|
UDP-GlcNAc
Uridine diphosphate ''N''-acetylglucosamine or UDP-GlcNAc is a nucleotide sugar and a coenzyme in metabolism. It is used by glycosyltransferases to transfer ''N''-acetylglucosamine residues to substrates. UDP-GlcNAc is used for making glycosaminoglycans, proteoglycans, and glycolipids. D-Glucosamine is made naturally in the form of glucosamine-6-phosphate, and is the biochemical precursor of all nitrogen-containing sugars. To be specific, glucosamine-6-phosphate is synthesized from fructose 6-phosphate and glutamine as the first step of the hexosamine biosynthesis pathway. The end-product of this pathway is UDP-GlcNAc. Some enzymes involved in the biosynthesis of UDP-GlcNAc vary between prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms, serving as potential drug targets for antibiotic development. Biosignaling UDP-GlcNAc is extensively involved in intracellular signaling as a substrate for ''O''-linked ''N''-acetylglucosamine transferases (OGTs) to install the ''O''-GlcNAc post-tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
O-GlcNAc
''O''-GlcNAc (short for ''O''-linked GlcNAc or ''O''-linked β-''N''-acetylglucosamine) is a reversible Enzyme, enzymatic post-translational modification that is found on serine and threonine residues of Cell nucleus, nucleoCytoplasm, cytoplasmic proteins. The modification is characterized by a Glycosidic bond, β-glycosidic bond between the Hydroxy group, hydroxyl group of serine or threonine side chains and N-Acetylglucosamine, ''N''-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc). ''O''-GlcNAc differs from other forms of protein glycosylation: (i) ''O''-GlcNAc is not elongated or modified to form more complex glycan structures, (ii) ''O''-GlcNAc is almost exclusively found on nuclear and cytoplasmic proteins rather than membrane proteins and secretory proteins, and (iii) ''O''-GlcNAc is a highly dynamic modification that turns over more rapidly than the proteins which it modifies. ''O''-GlcNAc is conserved across Animal, metazoans. Due to the dynamic nature of ''O''-GlcNAc and its presence on seri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
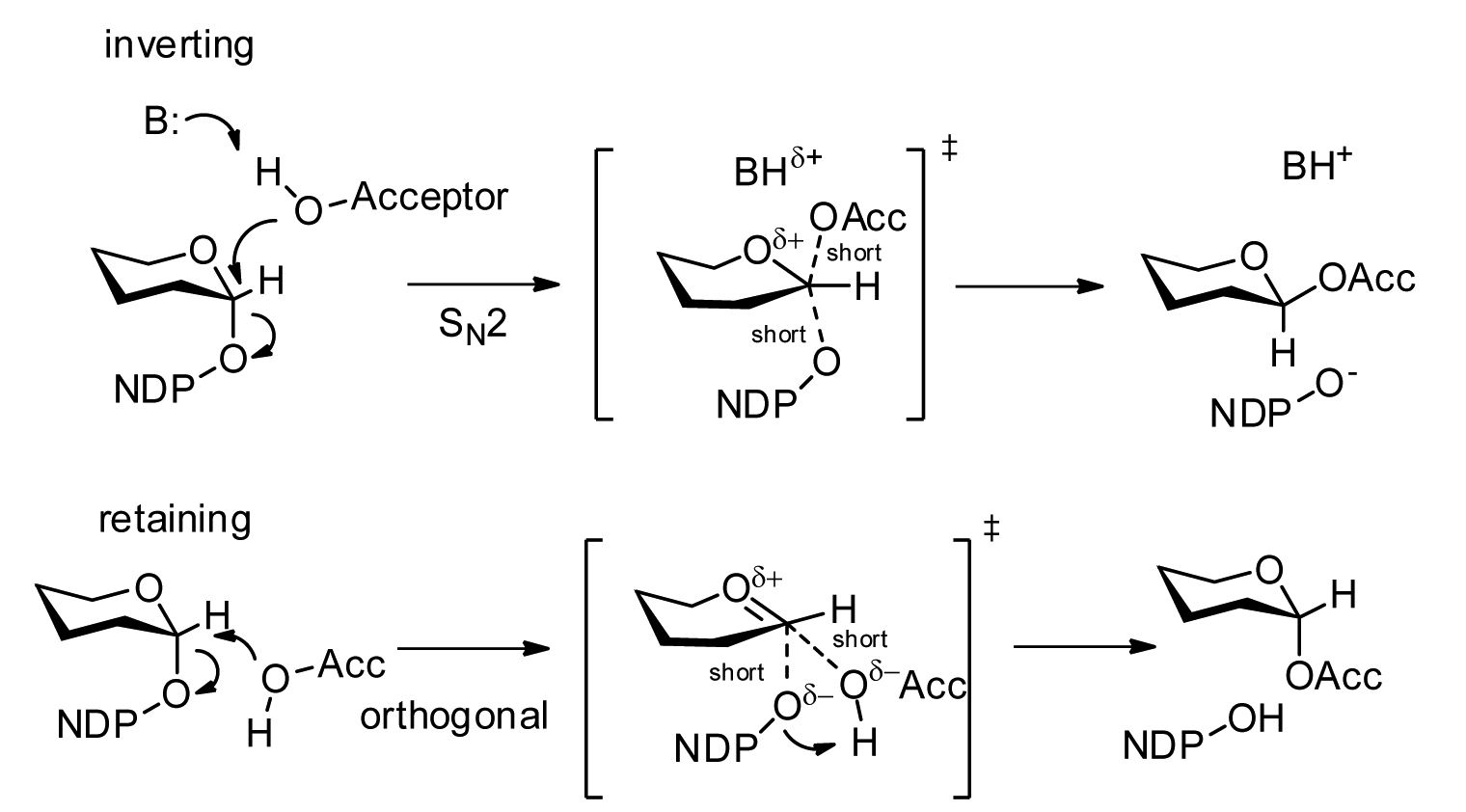
Protein O-GlcNAc Transferase
Protein ''O''-GlcNAc transferase also known as OGT or O-linked N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase is an enzyme () that in humans is encoded by the ''OGT'' gene. OGT catalyzes the addition of the ''O''-GlcNAc post-translational modification to proteins. Nomenclature Other names include: *''O''-GlcNAc transferase * OGTase *''O''-linked ''N''-acetylglucosaminyltransferase * Uridine diphospho-''N''-acetylglucosamine:polypeptide β-''N''-acetylglucosaminyltransferase Systematic name: UDP-''N''-α-acetyl--glucosamine: rotein3-''O''-''N''-acetyl-β--glucosaminyl transferase Function Glycosyltransferase OGT catalyzes the addition of a single ''N''-acetylglucosamine through an ''O''-glycosidic linkage to serine or threonine and an ''S''-glycosidic linkage to cysteine residues of nucleocytoplasmic proteins. Since both phosphorylation and ''O''-GlcNAcylation compete for similar serine or threonine residues, the two processes may compete for sites, or they may alter the substrate s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GlmU
Peptidoglycan or murein is a unique large macromolecule, a polysaccharide, consisting of sugars and amino acids that forms a mesh-like layer (sacculus) that surrounds the bacterial cytoplasmic membrane. The sugar component consists of alternating residues of β-(1,4) linked ''N''-acetylglucosamine (NAG) and ''N''-acetylmuramic acid (NAM). Attached to the ''N''-acetylmuramic acid is an oligopeptide chain made of three to five amino acids. The peptide chain can be cross-linked to the peptide chain of another strand forming the 3D mesh-like layer. Peptidoglycan serves a structural role in the bacterial cell wall, giving structural strength, as well as counteracting the osmotic pressure of the cytoplasm. This repetitive linking results in a dense peptidoglycan layer which is critical for maintaining cell form and withstanding high osmotic pressures, and it is regularly replaced by peptidoglycan production. Peptidoglycan hydrolysis and synthesis are two processes that must occur in ord ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glycosaminoglycan
Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) or mucopolysaccharides are long, linear polysaccharides consisting of repeating disaccharide units (i.e. two-sugar units). The repeating two-sugar unit consists of a uronic sugar and an amino sugar, except in the case of the sulfated glycosaminoglycan keratan, where, in place of the uronic sugar there is a galactose unit. GAGs are found in vertebrates, invertebrates and bacteria. Because GAGs are highly polar molecules and attract water; the body uses them as lubricants or shock absorbers. Mucopolysaccharidoses are a group of metabolic disorders in which abnormal accumulations of glycosaminoglycans occur due to enzyme deficiencies. Production Glycosaminoglycans vary greatly in molecular mass, disaccharide structure, and sulfation. This is because GAG synthesis is not template driven, as are proteins or nucleic acids, but constantly altered by processing enzymes. GAGs are classified into four groups, based on their core disaccharide structures: # H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleotide Sugar
Nucleotide sugars are the activated forms of monosaccharides. Nucleotide sugars act as glycosyl donors in glycosylation reactions. Those reactions are catalyzed by a group of enzymes called glycosyltransferases. History The anabolism of oligosaccharides - and, hence, the role of nucleotide sugars - was not clear until the 1950s when Leloir and his coworkers found that the key enzymes in this process are the glycosyltransferases. These enzymes transfer a glycosyl group from a sugar nucleotide to an acceptor. Biological importance and energetics To act as glycosyl donors, those monosaccharides should exist in a highly energetic form. This occurs as a result of a reaction between nucleoside triphosphate (NTP) and glycosyl monophosphate (phosphate at anomeric carbon). The recent discovery of the reversibility of many glycosyltransferase-catalyzed reactions calls into question the designation of sugar nucleotides as 'activated' donors. Types There are nine sugar nucleotides in hu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glycosyltransferase
Glycosyltransferases (GTFs, Gtfs) are enzymes ( EC 2.4) that establish natural glycosidic linkages. They catalyze the transfer of saccharide moieties from an activated nucleotide sugar (also known as the "glycosyl donor") to a nucleophilic glycosyl acceptor molecule, the nucleophile of which can be oxygen- carbon-, nitrogen-, or sulfur-based. The result of glycosyl transfer can be a carbohydrate, glycoside, oligosaccharide, or a polysaccharide. Some glycosyltransferases catalyse transfer to inorganic phosphate or water. Glycosyl transfer can also occur to protein residues, usually to tyrosine, serine, or threonine to give O-linked glycoproteins, or to asparagine to give N-linked glycoproteins. Mannosyl groups may be transferred to tryptophan to generate C-mannosyl tryptophan, which is relatively abundant in eukaryotes. Transferases may also use lipids as an acceptor, forming glycolipids, and even use lipid-linked sugar phosphate donors, such as dolichol phosphates in eukar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytoskeleton
The cytoskeleton is a complex, dynamic network of interlinking protein filaments present in the cytoplasm of all cells, including those of bacteria and archaea. In eukaryotes, it extends from the cell nucleus to the cell membrane and is composed of similar proteins in the various organisms. It is composed of three main components: microfilaments, intermediate filaments, and microtubules, and these are all capable of rapid growth and or disassembly depending on the cell's requirements. Cytoskeleton can perform many functions. Its primary function is to give the cell its shape and mechanical resistance to deformation, and through association with extracellular connective tissue and other cells it stabilizes entire tissues. The cytoskeleton can also contract, thereby deforming the cell and the cell's environment and allowing cells to migrate. Moreover, it is involved in many cell signaling pathways and in the uptake of extracellular material ( endocytosis), the segregation of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acetyltransferase
An acetyltransferase (also referred to as a transacetylase) is any of a class of transferase enzymes that transfers an acetyl group in a reaction called acetylation. In biological organisms, post-translational modification of a protein via acetylation can profoundly transform its functionality by altering various properties like hydrophobicity, solubility, and surface attributes. These alterations have the potential to influence the protein's conformation and its interactions with substrates, cofactors, and other macromolecules. Types of acetyltransferases Additional examples of acetyltransferases found in nature include: * Chloramphenicol acetyltransferase Structure The predicted three-dimensional structures of histone, choline, and serotonin acetyltransferases are shown below. As with all enzymes, the structures of acetyltransferases are essential for interactions between them and their substrates; alterations to the structures of these enzymes often result in a loss o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metabolism
Metabolism (, from ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cellular processes; the conversion of food to building blocks of proteins, lipids, nucleic acids, and some carbohydrates; and the elimination of metabolic wastes. These enzyme-catalyzed reactions allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their Structures#Biological, structures, and respond to their environments. The word ''metabolism'' can also refer to the sum of all chemical reactions that occur in living organisms, including digestion and the transportation of substances into and between different cells, in which case the above described set of reactions within the cells is called intermediary (or intermediate) metabolism. Metabolic reactions may be categorized as ''catabolic''—the ''breaking down'' of compounds (for example, of glucose to pyruvate by c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rho Family Of GTPases
The Rho family of GTPases is a family of small (~21 kDa) signaling G proteins, and is a subfamily of the Ras superfamily. The members of the Rho GTPase family have been shown to regulate many aspects of intracellular actin dynamics, and are found in all eukaryotic kingdoms, including yeasts and some plants. Three members of the family have been studied in detail: Cdc42, Rac1, and RhoA. All G proteins are "molecular switches", and Rho proteins play a role in organelle development, cytoskeletal dynamics, cell movement, and other common cellular functions. History Identification of the Rho family of GTPases began in the mid-1980s. The first identified Rho member was RhoA, isolated serendipitously in 1985 from a low stringency cDNA screening. Rac1 and Rac2 were identified next, in 1989 followed by Cdc42 in 1990. Eight additional mammalian Rho members were identified from biological screenings until the late 1990s, a turning point in biology where availability of complete genome sequenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clostridium Novyi
''Clostridium novyi'' (oedematiens) a Gram-positive, endospore- forming, obligate anaerobic bacteria of the class Clostridia. It is ubiquitous, being found in the soil and faeces. It is pathogenic, causing a wide variety of diseases in humans and animals. Growth in culture proceeds through 3 stages: Initial growth wherein no toxin is produced; vigorous growth wherein toxin is produced; and spore formation wherein endospores are formed and toxin production decreases. It is suggested that type C may be type B that forms spores more readily so does not go through the toxin-production stage. Isolating and identifying ''C novyi'' is difficult due to its extreme anaerobic nature. Commercial kits may not be adequate. It is also fastidious and difficult to culture, requiring the presence of thiols. Taxonomy ''Clostridium novyi'' is considered to be made up from three clades, labelled A, B and C, distinguished by the range of toxins they produce. While strains of type C were not linked ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |