|
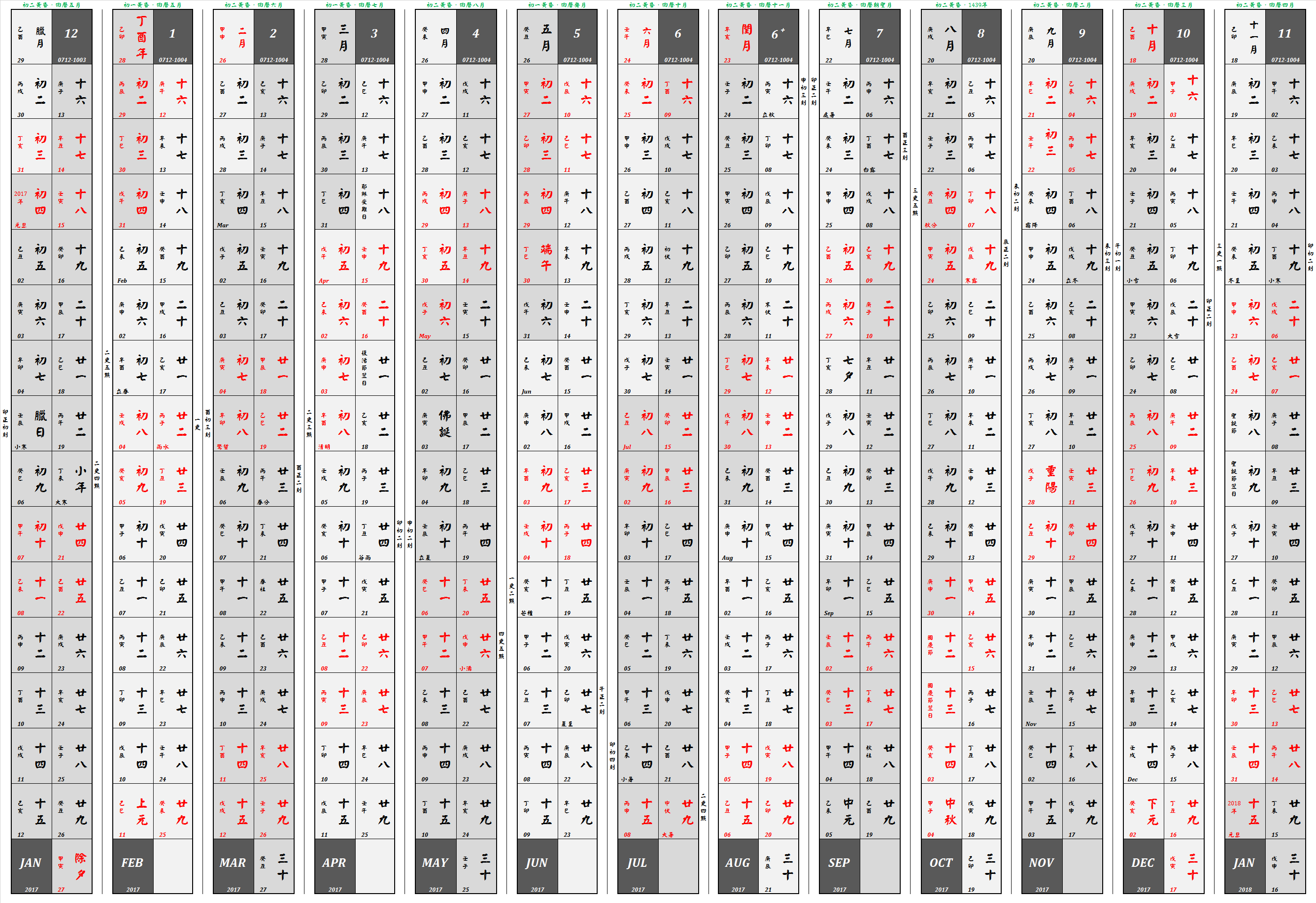
Tết Nguyên Đán
Tết (, ), short for (; ), is the most important celebration in Vietnamese culture. Tết celebrates the arrival of spring based on the Vietnamese calendar and usually falls on January or February in the Gregorian calendar. is not to be confused with Tết Trung Thu, which is also known as Children's Festival in Vietnam. "'" itself only means festival but it would generally refer to the Lunar New Year in Vietnamese, as it is often seen as the most important festival amongst the Vietnamese and the Vietnamese diaspora, with regarded as the second-most important. Vietnamese people celebrate annually, which is based on a Chinese calendar, lunisolar calendar (calculating both the Earth's orbit, motions of Earth around the Sun and orbit of the Moon, of the Moon around Earth). Tết is generally celebrated on the same day as Chinese New Year (also called Spring Festival), with the one-hour time difference between Vietnam and China resulting in the new moon occurring on different ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vietnamese People
The Vietnamese people (, ) or the Kinh people (), also known as the Viet people or the Viets, are a Southeast Asian ethnic group native to modern-day northern Vietnam and Dongxing, Guangxi, southern China who speak Vietnamese language, Vietnamese, the most widely spoken Austroasiatic language. Vietnamese Kinh people account for 85.32% of the population of Vietnam in the 2019 Vietnamese Census, 2019 census, and are officially designated and recognized as the ''Kinh'' people () to distinguish them from the other ethnic groups in Vietnam, minority groups residing in the country such as the Hmong people, Hmong, Chams, Cham, or Muong people, Mường. The Vietnamese are one of the four main groups of Vietic languages, Vietic speakers in Vietnam, the others being the Muong people, Mường, Thổ people, Thổ, and Chứt people. Diasporic descendants of the Vietnamese in China, known as the Gin people, Gin people, are one of 56 ethnic groups officially recognized by the People's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Calendar
The traditional Chinese calendar, dating back to the Han dynasty, is a lunisolar calendar that blends solar, lunar, and other cycles for social and agricultural purposes. While modern China primarily uses the Gregorian calendar for official purposes, the traditional calendar remains culturally significant. It determines the timing of Chinese New Year with traditions like the twelve animals of the Chinese zodiac, Chinese Zodiac still widely observed. The traditional Chinese calendar uses the Sexagenary cycle, sexagenary cycle, a repeating system of Heavenly Stems and Earthly Branches, to mark years, months, and days. This system, along with astronomical observations and mathematical calculations, was developed to align solar and lunar cycles, though some approximations are necessary due to the natural differences between these cycles. Over centuries, the calendar was refined through advancements in astronomy and horology, with dynasties introducing variations to improve accu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
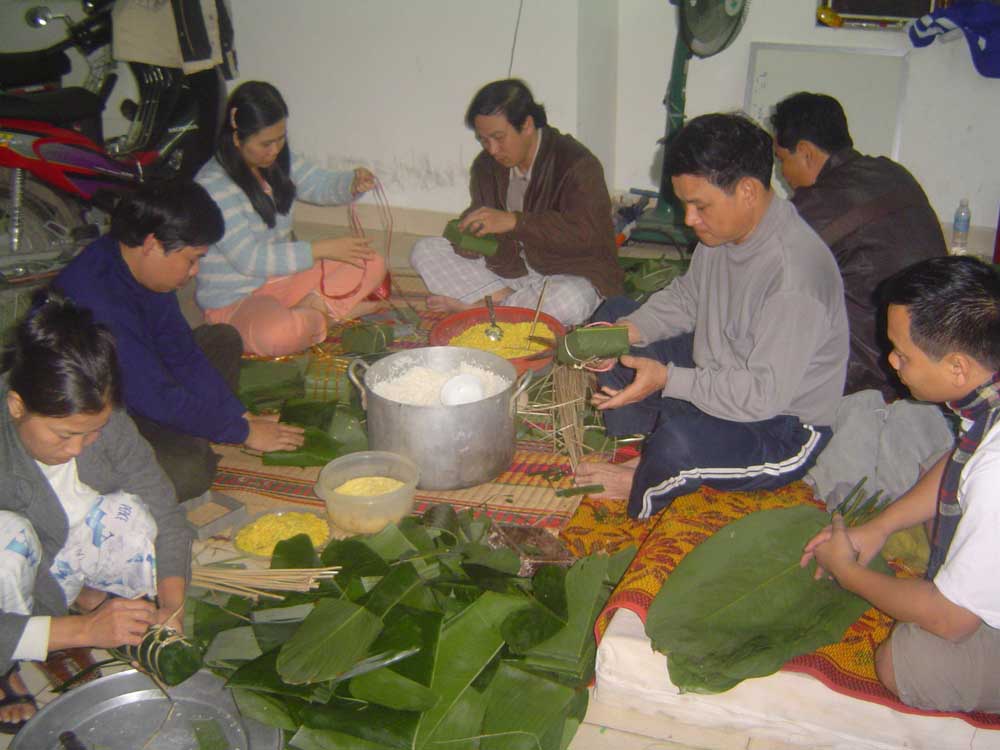
Bánh Chưng
''Bánh chưng'' or ''banh chung'' is a traditional Vietnamese dish which is made from glutinous rice, mung beans, pork, and other ingredients. According to legend, its origin traces back to Lang Liêu, a prince of the last king of the Sixth Hùng Dynasty. He earned his place as successor by creating ''bánh chưng'' and ''bánh giầy'', which symbolize the earth and the sky, respectively. Considered an essential element of the family altar on the occasion of ''Tết'', the preparation and consumption of ''bánh chưng'' are cherished traditions deeply rooted in Vietnamese culture. While closely associated with ''Tết'', ''bánh chưng'' is enjoyed year-round as a staple of Vietnamese cuisine. Origin and symbolism According to the book '' Lĩnh Nam chích quái'' (''Extraordinary stories of Lĩnh Nam'') published in the 14th century, the creation of ''bánh chưng'' was credited to Lang Liêu, a prince of the last Sixth Hùng Dynasty of the Hùng dynasty (c. 1712 – 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trần Văn Giáp
Trần Văn Giáp (, 1902 - 25 November 1973) was a Vietnamese historian who wrote the first widely published histories of Buddhism in Vietnam in French. The two volumes, for Annam and Tonkin respectively were published in Paris in 1932. Giáp was an authority on Hán-Nôm (i.e. both chữ Hán and chữ Nôm Chữ Nôm (, ) is a logographic writing system formerly used to write the Vietnamese language. It uses Chinese characters to represent Sino-Vietnamese vocabulary and some native Vietnamese words, with other words represented by new characters ...) literature. On his return to Vietnam he published various other histories in Vietnamese, both in Latin alphabet chữ Quốc ngữ and chữ Nho. Works *''Le Bouddhisme en Annam des origines au XIIIè siècle'' 1932 *''Esquisse d'une histoire du Bouddhisme au Tonkin'' 1932 *''Les chapitres bibliographiques de Lê Quý Đôn et de Phan Huy Chú'' 1938 *''Vần Quốc ngữ'' 1938 *''Lược khảo về khoa cử Việt Nam' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Summer Solstice
The summer solstice or estival solstice occurs when one of Earth's poles has its maximum tilt toward the Sun. It happens twice yearly, once in each hemisphere ( Northern and Southern). The summer solstice is the day with the longest period of daylight and shortest night of the year in that hemisphere, when the sun is at its highest position in the sky. At either pole there is continuous daylight at the time of its summer solstice. The opposite event is the winter solstice. The summer solstice occurs during the hemisphere's summer. In the Northern Hemisphere, this is the June solstice (20, 21 or 22 June) and in the Southern Hemisphere, this is the December solstice (20, 21, 22 or 23 of December). Since prehistory, the summer solstice has been a significant time of year in many cultures, and has been marked by festivals and rituals. Traditionally, in temperate regions (especially Europe), the summer solstice is seen as the middle of summer and referred to as midsum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Winter Solstice
The winter solstice, or hibernal solstice, occurs when either of Earth's geographical pole, poles reaches its maximum axial tilt, tilt away from the Sun. This happens twice yearly, once in each hemisphere (Northern Hemisphere, Northern and Southern Hemisphere, Southern). For that hemisphere, the winter solstice is the day with the shortest daytime, period of daylight and longest night of the year, and when the Sun is at its lowest culmination, daily maximum elevation in the sky. Each Polar Circle, polar region experiences polar night, continuous darkness or twilight around its winter solstice. The opposite event is the summer solstice. The winter solstice occurs during the hemisphere's winter. In the Northern Hemisphere, this is the December solstice (December 21 or 22) and in the Southern Hemisphere, this is the June solstice (June 20 or 21). Although the winter solstice itself lasts only a moment, the term also refers to the day on which it occurs. Traditionally, in many Tem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
September Equinox
The September equinox (or southward equinox) is the moment when the Sun appears to cross the celestial equator, heading southward. Because of differences between the calendar year and the tropical year, the September equinox may occur from September 21 to 24. At the equinox, the Sun as viewed from the equator rises due east and sets due west. Before the Southward equinox, the Sun rises and sets more northerly, and afterwards, it rises and sets more southerly. The equinox may be taken to mark the end of astronomical summer and the beginning of astronomical autumn (autumnal equinox) in the Northern Hemisphere, while marking the end of astronomical winter and the start of astronomical spring (vernal equinox) in the Southern Hemisphere. Occurrences The September equinox is one point in time commonly used to determine the length of the tropical year. The dates and times of the September equinoxes that occur from the year 2018 to 2028 (UTC) are listed as follows: Const ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
March Equinox
The March equinox or northward equinox is the equinox on the Earth when the subsolar point appears to leave the Southern Hemisphere and cross the celestial equator, heading northward as seen from Earth. The March equinox is known as the vernal equinox (or spring equinox) in the Northern Hemisphere and as the autumnal equinox (or fall equinox) in the Southern Hemisphere. On the Gregorian calendar at 0° longitude, the northward equinox can occur as early as 19 March (which happened most recently in 1796, and will happen next in 2044), and it can occur as late as 21 March (which happened most recently in 2007, and will happen next in 2102). For a common year the computed time slippage is about 5 hours 49 minutes ''later'' than the previous year, and for a leap year about 18 hours 11 minutes ''earlier'' than the previous year. Balancing the increases of the common years against the losses of the leap years keeps the calendar date of the March equinox from drifting more than ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vietnamese Zodiac
The Vietnamese zodiac ( Vietnamese: ''Mười hai con giáp'') is the traditional Vietnamese classification scheme based on the lunar calendar that assigns an animal and its reputed attributes to each year in a repeating 12-year cycle. The Vietnamese lunar calendar is divided into 60-year cycles known as ''hồi''. Each of these consists of five 12-year animal cycles. Zodiac The Vietnamese zodiac is originated from the Ancient Vietnamese people in its usage and arrangement of animals, with 2 different animals with the rest of other countries (water buffalo and cat). The Vietnamese zodiac was believed to come from the Chinese Ancient, but some researchs in modern day points out that it was the product of the Bach Viet (hundreds of Viet tribes). According to Jerry Norman, Tsu-lin Mei, Michel Ferlus, the Zodiac was formed in South Asian language. Also, according to Nguyen Cung Thong - independent language reseacher in Melbourne (Australia): Sửu has the original ancient phonetic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tang Dynasty
The Tang dynasty (, ; zh, c=唐朝), or the Tang Empire, was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 618 to 907, with an Wu Zhou, interregnum between 690 and 705. It was preceded by the Sui dynasty and followed by the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period. Historians generally regard the Tang as a high point in Chinese civilisation, and a Golden age (metaphor), golden age of cosmopolitan culture. Tang territory, acquired through the military campaigns of its early rulers, rivalled that of the Han dynasty. The House of Li, Li family founded the dynasty after taking advantage of a period of Sui decline and precipitating their final collapse, in turn inaugurating a period of progress and stability in the first half of the dynasty's rule. The dynasty was formally interrupted during 690–705 when Empress Wu Zetian seized the throne, proclaiming the Wu Zhou dynasty and becoming the only legitimate Chinese empress regnant. The An Lushan rebellion (755 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Han Dynasty
The Han dynasty was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China (202 BC9 AD, 25–220 AD) established by Liu Bang and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by the short-lived Qin dynasty (221–206 BC) and a warring interregnum known as the Chu–Han Contention (206–202 BC), and it was succeeded by the Three Kingdoms period (220–280 AD). The dynasty was briefly interrupted by the Xin dynasty (9–23 AD) established by the usurping regent Wang Mang, and is thus separated into two periods—the #Western Han (202 BC – 9 AD), Western Han (202 BC9 AD) and the #Eastern Han (25–220 AD), Eastern Han (25–220 AD). Spanning over four centuries, the Han dynasty is considered a Golden ages of China, golden age in Chinese history, and had a permanent impact on Chinese identity in later periods. The majority ethnic group of modern China refer to themselves as the "Han people" or "Han Chinese". The spoken Chinese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vietnam Under Chinese Rule
Vietnam under Chinese rule or ''Bắc thuộc'' (北屬, lit. "belonging to the north") (111 BCE–939 CE, 1407–1428 CE) refers to four historical periods when several portions of modern-day Northern Vietnam was under the rule of various Chinese dynasties. ''Bắc thuộc'' in Vietnamese historiography is traditionally considered to have started in 111 BC, when the Han dynasty conquered Nanyue (Vietnamese "Nam Việt") and lasted until 939, when the Ngô dynasty was founded. A fourth, relatively brief, 20-year rule by the Ming dynasty during the 15th century is usually excluded by historians in their discussion of the main, almost continuous, period of Chinese rule from 111 BC to 939 AD. Historians such as Keith W. Taylor, Catherine Churchman, and Jaymin Kim assert that these periods and stereotypes enveloped the narrative as modern constructs, however, and critique them as tools for various nationalist and irredentist causes in China, Vietnam, and other countries. Geographic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |