|
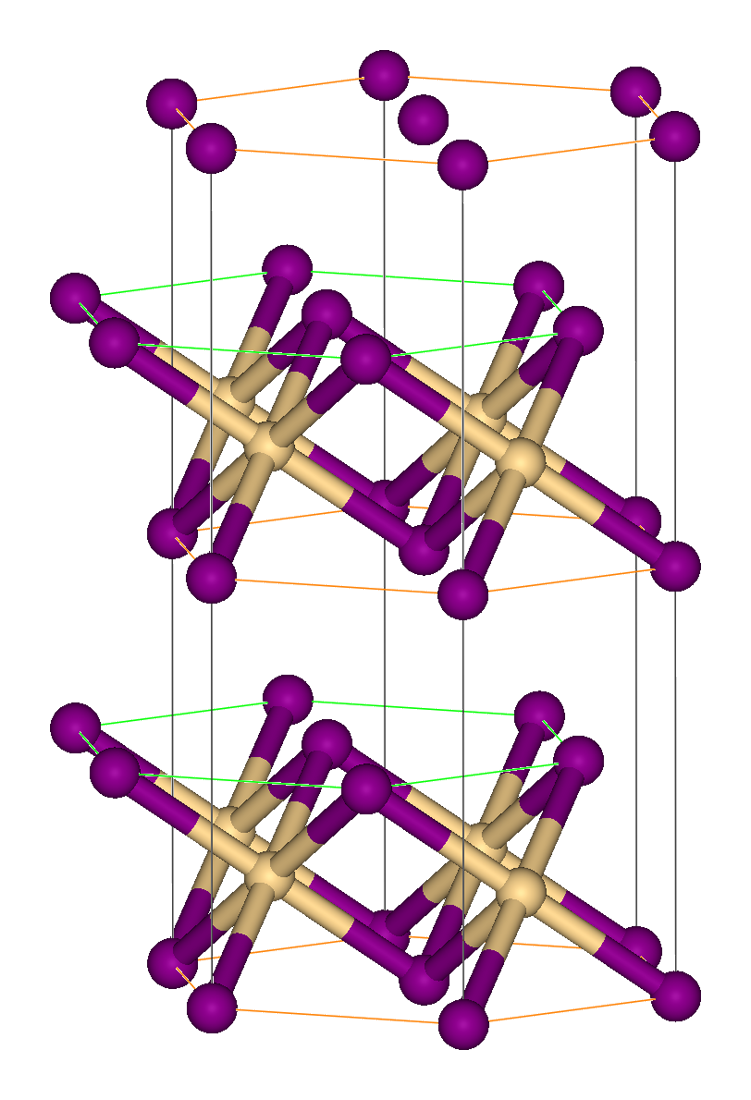
Vanadium(II) Chloride
Vanadium(II) chloride is the inorganic compound with the formula VCl2, and is the most reduced vanadium chloride. Vanadium(II) chloride is an apple-green solid that dissolves in water to give purple solutions. Preparation, properties, and related compounds Solid VCl2 is prepared by thermal decomposition of VCl3, which leaves a residue of VCl2:Young, R. C.; Smith, M. E. "Vanadium(II) Chloride" Inorganic Syntheses, 1953, volume IV, page 126-127. :2 VCl3 → VCl2 + VCl4 VCl2 dissolves in water to give the purple hexaaquo ion (H2O)6sup>2+. Evaporation of such solutions produces crystals of (H2O)6l2. Vanadium dichloride is used as a specialty reductant in organic chemistry. As an aqueous solution, it converts cyclohexylnitrate to cyclohexanone. It reduces phenyl azide into aniline. Structure Solid VCl2 adopts the cadmium iodide Cadmium iodide is an inorganic compound with the formula CdI2. It is a white hygroscopic solid. It also can be obtained as a mono- and tetrahydrate. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cadmium Iodide
Cadmium iodide is an inorganic compound with the formula CdI2. It is a white hygroscopic solid. It also can be obtained as a mono- and tetrahydrate. It has few applications. It is notable for its crystal structure, which is typical for compounds of the form MX2 with strong polarization effects. Preparation Cadmium iodide is prepared by the addition of cadmium metal, or its oxide, hydroxide or carbonate to hydroiodic acid. Also, the compound can be made by heating cadmium with iodine. Applications Historically, cadmium iodide was used as a catalyst for the Henkel process, a high-temperature isomerisation of dipotassium phthalate to yield the terephthalate. The salt was then treated with acetic acid to yield potassium acetate and commercially valuable terephthalic acid. While uneconomical compared to the production of terephthalic acid from ''p''-xylene, the Henkel method has been proposed as a potential route to produce terephthalic acid from furfural. As existing B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metal Aquo Complex
In chemistry, metal aquo complexes are coordination compounds containing metal ions with only water as a ligand. These complexes are the predominant species in aqueous solutions of many metal salts, such as metal nitrates, sulfates, and perchlorates. They have the general stoichiometry . Their behavior underpins many aspects of environmental, biological, and industrial chemistry. This article focuses on complexes where water is the only ligand (" homoleptic aquo complexes"), but of course many complexes are known to consist of a mix of aquo and other ligands. Stoichiometry and structure Hexa-aquo complexes Most aquo complexes are mono-nuclear, with the general formula , with or 3; they have an octahedral structure. The water molecules function as Lewis bases, donating a pair of electrons to the metal ion and forming a dative covalent bond with it. Typical examples are listed in the following table. Tutton's salts are crystalline compounds with the generic formula (wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vanadium(II) Compounds
Vanadium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol V and atomic number 23. It is a hard, silvery-grey, malleable transition metal. The elemental metal is rarely found in nature, but once isolated artificially, the formation of an oxide layer (passivation (chemistry), passivation) somewhat stabilizes the free metal against further oxidation. Spain, Spanish-Mexico, Mexican scientist Andrés Manuel del Río discovered compounds of vanadium in 1801 by analyzing a new lead-bearing mineral he called "brown lead". Though he initially presumed its qualities were due to the presence of a new element, he was later erroneously convinced by French chemist Hippolyte Victor Collet-Descotils that the element was just chromium. Then in 1830, Nils Gabriel Sefström generated chlorides of vanadium, thus proving there was a new element, and named it "vanadium" after the Scandinavian goddess of beauty and fertility, Vanadís (Freyja). The name was based on the wide range of colors fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cadmium Iodide
Cadmium iodide is an inorganic compound with the formula CdI2. It is a white hygroscopic solid. It also can be obtained as a mono- and tetrahydrate. It has few applications. It is notable for its crystal structure, which is typical for compounds of the form MX2 with strong polarization effects. Preparation Cadmium iodide is prepared by the addition of cadmium metal, or its oxide, hydroxide or carbonate to hydroiodic acid. Also, the compound can be made by heating cadmium with iodine. Applications Historically, cadmium iodide was used as a catalyst for the Henkel process, a high-temperature isomerisation of dipotassium phthalate to yield the terephthalate. The salt was then treated with acetic acid to yield potassium acetate and commercially valuable terephthalic acid. While uneconomical compared to the production of terephthalic acid from ''p''-xylene, the Henkel method has been proposed as a potential route to produce terephthalic acid from furfural. As existing B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aniline
Aniline (From , meaning ' indigo shrub', and ''-ine'' indicating a derived substance) is an organic compound with the formula . Consisting of a phenyl group () attached to an amino group (), aniline is the simplest aromatic amine. It is an industrially significant commodity chemical, as well as a versatile starting material for fine chemical synthesis. Its main use is in the manufacture of precursors to polyurethane, dyes, and other industrial chemicals. Like most volatile amines, it has the odor of rotten fish. It ignites readily, burning with a smoky flame characteristic of aromatic compounds. It is toxic to humans. Relative to benzene, aniline is "electron-rich". It thus participates more rapidly in electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions. Likewise, it is also prone to oxidation: while freshly purified aniline is an almost colorless oil, exposure to air results in gradual darkening to yellow or red, due to the formation of strongly colored, oxidized impurities. Ani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenyl Azide
Phenyl azide is an organic compound with the formula C6H5N3. It is one of the prototypical organic azides. It is a pale yellow oily liquid with a pungent odor. The structure consists of a linear azide substituent bound to a phenyl group. The C−N=N angle is approximately 116°. It was discovered in 1864 by Peter Griess by the reaction of ammonia and phenyldiazonium. Preparation Phenyl azide is prepared by the diazotization of phenylhydrazine with nitrous acid: :C6H5NHNH2 + HNO2 → C6H5N3 + 2 H2O Aryl iodides bearing electron-withdrawing substituents undergo metathesis with sodium azide in the presence of Cu(I), sodium ascorbate, and N,N'-dimethylethane-1,2-diamine (DMEDA): :RC6H4I + NaN3 → RC6H4N3 + NaI It can also be prepared by condensation of benzenediazonium salt with toluenesulfonamide, followed by hydrolysis. Chemical reactions Phenyl azide cycloadds to alkenes and especially alkynes, particularly those bearing electronegative substituents. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclohexanone
Cyclohexanone is the organic compound with the formula (CH2)5CO. The molecule consists of six-carbon cyclic molecule with a ketone functional group. This colorless oily liquid has a sweet odor reminiscent of benzaldehyde. Over time, samples of cyclohexanone assume a pale yellow color. Cyclohexanone is slightly soluble in water and miscible with common organic solvents. Millions of tonnes are produced annually, mainly as a precursor to nylon. History and synthesis The compound was discovered by in 1888 among the products of AC electrolysis of slightly acidified water solutions of phenol. He named it hydrophenoketone and correctly suggested that phenol was first hydrogenated by electrolytic hydrogen to cyclohexanol, which he wasn't able to isolate, and then oxidized by electrolytic oxygen. Laboratory synthesis Cyclohexanone can be prepared from cyclohexanol by oxidation with chromium trioxide ( Jones oxidation). An alternative method utilizes the safer and more readily avai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Chemistry
Organic chemistry is a subdiscipline within chemistry involving the science, scientific study of the structure, properties, and reactions of organic compounds and organic matter, organic materials, i.e., matter in its various forms that contain carbon atoms.Clayden, J.; Greeves, N. and Warren, S. (2012) ''Organic Chemistry''. Oxford University Press. pp. 1–15. . Study of structure determines their structural formula. Study of properties includes Physical property, physical and Chemical property, chemical properties, and evaluation of Reactivity (chemistry), chemical reactivity to understand their behavior. The study of organic reactions includes the organic synthesis, chemical synthesis of natural products, drugs, and polymers, and study of individual organic molecules in the laboratory and via theoretical (in silico) study. The range of chemicals studied chemistry includes hydrocarbons (compounds containing only carbon and hydrogen) as well as compounds based on carbon, but a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Formula
A chemical formula is a way of presenting information about the chemical proportions of atoms that constitute a particular chemical compound or molecule, using chemical element symbols, numbers, and sometimes also other symbols, such as parentheses, dashes, brackets, commas and ''plus'' (+) and ''minus'' (−) signs. These are limited to a single typographic line of symbols, which may include subscripts and superscripts. A chemical formula is not a chemical name since it does not contain any words. Although a chemical formula may imply certain simple chemical structures, it is not the same as a full chemical structural formula. Chemical formulae can fully specify the structure of only the simplest of molecules and chemical substances, and are generally more limited in power than chemical names and structural formulae. The simplest types of chemical formulae are called '' empirical formulae'', which use letters and numbers indicating the numerical ''proportions'' of atoms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vanadium(II) Fluoride
Vanadium(II) fluoride is a fluoride of vanadium, with the chemical formula of VF2. It forms blue crystals. Preparation Vanadium(II) fluoride can be produced by the reduction of vanadium trifluoride by hydrogen in a hydrogen fluoride atmosphere at 1150 °C:Lothar Kolditz: ''Anorganische Chemie Teil 2''. VEB Deutscher Verlag der Wissenschaften, Berlin, 1980, S. 641. : Properties Physical properties Vanadium(II) fluoride crystallizes in the tetragonal crystal system with space group ''P''42/''mnm'' (No. 136). Its lattice constants are a = 480.4 pm and c = 323.7 pm.J. W. Stout, W. O. J. Boo: ''Crystalline vanadium (II) fluoride, VF2. Preparation, structure, heat capacity from 5 to 300 K and magnetic ordering''. In: ''The Journal of Chemical Physics''. 71, 1, 1979, S. 1–8, . Reactions Vanadium(II) fluoride is a strong reducing agent that can reduce nitrogen to hydrazine in the presence of magnesium hydroxide Magnesium hydroxide is an inorganic compound with the chemi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inorganic Compound
An inorganic compound is typically a chemical compound that lacks carbon–hydrogen bondsthat is, a compound that is not an organic compound. The study of inorganic compounds is a subfield of chemistry known as ''inorganic chemistry''. Inorganic compounds comprise most of the Earth's crust, although the compositions of the deep Mantle (geology), mantle remain active areas of investigation. All allotropes (structurally different pure forms of an element) and some simple carbon compounds are often considered inorganic. Examples include the allotropes of carbon (graphite, diamond, buckminsterfullerene, graphene, etc.), carbon monoxide , carbon dioxide , carbides, and salt (chemistry), salts of inorganic anions such as carbonates, cyanides, cyanates, thiocyanates, isothiocyanates, etc. Many of these are normal parts of mostly organic systems, including organisms; describing a chemical as inorganic does not necessarily mean that it cannot occur within life, living things. History ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vanadium(III) Chloride
Vanadium(III) chloride describes the inorganic compound with the formula VCl3 and its hydrates. It forms a purple anhydrous form and a green hexahydrate Cl2(H2O)4l·2H2O. These hygroscopic salts are common precursors to other vanadium(III) complexes and is used as a mild reducing agent. Structure and electronic configuration VCl3 has the common layered BiI3 structure, a motif that features hexagonally closest-packed chloride framework with vanadium ions occupying the octahedral holes. VBr3 and VI3 adopt the same structure, but VF3 features a structure more closely related to ReO3. The V3+cation has a ''d''2 electronic configuration with two unpaired electrons, making the compound paramagnetic.Greenwood, N. N. and Earnshaw, A. (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd Edn.), Oxford:Butterworth-Heinemann. p. 990 . VCl3 is a Mott insulator and undergoes an antiferromagnetic transition at low temperatures. Solid hexahydrate, Cl2(H2O)4l·2H2O, has a monoclinic crystal structure an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |