perivascular space on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
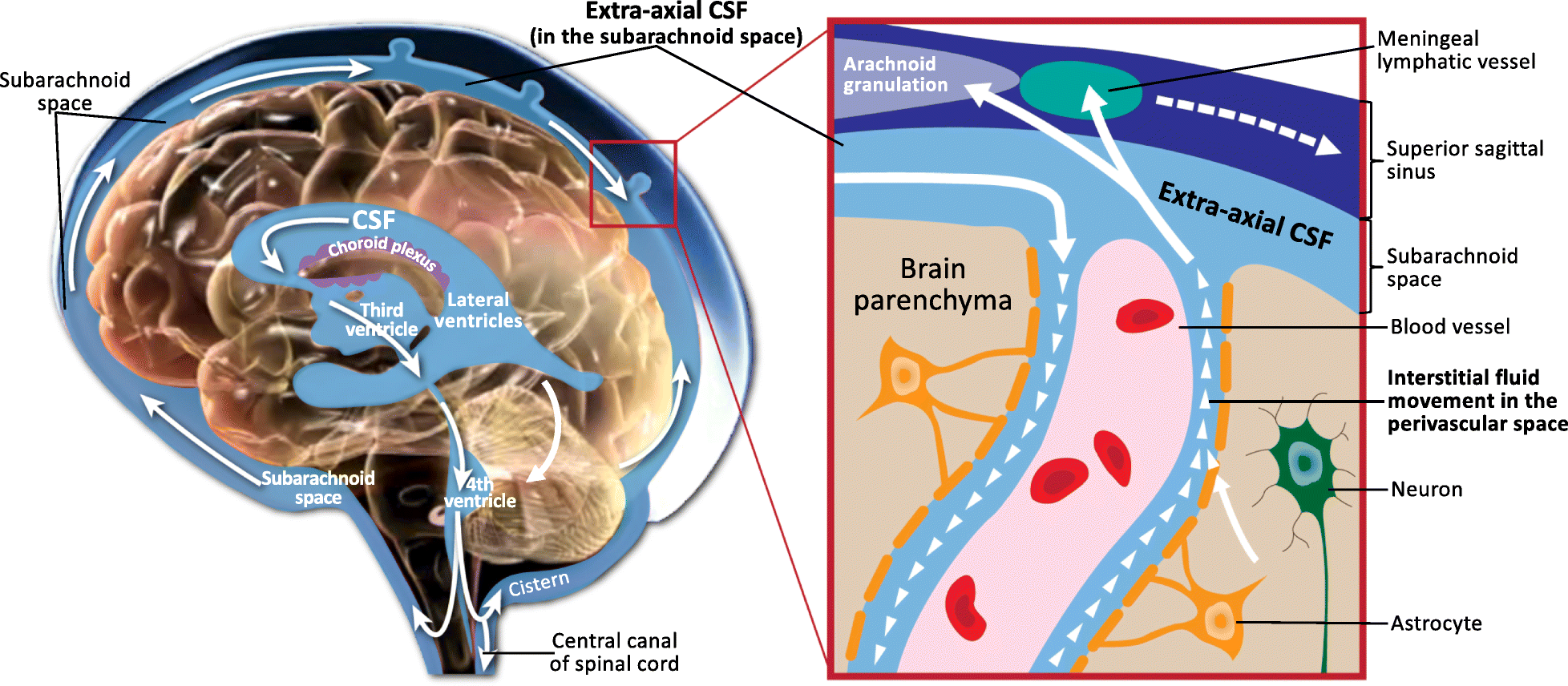 A perivascular space, also known as a Virchow–Robin space, is a fluid-filled space surrounding certain
A perivascular space, also known as a Virchow–Robin space, is a fluid-filled space surrounding certain
 A perivascular space, also known as a Virchow–Robin space, is a fluid-filled space surrounding certain
A perivascular space, also known as a Virchow–Robin space, is a fluid-filled space surrounding certain blood vessel
Blood vessels are the tubular structures of a circulatory system that transport blood throughout many Animal, animals’ bodies. Blood vessels transport blood cells, nutrients, and oxygen to most of the Tissue (biology), tissues of a Body (bi ...
s in several organs, including the brain, potentially having an immunological
Immunology is a branch of biology and medicine that covers the study of immune systems in all organisms.
Immunology charts, measures, and contextualizes the physiological functioning of the immune system in states of both health and disease ...
function, but more broadly a dispersive role for neural and blood-derived messengers. The brain pia mater
Pia mater ( or ),Entry "pia mater"
in
subarachnoid space. In the brain, ''perivascular cuffs'' are regions of leukocyte aggregation in the perivascular spaces, usually found in patients with
in
subarachnoid space. In the brain, ''perivascular cuffs'' are regions of leukocyte aggregation in the perivascular spaces, usually found in patients with
viral encephalitis
Viral encephalitis is inflammation of the brain parenchyma, called encephalitis, by a virus. The different forms of viral encephalitis are called viral encephalitides. It is the most common type of encephalitis and often occurs with viral meningiti ...
.
Perivascular spaces vary in dimension according to the type of blood vessel. In the brain where most capillaries have an imperceptible perivascular space, select structures of the brain, such as the circumventricular organs
Circumventricular organs (CVOs) (wiktionary:circum-, circum-: around ; ventricular: of Ventricular system, ventricle) are structures in the brain characterized by their extensive and highly vascular permeability, permeable capillary, capillarie ...
, are notable for having large perivascular spaces surrounding highly permeable
Permeability, permeable, and semipermeable may refer to:
Chemistry
*Drug permeability
*Semipermeable membrane, a membrane which will allow certain molecules or ions to pass through it by diffusion
*Vascular permeability, the movement of fluids a ...
capillaries, as observed by microscopy
Microscopy is the technical field of using microscopes to view subjects too small to be seen with the naked eye (objects that are not within the resolution range of the normal eye). There are three well-known branches of microscopy: optical mic ...
. The median eminence
The median eminence is generally defined as the portion of the ventral hypothalamus from which the portal vessels arise. The median eminence is a small swelling on the tuber cinereum, posterior to and on top of the pituitary stalk; it lies in th ...
, a brain structure at the base of the hypothalamus
The hypothalamus (: hypothalami; ) is a small part of the vertebrate brain that contains a number of nucleus (neuroanatomy), nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions is to link the nervous system to the endocrin ...
, contains capillaries with wide perivascular spaces.
In humans, perivascular spaces surround arteries and veins can usually be seen as areas of dilatation on MRI images. While many normal brains will show a few dilated spaces, an increase in these spaces may correlate with the incidence of several neurodegenerative
A neurodegenerative disease is caused by the progressive loss of neurons, in the process known as neurodegeneration. Neuronal damage may also ultimately result in their death. Neurodegenerative diseases include amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, mul ...
diseases, making the spaces a topic of research.
Structure
Perivascular spaces are gaps containinginterstitial fluid
In cell biology, extracellular fluid (ECF) denotes all body fluid outside the Cell (biology), cells of any multicellular organism. Body water, Total body water in healthy adults is about 50–60% (range 45 to 75%) of total body weight; women ...
that span between blood vessels
Blood vessels are the tubular structures of a circulatory system that transport blood throughout many animals’ bodies. Blood vessels transport blood cells, nutrients, and oxygen to most of the tissues of a body. They also take waste an ...
and their host organ, such as the brain, which they penetrate and serve as extravascular channels through which solutes can pass. Like the blood vessels around which they form, perivascular spaces are found in both the brain subarachnoid space and the subpial space.
Perivascular spaces surrounding arteries
An artery () is a blood vessel in humans and most other animals that takes oxygenated blood away from the heart in the systemic circulation to one or more parts of the body. Exceptions that carry deoxygenated blood are the pulmonary arteries in ...
in the cerebral cortex
The cerebral cortex, also known as the cerebral mantle, is the outer layer of neural tissue of the cerebrum of the brain in humans and other mammals. It is the largest site of Neuron, neural integration in the central nervous system, and plays ...
and the basal ganglia
The basal ganglia (BG) or basal nuclei are a group of subcortical Nucleus (neuroanatomy), nuclei found in the brains of vertebrates. In humans and other primates, differences exist, primarily in the division of the globus pallidus into externa ...
are separated from the subpial space by one or two layers of leptomeninges, respectively, as well as the pia mater
Pia mater ( or ),Entry "pia mater"
in
veins Veins () are blood vessels in the circulatory system of humans and most other animals that carry blood towards the heart. Most veins carry deoxygenated blood from the tissues back to the heart; exceptions are those of the pulmonary and fetal c ...
. Use of the in
veins Veins () are blood vessels in the circulatory system of humans and most other animals that carry blood towards the heart. Most veins carry deoxygenated blood from the tissues back to the heart; exceptions are those of the pulmonary and fetal c ...
scanning electron microscope
A scanning electron microscope (SEM) is a type of electron microscope that produces images of a sample by scanning the surface with a focused beam of electrons. The electrons interact with atoms in the sample, producing various signals that ...
has determined that the spaces surrounding blood vessels in the subarachnoid space are not continuous with the subarachnoid space because of the presence of pia mater cells joined by desmosomes
A desmosome (; "binding body"), also known as a macula adherens (plural: maculae adherentes) (Latin for ''adhering spot''), is a cell structure specialized for cell-to-cell adhesion. A type of junctional complex, they are localized spot-like ad ...
.
Perivascular spaces, especially around fenestra
A fenestra (fenestration; : fenestrae or fenestrations) is any small opening or pore, commonly used as a term in the biology, biological sciences. It is the Latin word for "window", and is used in various fields to describe a pore in an anatomy, ...
ted capillaries, are found in many organs, such as the thymus
The thymus (: thymuses or thymi) is a specialized primary lymphoid organ of the immune system. Within the thymus, T cells mature. T cells are critical to the adaptive immune system, where the body adapts to specific foreign invaders. The thymus ...
, liver
The liver is a major metabolic organ (anatomy), organ exclusively found in vertebrates, which performs many essential biological Function (biology), functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the Protein biosynthesis, synthesis of var ...
, kidney
In humans, the kidneys are two reddish-brown bean-shaped blood-filtering organ (anatomy), organs that are a multilobar, multipapillary form of mammalian kidneys, usually without signs of external lobulation. They are located on the left and rig ...
s, spleen
The spleen (, from Ancient Greek '' σπλήν'', splḗn) is an organ (biology), organ found in almost all vertebrates. Similar in structure to a large lymph node, it acts primarily as a blood filter.
The spleen plays important roles in reg ...
, bone
A bone is a rigid organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells, store minerals, provide structure and support for the body, ...
s, and pineal gland
The pineal gland (also known as the pineal body or epiphysis cerebri) is a small endocrine gland in the brain of most vertebrates. It produces melatonin, a serotonin-derived hormone, which modulates sleep, sleep patterns following the diurnal c ...
. Particularly within the brain circumventricular organs – subfornical organ
The subfornical organ (SFO) is one of the circumventricular organs of the brain. Its name comes from its location on the ventral surface of the fornix near the interventricular foramina (foramina of Monro), which interconnect the lateral ventric ...
, area postrema
The area postrema, a paired structure in the medulla oblongata of the brainstem, is a circumventricular organ having permeable capillaries and sensory neurons that enable its role to detect circulating chemical messengers in the blood and tra ...
, and median eminence – large perivascular spaces are present around fenestrated capillaries, indicating that the spaces serve a dispersive role for brain- or bloodborne
is a 2015 action role-playing game developed by FromSoftware and published by Sony Computer Entertainment for the PlayStation 4. The game follows a Hunter through the decrepit Gothic, Victorian-era–inspired city of Yharnam, whose inhabita ...
messengers.
Perivascular spaces may be enlarged to a diameter of five millimeters in healthy humans and do not imply disease. When enlarged, they can disrupt the function of the brain regions into which they project. Dilation can occur on one or both sides of the brain.
Dilated perivascular spaces are categorized into three types:
* Type 1 are located on the lenticulostriate arteries projecting into the basal ganglia
The basal ganglia (BG) or basal nuclei are a group of subcortical Nucleus (neuroanatomy), nuclei found in the brains of vertebrates. In humans and other primates, differences exist, primarily in the division of the globus pallidus into externa ...
* Type 2 are located in the cortex following the path of the medullary arteries
* Type 3 are located in the midbrain
The midbrain or mesencephalon is the uppermost portion of the brainstem connecting the diencephalon and cerebrum with the pons. It consists of the cerebral peduncles, tegmentum, and tectum.
It is functionally associated with vision, hearing, mo ...
Perivascular spaces are most commonly located in the basal ganglia
The basal ganglia (BG) or basal nuclei are a group of subcortical Nucleus (neuroanatomy), nuclei found in the brains of vertebrates. In humans and other primates, differences exist, primarily in the division of the globus pallidus into externa ...
and white matter
White matter refers to areas of the central nervous system that are mainly made up of myelinated axons, also called Nerve tract, tracts. Long thought to be passive tissue, white matter affects learning and brain functions, modulating the distr ...
of the cerebrum
The cerebrum (: cerebra), telencephalon or endbrain is the largest part of the brain, containing the cerebral cortex (of the two cerebral hemispheres) as well as several subcortical structures, including the hippocampus, basal ganglia, and olfac ...
, and along the optic tract
In neuroanatomy, the optic tract () is a part of the visual system in the brain. It is a continuation of the optic nerve that relays information from the optic chiasm to the ipsilateral lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN), pretectal nuclei, and su ...
.
The ideal method used to visualize perivascular spaces is T2-weighted MRI. The MR images of other neurological
Neurology (from , "string, nerve" and the suffix -logia, "study of") is the branch of medicine dealing with the diagnosis and treatment of all categories of conditions and disease involving the nervous system, which comprises the brain, the s ...
disorder
Disorder may refer to randomness, a lack of intelligible pattern, or:
Healthcare
* Disorder (medicine), a functional abnormality or disturbance
* Mental disorder or psychological disorder, a psychological pattern associated with distress or disab ...
s can be similar to those of the dilated spaces. These disorders are:
* cystic neoplasms
* lacunar infarctions
* cystic periventricular leukomalacia
*cryptococcosis
Cryptococcosis is a potentially fatal fungal infection of mainly the lungs, presenting as a pneumonia, and in the brain, where it appears as a meningitis. Coughing, difficulty breathing, chest pain and fever are seen when the lungs are infect ...
*multiple sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is an autoimmune disease resulting in damage to myelinthe insulating covers of nerve cellsin the brain and spinal cord. As a demyelinating disease, MS disrupts the nervous system's ability to Action potential, transmit ...
*mucopolysaccharidoses
Mucopolysaccharidoses are a group of metabolic disorders caused by the absence or malfunctioning of lysosomal enzymes needed to break down molecules called glycosaminoglycans (GAGs). These long chains of sugar carbohydrates occur within the cel ...
*neurocysticercosis
Neurocysticercosis (NCC) is a Parasitic disease, parasitic infection of the central nervous system, nervous system caused by the larvae of the tapeworm ''Taenia solium,'' also known as the "pork tapeworm". The disease is primarily transmitted ...
* arachnoid cysts
* neuroepithelial cysts
Perivascular spaces are distinguished on an MRI by several key features. The spaces appear as distinct round or oval entities with a signal intensity visually equivalent to that of cerebrospinal fluid
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is a clear, colorless Extracellular fluid#Transcellular fluid, transcellular body fluid found within the meninges, meningeal tissue that surrounds the vertebrate brain and spinal cord, and in the ventricular system, ven ...
in the subarachnoid space. In addition, a perivascular space has no mass effect and is located along the blood vessel around which it forms.
Function
One of the most basic roles of the perivascular space is the regulation of fluid movement in thecentral nervous system
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain, spinal cord and retina. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity o ...
and its drainage. The spaces ultimately drain fluid from neuronal cell bodies to the cervical lymph nodes
Cervical lymph nodes are lymph nodes found in the neck. Of the 800 lymph nodes in the human body, 300 are in the neck. Cervical lymph nodes are subject to a number of different pathological conditions including tumours, infection and inflamma ...
. In particular, the "tide hypothesis" suggests that the cardiac contraction creates and maintains pressure waves to modulate the flow to and from the subarachnoid space and the perivascular space. By acting as a sort of sponge, they are essential for signal transmission and the maintenance of extracellular fluid
In cell biology, extracellular fluid (ECF) denotes all body fluid outside the cells of any multicellular organism. Total body water in healthy adults is about 50–60% (range 45 to 75%) of total body weight; women and the obese typically ha ...
.
Another function is as an integral part of the blood–brain barrier
The blood–brain barrier (BBB) is a highly selective semipermeable membrane, semipermeable border of endothelium, endothelial cells that regulates the transfer of solutes and chemicals between the circulatory system and the central nervous system ...
(BBB). While the BBB is often described as the tight junctions between the endothelial cells, this is an oversimplification that neglects the intricate role that perivascular spaces take in separating the venous blood from the parenchyma of the brain. Often, cell debris and foreign particles, which are impermeable to the BBB will get through the endothelial cells, only to be phagocytosed
Phagocytosis () is the process by which a cell uses its plasma membrane to engulf a large particle (≥ 0.5 μm), giving rise to an internal compartment called the phagosome. It is one type of endocytosis. A cell that performs phagocytosis is c ...
in the perivascular spaces. This holds true for many T and B cell
B cells, also known as B lymphocytes, are a type of the lymphocyte subtype. They function in the humoral immunity component of the adaptive immune system. B cells produce antibody molecules which may be either secreted or inserted into the plasm ...
s, as well as monocyte
Monocytes are a type of leukocyte or white blood cell. They are the largest type of leukocyte in blood and can differentiate into macrophages and monocyte-derived dendritic cells. As a part of the vertebrate innate immune system monocytes also ...
s, giving this small fluid filled space an important immunological
Immunology is a branch of biology and medicine that covers the study of immune systems in all organisms.
Immunology charts, measures, and contextualizes the physiological functioning of the immune system in states of both health and disease ...
role.
Perivascular spaces also play an important role in immunoregulation; they not only contain interstitial and cerebrospinal fluid, but they also have a constant flux of macrophage
Macrophages (; abbreviated MPhi, φ, MΦ or MP) are a type of white blood cell of the innate immune system that engulf and digest pathogens, such as cancer cells, microbes, cellular debris and foreign substances, which do not have proteins that ...
s, which is regulated by blood-borne mononuclear cells, but do not pass the basement membrane of the glia limitans
The glia limitans, or the glial limiting membrane, is a thin barrier of astrocyte foot processes associated with the brain parenchyma, parenchymal basal lamina surrounding the brain and spinal cord. It is the outermost layer of neural tissue, and ...
. Similarly, as part of its role in signal transmission, perivascular spaces contain vasoactive
A vasoactive substance is an endogenous agent or pharmaceutical drug that has the effect of either increasing or decreasing blood pressure and/or heart rate through its vasoactivity, that is, vascular activity (effect on blood vessels). By adjust ...
neuropeptide
Neuropeptides are chemical messengers made up of small chains of amino acids that are synthesized and released by neurons. Neuropeptides typically bind to G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) to modulate neural activity and other tissues like the ...
s (VNs), which, aside from regulating blood pressure and heart rate, have an integral role in controlling microglia
Microglia are a type of glia, glial cell located throughout the brain and spinal cord of the central nervous system (CNS). Microglia account for about around 5–10% of cells found within the brain. As the resident macrophage cells, they act as t ...
. VNs serve to prevent inflammation by activating the enzyme adenylate cyclase
Adenylate cyclase (EC 4.6.1.1, also commonly known as adenyl cyclase and adenylyl cyclase, abbreviated AC) is an enzyme with systematic name ATP diphosphate-lyase (cyclizing; 3′,5′-cyclic-AMP-forming). It catalyzes the following reaction:
:A ...
which then produces cAMP
Camp may refer to:
Areas of confinement, imprisonment, or for execution
* Concentration camp, an internment camp for political prisoners or politically targeted demographics, such as members of national or minority ethnic groups
* Extermination ...
. The production of cAMP aids in the modulation of auto-reactive T cells
T cells (also known as T lymphocytes) are an important part of the immune system and play a central role in the adaptive immune response. T cells can be distinguished from other lymphocytes by the presence of a T-cell receptor (TCR) on their ce ...
by regulatory T cells. . The perivascular space is susceptible space for VN compromise and when their function is reduced in the space, immune response is adversely affected and the potential for degradation increases. When inflammation by T cells begins, astrocyte
Astrocytes (from Ancient Greek , , "star" and , , "cavity", "cell"), also known collectively as astroglia, are characteristic star-shaped glial cells in the brain and spinal cord. They perform many functions, including biochemical control of en ...
s begin to undergo apoptosis
Apoptosis (from ) is a form of programmed cell death that occurs in multicellular organisms and in some eukaryotic, single-celled microorganisms such as yeast. Biochemistry, Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes (Morphology (biol ...
, due to their CD95 receptor, to open up the glia limitans and let T cells into the parenchyma of the brain. Because this process is aided by the perivascular macrophages, these tend to accumulate during neuroinflammation and cause dilation of the spaces.
Clinical significance
The clinical significance of perivascular spaces comes primarily from their tendency to dilate. The importance of dilation is hypothesized to be based on changes in shape rather than size. Enlarged spaces have been observed most commonly in thebasal ganglia
The basal ganglia (BG) or basal nuclei are a group of subcortical Nucleus (neuroanatomy), nuclei found in the brains of vertebrates. In humans and other primates, differences exist, primarily in the division of the globus pallidus into externa ...
, specifically on the lenticulostriate arteries. They have also been observed along the paramedial mesencephalothalamic artery and the substantia nigra
The substantia nigra (SN) is a basal ganglia structure located in the midbrain that plays an important role in reward and movement. ''Substantia nigra'' is Latin for "black substance", reflecting the fact that parts of the substantia nigra a ...
in the mesencephalon
The midbrain or mesencephalon is the uppermost portion of the brainstem connecting the diencephalon and cerebrum with the pons. It consists of the cerebral peduncles, tegmentum, and tectum.
It is functionally associated with vision, hearing, mo ...
, the brain region below the insula, the dentate nucleus in the cerebellum
The cerebellum (: cerebella or cerebellums; Latin for 'little brain') is a major feature of the hindbrain of all vertebrates. Although usually smaller than the cerebrum, in some animals such as the mormyrid fishes it may be as large as it or eve ...
, and the corpus callosum
The corpus callosum (Latin for "tough body"), also callosal commissure, is a wide, thick nerve tract, consisting of a flat bundle of commissural fibers, beneath the cerebral cortex in the brain. The corpus callosum is only found in placental ...
, as well as the brain region directly above it, the cingulate gyrus
The cingulate cortex is a part of the brain situated in the medial aspect of the cerebral cortex. The cingulate cortex includes the entire cingulate gyrus, which lies immediately above the corpus callosum, and the continuation of this in the cin ...
. Upon the clinical application of MRI, it was shown in several studies that perivascular space dilation and lacunar stroke
Lacunar stroke or lacunar cerebral infarct (LACI) is the most common type of ischemic stroke, resulting from the Vascular occlusion, occlusion of small penetrating artery, arteries that provide blood to the brain's deep structures. Patients who pr ...
s are the most commonly observed histological correlates of signaling abnormalities.
Senescence
Dilation is most commonly and closely associated with aging. Dilation of perivascular spaces has been shown to correlate best with age, even when accompanying factors includinghypertension
Hypertension, also known as high blood pressure, is a Chronic condition, long-term Disease, medical condition in which the blood pressure in the artery, arteries is persistently elevated. High blood pressure usually does not cause symptoms i ...
, dementia
Dementia is a syndrome associated with many neurodegenerative diseases, characterized by a general decline in cognitive abilities that affects a person's ability to perform activities of daily living, everyday activities. This typically invo ...
, and white matter
White matter refers to areas of the central nervous system that are mainly made up of myelinated axons, also called Nerve tract, tracts. Long thought to be passive tissue, white matter affects learning and brain functions, modulating the distr ...
lesions are considered. In the elderly, such dilation has been correlated with many symptoms and conditions that often affect the arterial walls, including vascular hypertension, arteriosclerosis
Arteriosclerosis, literally meaning "hardening of the arteries", is an umbrella term for a vascular disorder characterized by abnormal thickening, hardening, and loss of elasticity of the walls of arteries; this process gradually restricts th ...
, reduced cognitive capacity, dementia, and low post-mortem brain weight. In addition to dilation among the elderly, dilation in young, healthy individuals can also be observed. This occurrence is rare and there has been no observed association in such cases with reduced cognitive function or white matter abnormalities. When dilated VRS are observed in the corpus callosum, there is generally no neurological deficit associated. They are often observed in this region as cystic lesions with cerebrospinal-like fluid.
Symptoms of dilation
Extreme dilation has been associated with several specific clinical symptoms. In cases of severe dilation in only one hemisphere, symptoms reported include a non-specific fainting attack,hypertension
Hypertension, also known as high blood pressure, is a Chronic condition, long-term Disease, medical condition in which the blood pressure in the artery, arteries is persistently elevated. High blood pressure usually does not cause symptoms i ...
, positional vertigo
Vertigo is a condition in which a person has the sensation that they are moving, or that objects around them are moving, when they are not. Often it feels like a spinning or swaying movement. It may be associated with nausea, vomiting, perspira ...
, headache, early recall disturbances, and hemifacial tics. Symptoms associated with severe bilateral dilation include ear pain (which was reported to have resolved on its own), dementia, and seizures. This data was compiled from case studies of individuals with severe VRS dilation. Considering the anatomical abnormality presented in such cases, these findings were considered surprising in that the symptoms were relatively mild. In most cases, there is in fact no mass effect associated with some VRS dilation. An exception to the mildness of clinical symptoms associated with VRS dilation is when there is extreme dilation in the lower mesencephalon
The midbrain or mesencephalon is the uppermost portion of the brainstem connecting the diencephalon and cerebrum with the pons. It consists of the cerebral peduncles, tegmentum, and tectum.
It is functionally associated with vision, hearing, mo ...
at the junction between the substantia nigra
The substantia nigra (SN) is a basal ganglia structure located in the midbrain that plays an important role in reward and movement. ''Substantia nigra'' is Latin for "black substance", reflecting the fact that parts of the substantia nigra a ...
and cerebral peduncle
The cerebral peduncles (In Latin, ''ped-'' means 'foot'.) are the two stalks that attach the cerebrum to the brainstem. They are structures at the front of the midbrain which arise from the ventral pons and contain the large ascending (sensor ...
. In such cases, mild to moderate obstructive hydrocephalus
Hydrocephalus is a condition in which cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) builds up within the brain, which can cause pressure to increase in the skull. Symptoms may vary according to age. Headaches and double vision are common. Elderly adults with n ...
was reported in most patients. Associated symptoms ranged from headaches to symptoms more severe than those just discussed in the cases of dilation in the cerebral hemispheres. Other general symptoms associated with VRS dilation include headaches, dizziness, memory impairment, poor concentration, dementia, visual changes, oculomotor abnormality, tremors, seizures, limb weakness, and ataxia
Ataxia (from Greek α- negative prefix+ -τάξις rder= "lack of order") is a neurological sign consisting of lack of voluntary coordination of muscle movements that can include gait abnormality, speech changes, and abnormalities in e ...
.
Associated disorders
Dilation is a typical characteristic of several diseases and disorders. These include diseases from metabolic and genetic disorders such asmannosidosis
Mannosidosis is a deficiency in mannosidase, an enzyme. There are two types: alpha-mannosidosis and beta-mannosidosis. Both disorders are related to the lysosome and have similar presentation; the former is caused by defective lysosomal α-man ...
, myotonic dystrophy
Myotonic dystrophy (DM) is a type of muscular dystrophy, a group of genetic disorders that cause progressive muscle loss and weakness. In DM, muscles are often myotonia, unable to relax after contraction. Other manifestations may include catarac ...
, Lowe syndrome
Oculocerebrorenal syndrome (also called Lowe syndrome) is a rare X-linked recessive disorder characterized by congenital cataracts, hypotonia, intellectual disability, proximal tubular acidosis, aminoaciduria and low-molecular-weight proteinur ...
, and Coffin–Lowry syndrome
Coffin–Lowry syndrome is a genetic disorder that is X-linked dominant and which causes severe mental problems sometimes associated with abnormalities of growth, cardiac abnormalities, kyphoscoliosis, and auditory and visual abnormalities.
Pres ...
. Dilation is also a common characteristic of diseases or disorders of vascular pathologies, including CADASIL
CADASIL or CADASIL syndrome, involving cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalopathy, is the most common form of hereditary stroke disorder and is thought to be caused by mutations of the '' NOTCH3'' gen ...
(cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalopathy), hereditary infantile hemiparesis, retinal arteriolar tortuosity and leukoencephalopathy, migraines, and vascular dementia. A third group of disorders typically associated with VRS dilation is neuroectodermal syndromes. This includes polycystic brains associated with ectodermal dysplasia
Dysplasia is any of various types of abnormal growth or development of cells (microscopic scale) or organs (macroscopic scale), and the abnormal histology or anatomical structure(s) resulting from such growth. Dysplasias on a mainly microscopic ...
, frontonasal dysplasia, and Joubert syndrome
Joubert syndrome is a rare autosomal recessive genetic disorder that affects the cerebellum, an area of the Human brain, brain that controls balance and coordination.
Joubert syndrome is one of the many genetic syndromes associated with syndromic ...
. There is a fourth miscellaneous group of disorders typically associated with dilation that includes autism
Autism, also known as autism spectrum disorder (ASD), is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by differences or difficulties in social communication and interaction, a preference for predictability and routine, sensory processing d ...
in children, megalencephalopathy, secondary Parkinson's disease
Parkinson's disease (PD), or simply Parkinson's, is a neurodegenerative disease primarily of the central nervous system, affecting both motor system, motor and non-motor systems. Symptoms typically develop gradually and non-motor issues become ...
, recent-onset multiple sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is an autoimmune disease resulting in damage to myelinthe insulating covers of nerve cellsin the brain and spinal cord. As a demyelinating disease, MS disrupts the nervous system's ability to Action potential, transmit ...
, and chronic alcoholism
Alcoholism is the continued drinking of alcohol despite it causing problems. Some definitions require evidence of dependence and withdrawal. Problematic use of alcohol has been mentioned in the earliest historical records. The World He ...
. Because dilation can be associated with several diseases but also observed in healthy patients, it is always important in the evaluation of VRS to study the tissue around the dilation via MRI and to consider the entire clinical context.
Current research
Causes of dilated VRS
Much of the current research concerning Virchow–Robin spaces relates to their known tendency to dilate. Research is presently being performed in order to determine the exact cause of dilation in these perivascular spaces. Current theories include mechanical trauma resulting fromcerebrospinal fluid
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is a clear, colorless Extracellular fluid#Transcellular fluid, transcellular body fluid found within the meninges, meningeal tissue that surrounds the vertebrate brain and spinal cord, and in the ventricular system, ven ...
pulsation, elongation of ectactic penetrating blood vessels, and abnormal vascular permeability leading to increased fluid exudation. Further research has implicated shrinkage or atrophy
Atrophy is the partial or complete wasting away of a part of the body. Causes of atrophy include mutations (which can destroy the gene to build up the organ), malnutrition, poor nourishment, poor circulatory system, circulation, loss of hormone, ...
of surrounding brain tissue, perivascular demyelination, coiling of the arteries as they age, altered permeability of the arterial wall and obstruction of lymphatic drainage pathways. In addition, insufficient fluid draining and injury to ischemic
Ischemia or ischaemia is a restriction in blood supply to any tissue, muscle group, or organ of the body, causing a shortage of oxygen that is needed for cellular metabolism (to keep tissue alive). Ischemia is generally caused by problems ...
perivascular tissue resulting in an ex vacuo effect have been suggested as possible causes for dilated VRS.Dilated VRS might also be linked to vascular damage, blood leakage and microaneurysm formation.
Association of dilated VRS and other diseases
Recent and ongoing research has found associations between enlarged VRS and several disorders.Dementia
At one point in time, dilated Virchow–Robin spaces were so commonly noted in autopsies of persons withdementia
Dementia is a syndrome associated with many neurodegenerative diseases, characterized by a general decline in cognitive abilities that affects a person's ability to perform activities of daily living, everyday activities. This typically invo ...
, they were believed to cause the disease. However, additional research is currently being performed in order to confirm or refute a direct connection between dilation of VRS and dementia.
Analysis of VRS may distinguish dementia caused by arteriosclerotic
Atherosclerosis is a pattern of the disease arteriosclerosis, characterized by development of abnormalities called lesions in walls of arteries. This is a chronic inflammatory disease involving many different cell types and is driven by elev ...
microvascular disease Microangiopathy (also known as microvascular disease, small vessel disease (SVD) or microvascular dysfunction) is a disease of the microvessels, small blood vessels in the microcirculation. It can be contrasted to macroangiopathies such as atherosc ...
from dementia caused by neurodegenerative
A neurodegenerative disease is caused by the progressive loss of neurons, in the process known as neurodegeneration. Neuronal damage may also ultimately result in their death. Neurodegenerative diseases include amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, mul ...
disease. A 2005 study has evidenced that a substantial amount of VRS in the substantia innominata
The substantia innominata, also innominate substance or substantia innominata of Meynert (Latin for unnamed substance), is a series of layers in the human brain consisting partly of gray and partly of white matter, which lies below the anterior par ...
, lentiform nucleus
The lentiform nucleus (or lentiform complex, lenticular nucleus, or lenticular complex) are the putamen (laterally) and the globus pallidus (medially), collectively. Due to their proximity, these two structures were formerly considered one, howev ...
, and the caudate nucleus
The caudate nucleus is one of the structures that make up the corpus striatum, which is part of the basal ganglia in the human brain. Although the caudate nucleus has long been associated with motor processes because of its relation to Parkinso ...
of the basal ganglia may implicate dementia due to arteriosclerotic microvascular disease, in particular Ischemic Vascular Dementia, as opposed dementia due to neurodegenerative disease, specifically Alzheimer's disease and frontotemporal dementia
Frontotemporal dementia (FTD), also called frontotemporal degeneration disease or frontotemporal neurocognitive disorder, encompasses several types of dementia involving the progressive degeneration of the brain's frontal lobe, frontal and tempor ...
. Thus, perhaps VRS dilation can be used to distinguish between diagnoses of vascular dementias and degenerative dementias.
Alzheimer's disease
Some studies have assessed the spatial distribution and prevalence of VRS in people withAlzheimer's disease
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disease and the cause of 60–70% of cases of dementia. The most common early symptom is difficulty in remembering recent events. As the disease advances, symptoms can include problems wit ...
versus those without the disease. Researchers have found that while VRS appear to be correlated with natural aging, MR imaging reveals a greater prevalence of VRS in those with Alzheimer's.
Cerebral amyloid angiopathy (CAA), a blood vessel failure often associated with Alzheimer's disease, utilizes dilated VRS to spread inflammation to the parenchyma. Because the VRS often have an extra membrane in gray matter, the ischemic CAA response is often observed in white matter.
It has been hypothesized that the structure of VRS in the cerebral cortex
The cerebral cortex, also known as the cerebral mantle, is the outer layer of neural tissue of the cerebrum of the brain in humans and other mammals. It is the largest site of Neuron, neural integration in the central nervous system, and plays ...
may contribute to the development of Alzheimer's disease. In contrast to VRS of the basal ganglia
The basal ganglia (BG) or basal nuclei are a group of subcortical Nucleus (neuroanatomy), nuclei found in the brains of vertebrates. In humans and other primates, differences exist, primarily in the division of the globus pallidus into externa ...
, VRS in the cerebral cortex are surrounded by only one layer of leptomeninges. As such, VRS in the cerebral cortex may drain β-amyloid
Amyloid beta (Aβ, Abeta or beta-amyloid) denotes peptides of 36–43 amino acids that are the main component of the amyloid plaques found in the brains of people with Alzheimer's disease. The peptides derive from the amyloid-beta precursor prot ...
in interstitial fluid
In cell biology, extracellular fluid (ECF) denotes all body fluid outside the Cell (biology), cells of any multicellular organism. Body water, Total body water in healthy adults is about 50–60% (range 45 to 75%) of total body weight; women ...
less effectively than VRS in the basal ganglia. The less-effective drainage may lead to the development of the β-amyloid plaques that characterize Alzheimer's disease. In support of this hypothesis, studies have noted the greater frequency of β-amyloid plaques in the cerebral cortex than in the basal ganglia of Alzheimer's disease patients.
Stroke
Because dilated perivascular spaces are so closely correlated withcerebrovascular disease
Cerebrovascular disease includes a variety of medical conditions that affect the blood vessels of the brain and the cerebral circulation. Arteries supplying oxygen and nutrients to the brain are often damaged or deformed in these disorders. Th ...
, there is much current research on their use as a diagnostic tool. In a recent study of 31 subjects, abnormal dilation, along with irregular CSF pulsation, were correlated with those subjects having three or more risk factors
In epidemiology, a risk factor or determinant is a variable associated with an increased risk of disease or infection.
Due to a lack of harmonization across disciplines, determinant, in its more widely accepted scientific meaning, is often ...
for strokes. Therefore, perivascular spaces are a possible novel biomarker
In biomedical contexts, a biomarker, or biological marker, is a measurable indicator of some biological state or condition. Biomarkers are often measured and evaluated using blood, urine, or soft tissues to examine normal biological processes, ...
for hemorrhagic strokes.
CADASIL syndrome
CADASIL or CADASIL syndrome, involving cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalopathy, is the most common form of hereditary stroke disorder and is thought to be caused by mutations of the '' NOTCH3'' gen ...
(cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalopathy syndrome) is a hereditary stroke condition due to a Notch 3
Neurogenic locus notch homolog protein 3 (Notch 3) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''NOTCH3'' gene.
Function
This gene encodes the third discovered human homologue of the ''Drosophila melanogaster'' type I membrane protein Notch ...
gene mutation on Chromosome 19. Studies have noted that in comparison to family members lacking the affected haplotype
A haplotype (haploid genotype) is a group of alleles in an organism that are inherited together from a single parent.
Many organisms contain genetic material (DNA) which is inherited from two parents. Normally these organisms have their DNA orga ...
that leads to the condition, an increased number of dilated spaces is observed in individuals with CADASIL. These perivascular spaces are localized primarily in the putamen
The putamen (; from Latin, meaning "nutshell") is a subcortical nucleus (neuroanatomy), nucleus with a rounded structure, in the basal ganglia nuclear group. It is located at the base of the forebrain and above the midbrain.
The putamen and c ...
and temporal subcortical white matter
White matter refers to areas of the central nervous system that are mainly made up of myelinated axons, also called Nerve tract, tracts. Long thought to be passive tissue, white matter affects learning and brain functions, modulating the distr ...
and they appear to correlate with age of the individual with the condition rather than severity of the disease itself.
There has been a high risk of stroke
Stroke is a medical condition in which poor cerebral circulation, blood flow to a part of the brain causes cell death. There are two main types of stroke: brain ischemia, ischemic, due to lack of blood flow, and intracranial hemorrhage, hemor ...
associated with dilated perivascular spaces in the elderly according to the Framingham Stroke Risk Score. In contrast, other studies have concluded that the dilation of these spaces is a normal phenomenon in aging with no association with arterosclerosis. This remains, therefore, an important point of research in the field.
Multiple sclerosis
Similar to the research concerning a potential connection between perivascular spaces and Alzheimer's, MRI scans of people recently diagnosed withmultiple sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is an autoimmune disease resulting in damage to myelinthe insulating covers of nerve cellsin the brain and spinal cord. As a demyelinating disease, MS disrupts the nervous system's ability to Action potential, transmit ...
(MS) have been studied. Larger, more prevalent spaces have been observed in those with MS. Additional studies with similar findings have suggested that the inflammatory cells which contribute to the demyelination that characterizes MS also attack the perivascular spaces. Studies using advanced MRI techniques will be necessary to determine if the perivascular spaces can be implicated as a potential marker of the disease.
Autism
Dilated perivascular spaces are common among the elderly and uncommon in children. Studies have noted the association between bothdevelopmental delay
The term developmental delay can refer to:
*Global developmental delay, an umbrella term used when children are significantly delayed in two or more areas of development
*Specific developmental disorder, a classification of disorders characterize ...
and non-syndromic autism and enlarged or dilated perivascular spaces. Non-syndromic autism categorizes autistic patients for which there is no known cause.
History
The appearance of perivascular spaces was first noted in 1843 by Durant-Fardel. In 1851,Rudolph Virchow
Rudolf Ludwig Carl Virchow ( ; ; 13 October 18215 September 1902) was a German physician, anthropologist, pathologist, prehistorian, biologist, writer, editor, and politician. He is known as "the father of modern pathology" and as the founder o ...
was the first to provide a detailed description of these microscopic spaces between the outer and inner/middle lamina of the brain vessels. Charles-Philippe Robin
Charles-Philippe Robin (; 4 June 1821 – 6 October 1885) was a French anatomist, biologist, and histologist born in Jasseron, département Ain. He was a founder of the French Society for Biology in which he advocated Positivism, positivist philos ...
confirmed these findings in 1859 and was the first to describe the perivascular spaces as channels that existed in normal anatomy. The spaces were called ''Virchow-Robin spaces'' and are still also known as such. The immunological significance was discovered by Wilhelm His, Sr.
__NOTOC__
Wilhelm His Sr. (9 July 1831 – 1 May 1904) was a Swiss anatomist and professor who invented the microtome. By treating animal tissue with acids and salts to harden it and then slicing it very thinly with the microtome, scientists wer ...
in 1865 based on his observations of the flow of interstitial fluid over the spaces to the lymphatic system.
For many years after Virchow-Robin spaces were first described, it was thought that they were in free communication with the cerebrospinal fluid
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is a clear, colorless Extracellular fluid#Transcellular fluid, transcellular body fluid found within the meninges, meningeal tissue that surrounds the vertebrate brain and spinal cord, and in the ventricular system, ven ...
in the subarachnoid space. It was later shown with the use of electron microscopy that the pia mater
Pia mater ( or ),Entry "pia mater"
in
MRI Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to generate pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes inside the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and rad ...
, measurements of the differences of signal intensity between the perivascular spaces and cerebrospinal fluid supported these findings. As research technologies continued to expand, so too did information regarding their function, anatomy and clinical significance.
in
MRI Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to generate pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes inside the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and rad ...
References
{{Meninges Rudolf Virchow Meninges Neurohistology