|
Tuber Cinereum
The tuber cinereum is the portion of hypothalamus forming the floor of the third ventricle situated between the optic chiasm, and the mammillary bodies. The tuberal region is one of the three regions of the hypothalamus, the other two being the chiasmatic region and the mamillary region. Structure The tuber cinereum is a convex mass of grey matter, a ventral/inferior distention of the hypothalamus forming the floor of the third ventricle. The portion of the tuber cinereum at the base of the infundibulum (pituitary stalk) is the median eminence; the infundibulum extends ventrally/inferiorly from the median eminence to become continuous with the infundibulum. The arcuate nucleus is a part of the tuber cinereum. The lateral portions of tuber cinereum lodge the lateral tuberal nucleus, and tuberomammillary nucleus. The basolateral aspect of the tuber cinereum often presents slight elevations produced by the underlying lateral tuberal nucleus - the lateral eminence. Relations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tuberculum Cinereum
The trigeminal tubercle or tuberculum cinereum is a raised area upon (the caudal/inferior portion of) the lateral dorsal/posterior aspect of the medulla oblongata produced by the underlying spinal tract of the trigeminal nerve (cranial nerve V). It is situated just lateral to the tuberculum cuneatus (of nucleus cuneatus), between the rootlets of the accessory nerve The accessory nerve, also known as the eleventh cranial nerve, cranial nerve XI, or simply CN XI, is a cranial nerve that supplies the sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscles. It is classified as the eleventh of twelve pairs of cranial nerv ... and posterolateral sulcus. References Neuroanatomy {{Neuroanatomy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optic Tract
In neuroanatomy, the optic tract () is a part of the visual system in the brain. It is a continuation of the optic nerve that relays information from the optic chiasm to the ipsilateral lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN), pretectal nuclei, and superior colliculus. It is composed of two individual tracts, the left optic tract and the right optic tract, each of which conveys visual information exclusive to its respective contralateral half of the visual field. Each of these tracts is derived from a combination of temporal and nasal retinal fibers from each eye that corresponds to one half of the visual field. In more specific terms, the optic tract contains fibers from the ipsilateral temporal hemiretina and contralateral nasal hemiretina. Anatomy Arterial supply The optic tract receives arterial supply from the anterior choroidal artery, and posterior communicating artery. Function Visual function The optic tract carries retinal information relating to the whole visua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tuber Cinereum Hamartoma
Tuber cinereum hamartoma is a benign tumor in which a disorganized collection of neurons and glia accumulate at the tuber cinereum of the hypothalamus on the floor of the third ventricle. It is a congenital malformation, included on the spectrum of gray matter heterotopias. Formation occurs during embryogenesis, typically between days 33 and 41 of gestation. Size of the tumor varies from one to three centimeters in diameter, with the mean being closer to the low end of this range. It is estimated to occur at a frequency of one in one million individuals. Signs and symptoms The classic presentation is gelastic or laughing epilepsy, a disorder characterized by spells of involuntary laughter with interval irritability and depressed mood. The tumor can be associated with other seizure types as well as precocious puberty and behavioral disorders. Gelastic epilepsy has been more classically associated with sessile lesions and precocious puberty reported with pedunculated morphology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
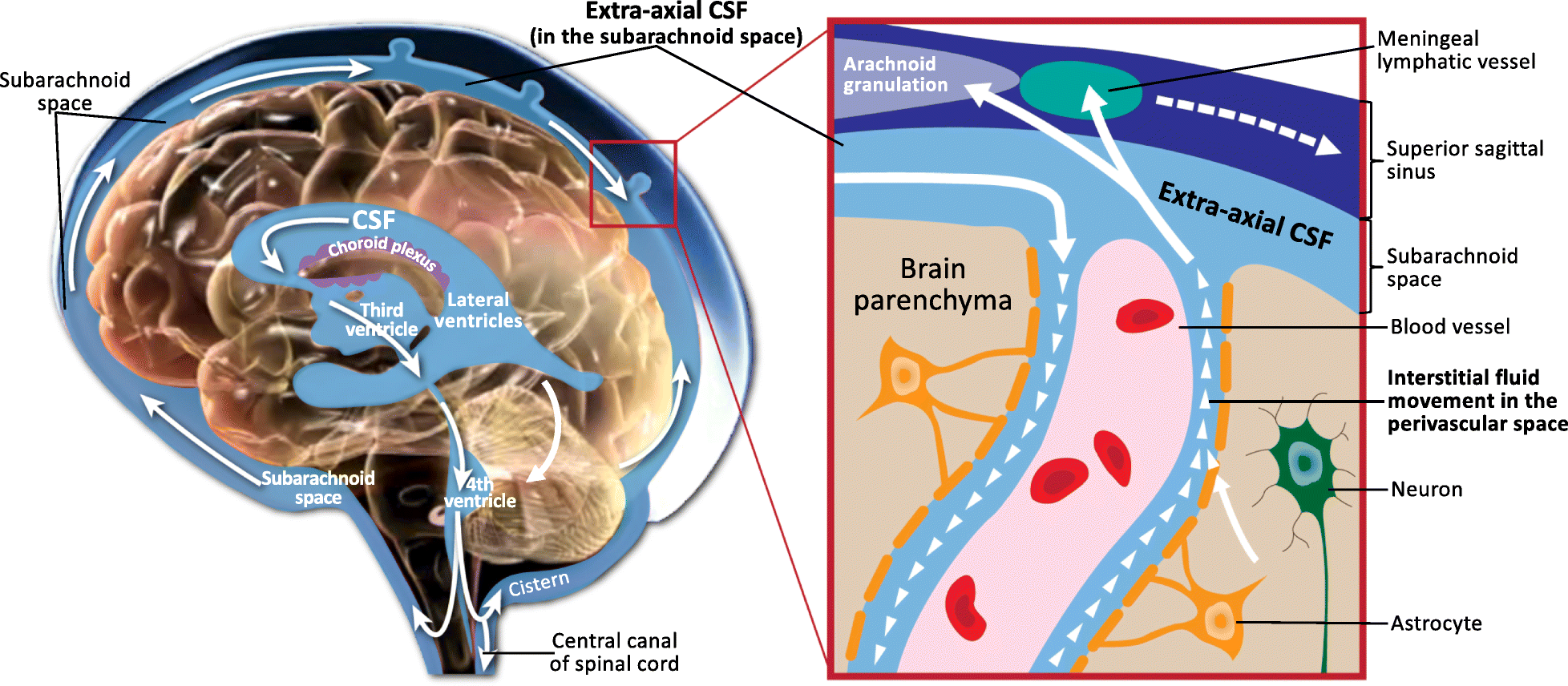
Perivascular Space
A perivascular space, also known as a Virchow–Robin space, is a fluid-filled space surrounding certain blood vessels in several organs, including the brain, potentially having an immune system, immunological function, but more broadly a dispersive role for neural and blood-derived messengers. The brain pia mater is reflected from the surface of the brain onto the surface of blood vessels in the subarachnoid space. In the brain, ''perivascular cuffs'' are regions of leukocyte aggregation in the perivascular spaces, usually found in patients with viral encephalitis. Perivascular spaces vary in dimension according to the type of blood vessel. In the brain where most capillaries have an imperceptible perivascular space, select structures of the brain, such as the circumventricular organs, are notable for having large perivascular spaces surrounding highly vascular permeability, permeable capillaries, as observed by microscopy. The median eminence, a brain structure at the base o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
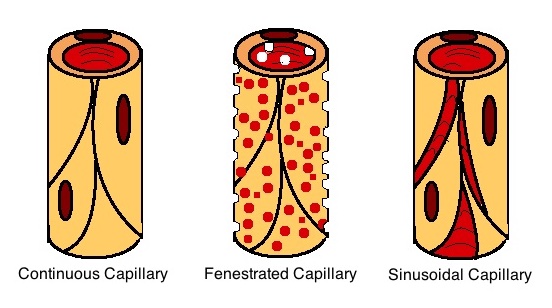
Vascular Permeability
Vascular permeability, often in the form of capillary permeability or microvascular permeability, characterizes the permeability of a blood vessel wall–in other words, the blood vessel wall's capacity to allow for the flow of small molecules (such as drugs, nutrients, water, or ions) or even whole cells (such as lymphocytes on their way to a site of inflammation) in and out of the vessel. Blood vessel walls are lined by a single layer of endothelial cells. The gaps between endothelial cells (cell junctions) are strictly regulated depending on the type and physiological state of the tissue. There are several techniques to measure vascular permeability to certain molecules. For instance, the cannulation of a single microvessel with a micropipette: the microvessel is perfused with a certain pressure, occluded downstream, and then the velocity of some cells will be related to the permeability.Michel, C. C., Mason, J. C., Curry, F. E. & Tooke, J. E. Development of Landis Techn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypophyseal Portal System
The hypophyseal portal system is a system of blood vessels in the microcirculation at the base of the brain, connecting the hypothalamus with the anterior pituitary. Its main function is to quickly transport and exchange hormones between the hypothalamus arcuate nucleus and anterior pituitary gland. The capillaries in the portal system are fenestrated (have many small channels with high vascular permeability) which allows a rapid exchange between the hypothalamus and the pituitary. The main hormones transported by the system include gonadotropin-releasing hormone, corticotropin-releasing hormone, growth hormone–releasing hormone, and thyrotropin-releasing hormone. Structure The blood supply and direction of flow in the hypophyseal portal system has been studied over many years on laboratory animals and human cadaver specimens with injection and vascular corrosion casting methods. Short portal vessels between the neural and anterior pituitary lobes provide an avenue for rap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Confluence
In geography, a confluence (also ''conflux'') occurs where two or more watercourses join to form a single channel (geography), channel. A confluence can occur in several configurations: at the point where a tributary joins a larger river (main stem); or where two streams meet to become the river source, source of a river of a new name (such as the confluence of the Monongahela River, Monongahela and Allegheny River, Allegheny rivers, forming the Ohio River); or where two separated channels of a river (forming a river island) rejoin downstream from their point of separation. Scientific study Confluences are studied in a variety of sciences. Hydrology studies the characteristic flow patterns of confluences and how they give rise to patterns of erosion, bars, and scour pools. The water flows and their consequences are often studied with mathematical models. Confluences are relevant to the distribution of living organisms (i.e., ecology) as well; "the general pattern [downstream o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capillary
A capillary is a small blood vessel, from 5 to 10 micrometres in diameter, and is part of the microcirculation system. Capillaries are microvessels and the smallest blood vessels in the body. They are composed of only the tunica intima (the innermost layer of an artery or vein), consisting of a thin wall of simple squamous endothelial cells. They are the site of the exchange of many substances from the surrounding interstitial fluid, and they convey blood from the smallest branches of the arteries (arterioles) to those of the veins (venules). Other substances which cross capillaries include water, oxygen, carbon dioxide, urea, glucose, uric acid, lactic acid and creatinine. Lymph capillaries connect with larger lymph vessels to drain lymphatic fluid collected in microcirculation. Etymology ''Capillary'' comes from the Latin word , meaning "of or resembling hair", with use in English beginning in the mid-17th century. The meaning stems from the tiny, hairlike diameter of a capi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anterior Choroidal Artery
The anterior choroidal artery is a bilaterally paired artery of the brain. It is typically a branch of the internal carotid artery which supplies the choroid plexus of lateral ventricle and third ventricle as well as numerous structures of the brain. Occlusion of the artery can result in loss of sensation, loss of part of the visual field, and impaired movement, all on the opposite side of the body as the occlusion. Structure Origin The anterior choroidal artery typically originates from the internal carotid artery. It may (rarely) instead arise from the middle cerebral artery. It originates from the distal internal carotid artery (ICA) 5 mm distal to the origin of the posterior communicating artery and just proximal to the terminal bifurcation of the ICA. Course It initially course posterolaterally on the inferior surface of the cerebral hemisphere alongside the optic tract, crossing the tract medial-to-lateral inferior to the tract. At the level of the lateral geniculat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anterior Perforated Substance
The anterior perforated substance is a part of the brain. It is bilateral. It is irregular and quadrilateral. It lies in front of the optic tract and behind the olfactory trigone. Structure The anterior perforated substance is bilateral. It lies in front of the optic tract. It lies behind the olfactory trigone, separated by the fissure prima. Medially and in front, it is continuous with the subcallosal gyrus. Laterally, it is bounded by the lateral stria of the olfactory tract, and is continued into the uncus. Its gray substance is confluent above with that of the corpus striatum, and is perforated anteriorly by numerous small blood vessels that supply such areas as the internal capsule. The anterior cerebral artery arises just below the anterior perforated substance. The middle cerebral artery passes through its lateral two thirds. Blood supply The anterior perforated substance is supplied by lenticulostriate arteries, which branch from the middle cerebral arte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lamina Terminalis
The lamina terminalis is a thin layer that forms the median portion of the wall of the forebrain. It stretches from the interventricular foramen (foramen of Monro) to the recess at the base of the optic stalk (optic nerve) and contains the vascular organ of the lamina terminalis, which regulates the osmotic concentration of the blood. The lamina terminalis is immediately anterior to the tuber cinereum; together they form the pituitary stalk. The lamina terminalis can be opened via endoscopic neurosurgery in an attempt to create a path that cerebrospinal fluid can flow through when a person has hydrocephalus and when it is not possible to perform an endoscopic third ventriculostomy, but the effectiveness of this technique is not certain. This is the rostral end (tip) of the neural tube (embryological central nervous system) in the early weeks of development. Failure of the lamina terminalis to close properly at this stage of development will result in anencephaly or meroencep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tuberomammillary Nucleus
The tuberomammillary nucleus (TMN) is a histaminergic nucleus located within the posterior third of the hypothalamus. It is part of the tuber cinereum. It largely consists of histaminergic neurons (i.e. histamine-releasing neurons). It is involved with the control of arousal, learning, memory, sleep and energy balance. Efferents The tuberomammillary nucleus is the sole source of histamine pathways in the human brain. The densest axonal projections from the tuberomammillary nucleus are sent to the cerebral cortex, hippocampus, neostriatum, nucleus accumbens, amygdala, and other parts of the hypothalamus. The projections to the cerebral cortex directly increase cortical activation and arousal, and projections to acetylcholinergic neurons of the basal forebrain and dorsal pons do so indirectly, by increasing the release of acetylcholine Acetylcholine (ACh) is an organic compound that functions in the brain and body of many types of animals (including humans) as a neurotr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |