universal Register'', adopting its current name on 1 January 1788. ''The Times'' and its sister paper '' The Sunday Times'' ...
'' and the ''Journal of the Röntgen Society''.
The first cathode-ray tube to use a hot cathode was developed by John Bertrand Johnson (who gave his name to the term Johnson noise
Johnson is a surname of Anglo-Norman origin meaning "Son of John". It is the second most common in the United States and 154th most common in the world. As a common family name in Scotland, Johnson is occasionally a variation of ''Johnston'', a ...
) and Harry Weiner Weinhart of Western Electric, and became a commercial product in 1922. The introduction of hot cathodes allowed for lower acceleration anode voltages and higher electron beam currents, since the anode now only accelerated the electrons emitted by the hot cathode, and no longer had to have a very high voltage to induce electron emission from the cold cathode.
Development
In 1926, Kenjiro Takayanagi demonstrated a CRT television receiver with a mechanical video camera that received images with a 40-line resolution. By 1927, he improved the resolution to 100 lines, which was unrivaled until 1931. By 1928, he was the first to transmit human faces in half-tones on a CRT display. In 1927, Philo Farnsworth created a television prototype. The CRT was named in 1929 by inventorVladimir K. Zworykin
Vladimir Kosma Zworykin; or with the patronymic as ''Kosmich''; or russian: Кузьмич, translit=Kuz'mich, label=none. Zworykin anglicized his name to ''Vladimir Kosma Zworykin'', replacing the patronymic with the name ''Kosma'' as a middle na ...
. RCA was granted a trademark for the term (for its cathode-ray tube) in 1932; it voluntarily released the term to the public domain in 1950.
In the 1930s, Allen B. DuMont made the first CRTs to last 1,000 hours of use, which was one of the factors that led to the widespread adoption of television.
The first commercially made electronic television sets with cathode-ray tubes were manufactured by Telefunken
Telefunken was a German radio and television apparatus company, founded in Berlin in 1903, as a joint venture of Siemens & Halske and the ''Allgemeine Elektrizitäts-Gesellschaft'' (AEG) ('General electricity company').
The name "Telefunken" app ...
in Germany in 1934.
In 1947, the cathode-ray tube amusement device
The cathode-ray tube amusement device is the earliest known interactive electronic game as well as the first game to incorporate an electronic display. The device simulates an artillery shell arcing towards targets on a cathode-ray tube (CRT) scre ...
, the earliest known interactive electronic game as well as the first to incorporate a cathode-ray tube screen, was created.
From 1949 to the early 1960s, there was a shift from circular CRTs to rectangular CRTs, although the first rectangular CRTs were made in 1938 by Telefunken.
While circular CRTs were the norm, European TV sets often blocked portions of the screen to make it appear somewhat rectangular while American sets often left the entire front of the CRT exposed o