|
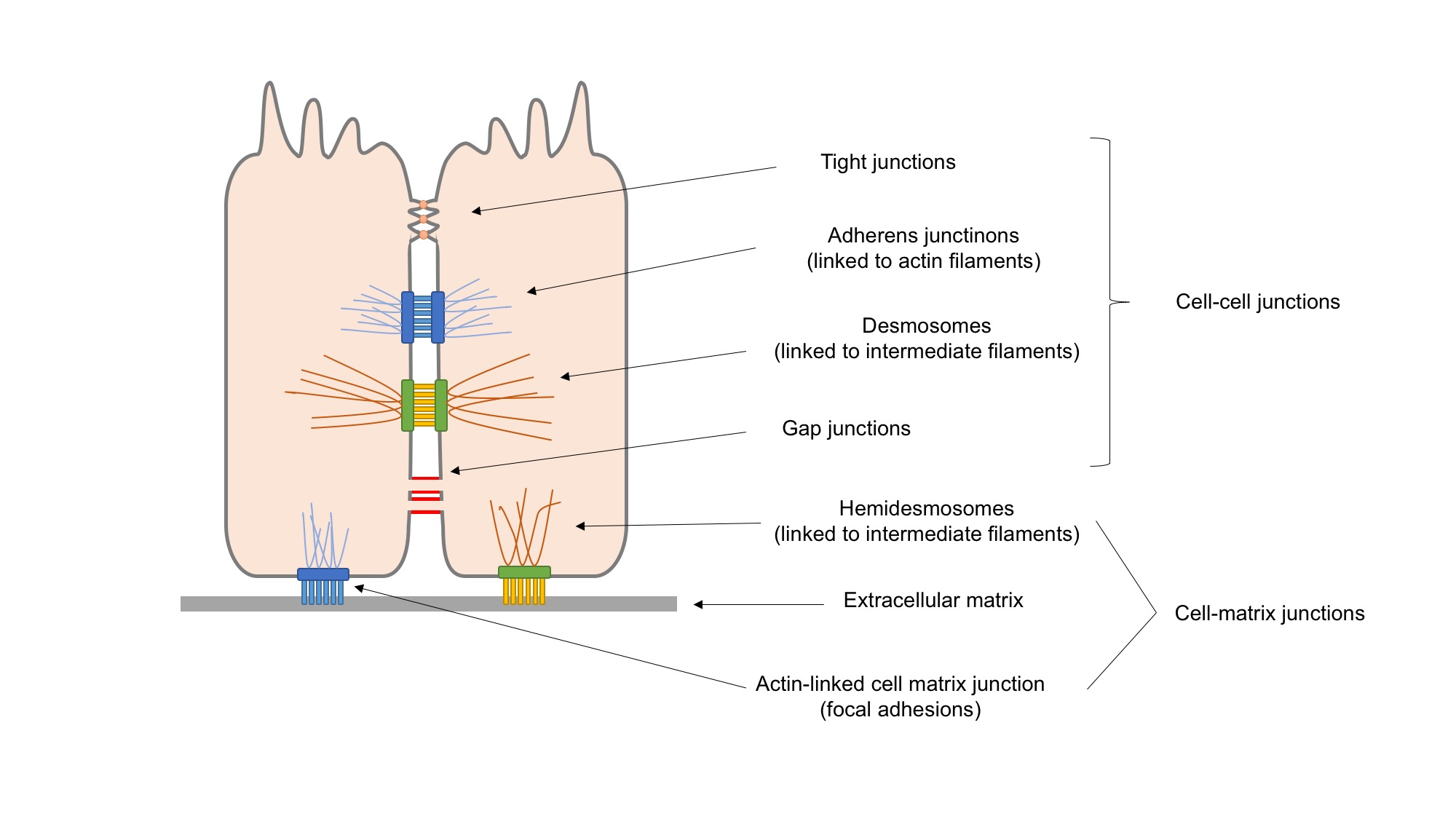
Desmosomes
A desmosome (; "binding body"), also known as a macula adherens (plural: maculae adherentes) (Latin for ''adhering spot''), is a cell structure specialized for cell-to-cell adhesion. A type of junctional complex, they are localized spot-like adhesions randomly arranged on the lateral sides of plasma membranes. Desmosomes are one of the stronger cell-to-cell adhesion types and are found in tissue that experience intense mechanical stress, such as cardiac muscle tissue, bladder tissue, gastrointestinal mucosa, and epithelia. Structure Desmosomes are composed of desmosome-intermediate filament complexes (DIFCs), a network of cadherin proteins, linker proteins and intermediate filaments. The DIFCs can be broken into three regions: the extracellular core region ("desmoglea"), the outer dense plaque (ODP), and the inner dense plaque (IDP). The extracellular core region, approximately 34 nm in length, contains desmoglein and desmocollin, which are in the cadherin family of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Adhesion
Cell adhesion is the process by which cells interact and attach to neighbouring cells through specialised molecules of the cell surface. This process can occur either through direct contact between cell surfaces such as Cell_junction, cell junctions or indirect interaction, where cells attach to surrounding extracellular matrix (ECM), a gel-like structure containing molecules released by cells into spaces between them. Cells adhesion occurs from the interactions between cell adhesion molecules, cell-adhesion molecules (CAMs), transmembrane proteins located on the cell surface. Cell adhesion links cells in different ways and can be involved in signal transduction for cells to detect and respond to changes in the surroundings. Other cellular processes regulated by cell adhesion include cell migration and tissue development in multicellular organisms. Alterations in cell adhesion can disrupt important cellular processes and lead to a variety of diseases, including cancer and arthrit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Junction
Cell junctions or junctional complexes are a class of cellular structures consisting of multiprotein complexes that provide contact or adhesion between neighboring Cell (biology), cells or between a cell and the extracellular matrix in animals. They also maintain the paracellular barrier of epithelia and control paracellular transport. Cell junctions are especially abundant in epithelial tissues. Combined with cell adhesion molecules and extracellular matrix, cell junctions help hold animal cells together. Cell junctions are also especially important in enabling communication between neighboring cells via specialized protein complexes called gap junction, communicating (gap) junctions. Cell junctions are also important in reducing stress placed upon cells. In plants, similar communication channels are known as plasmodesmata, and in fungus, fungi they are called septal pores. Types In vertebrates, there are three major types of cell junction: *Adherens junctions, desmosomes and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Desmoplakin
Desmoplakin is a protein in humans that is encoded by the ''DSP'' gene. Desmoplakin is a critical component of desmosome structures in cardiac muscle and epidermal cells, which function to maintain the structural integrity at adjacent cell contacts. In cardiac muscle, desmoplakin is localized to intercalated discs which mechanically couple cardiac cells to function in a coordinated syncytial structure. Mutations in desmoplakin have been shown to play a role in dilated cardiomyopathy and arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy, where it may present with acute myocardial injury; striate palmoplantar keratoderma, Carvajal syndrome and paraneoplastic pemphigus. Structure Desmoplakin exists as two predominant isoforms; the first, known as "DPII", has molecular weight 260.0 kDa (2272 amino acids) and the second, known as "DPI", has molecular weight 332.0 kDa (2871 amino acids). These isoforms are identical except for the shorter rod domain in DPII. DPI is the predomi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DSC2
Desmocollin-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''DSC2'' gene. Desmocollin-2 is a cadherin-type protein that functions to link adjacent cells together in specialized regions known as desmosomes. Desmocollin-2 is widely expressed, and is the only desmocollin isoform expressed in cardiac muscle, where it localizes to intercalated discs. Mutations in ''DSC2'' have been causally linked to arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy. Structure Desmocollin-2 is a calcium-dependent glycoprotein that is a member of the desmocollin subfamily of the cadherin superfamily. Three different posttranslational modifications (''N''-Glycosylations, ''O''-Mannosylations and disulfide bridges) were present in the extracellular domain of desmocollin-2. The desmocollin family members are arranged as closely linked genes on human chromosome 18q12.1. Human ''DSC2'' consists of greater than 32 kb of DNA and has 17 exons, with exon 16 being alternatively spliced and encoding dist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plakoglobin
Plakoglobin, also known as junction plakoglobin or gamma-catenin, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''JUP'' gene. Plakoglobin is a member of the catenin protein family and homologous to β-catenin. Plakoglobin is a cytoplasmic component of desmosomes and adherens junctions structures located within intercalated discs of cardiac muscle that function to anchor sarcomeres and join adjacent cells in cardiac muscle. Mutations in plakoglobin are associated with arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia. Structure Human plakoglobin is 81.7 kDa in molecular weight and 745 amino acids long. The ''JUP'' gene contains 13 exons spanning 17 kb on chromosome 17q21. Plakoglobin is a member of the catenin family, since it contains a distinct repeating amino acid motif called the armadillo repeat. Plakoglobin is highly similar to β-catenin; both have 12 armadillo repeats as well as N-terminal and C-terminal globular domains of unknown structure. Plakoglobin was originally ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pemphigus Vulgaris
Pemphigus vulgaris is a rare chronic blistering skin disease and the most common form of pemphigus. Pemphigus was derived from the Greek word ''pemphix'', meaning blister. It is classified as a type II hypersensitivity reaction in which antibody, antibodies are formed against desmosomes, components of the skin that function to keep certain layers of skin bound to each other. As desmosomes are attacked, the layers of skin separate and the clinical picture resembles a blister. These blisters are due to acantholysis, or breaking apart of intercellular connections through an autoantibody-mediated response. Over time the condition inevitably progresses without treatment: lesions increase in size and distribution throughout the body, behaving physiologically like a severe burn. Before the advent of modern treatments, mortality for the disease was close to 90%. Today, the mortality rate with treatment is in the range of 5% to 15%, after the introduction of corticosteroids as primary tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DSG3
Desmoglein-3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''DSG3'' gene. In the skin epidermis Desmoglein-3 is expressed in the basal lower layers of the epidermis, and dominates in terms of expression on mucosal surfaces compared to Desmoglein-1. Function Desmosomes are cell-cell junctions between epithelial, myocardial, and certain other cell types. Desmoglein 3 is a calcium-binding transmembrane glycoprotein component of desmosomes in vertebrate epithelial cells. Currently, four desmoglein subfamily members have been identified and all are members of the cadherin cell adhesion molecule superfamily. These desmoglein gene family members are located in a cluster on chromosome 18. This protein, along with Desmoglein-1, has been identified as the autoantigen of the autoimmune skin blistering disease pemphigus vulgaris. The mucosal dominant form of pemphigus vulgaris only involves antibodies against Desmoglein-3 and causes mucosal erosions, but no skin lesions. Desmoglein-3 serve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Desmosome
A desmosome (; "binding body"), also known as a macula adherens (plural: maculae adherentes) (Latin for ''adhering spot''), is a cell structure specialized for cell-to-cell adhesion. A type of junctional complex, they are localized spot-like adhesions randomly arranged on the lateral sides of plasma membranes. Desmosomes are one of the stronger cell-to-cell adhesion types and are found in tissue that experience intense mechanical stress, such as cardiac muscle tissue, bladder tissue, gastrointestinal mucosa, and epithelia. Structure Desmosomes are composed of desmosome-intermediate filament complexes (DIFCs), a network of cadherin proteins, linker proteins and intermediate filaments. The DIFCs can be broken into three regions: the extracellular core region ("desmoglea"), the outer dense plaque (ODP), and the inner dense plaque (IDP). The extracellular core region, approximately 34 nm in length, contains desmoglein and desmocollin, which are in the cadherin family of cel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
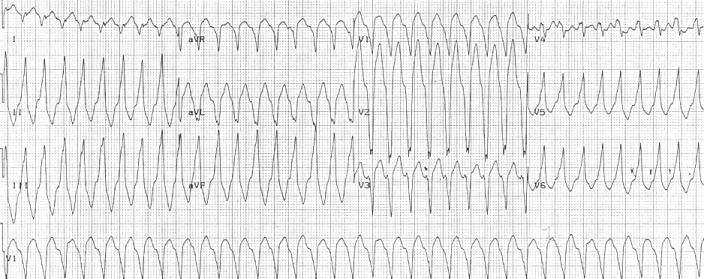
Arrhythmogenic Cardiomyopathy
Arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy (ACM) is an inherited heart disease. ACM is caused by genetic defects of parts of the cardiac muscle known as desmosomes, areas on the surface of muscle cells which link them together. The desmosomes are composed of several proteins, and many of those proteins can have harmful mutations. ARVC can also develop in intense endurance athletes in the absence of desmosomal abnormalities. Exercise-induced ARVC is possibly a result of excessive right ventricular wall stress during high intensity exercise. The disease is a type of non-ischemic cardiomyopathy that primarily involves the right ventricle, though cases of exclusive left ventricular disease have been reported. It is characterized by hypokinetic areas involving the free wall of the ventricle, with fibrofatty replacement of the myocardium, with associated arrhythmias often originating in the right ventricle. The nomenclature ARVD is currently thought to be inappropriate and misleading as ACM do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epithelium
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is a thin, continuous, protective layer of cells with little extracellular matrix. An example is the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. Epithelial ( mesothelial) tissues line the outer surfaces of many internal organs, the corresponding inner surfaces of body cavities, and the inner surfaces of blood vessels. Epithelial tissue is one of the four basic types of animal tissue, along with connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. These tissues also lack blood or lymph supply. The tissue is supplied by nerves. There are three principal shapes of epithelial cell: squamous (scaly), columnar, and cuboidal. These can be arranged in a singular layer of cells as simple epithelium, either simple squamous, simple columnar, or simple cuboidal, or in layers of two or more cells deep as stratified (layered), or ''compound'', either squamous, columnar or cuboidal. In some tissues, a layer of columnar cells may appear to be stratified d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intermediate Filament
Intermediate filaments (IFs) are cytoskeleton, cytoskeletal structural components found in the cells of vertebrates, and many invertebrates. Homologues of the IF protein have been noted in an invertebrate, the cephalochordate ''Branchiostoma''. Intermediate filaments are composed of a family of related proteins sharing common structural and sequence features. Initially designated 'intermediate' because their average diameter (10 Nanometre, nm) is between those of narrower microfilaments (actin) and wider myosin filaments found in muscle cells, the diameter of intermediate filaments is now commonly compared to actin microfilaments (7 nm) and microtubules (25 nm). Animal intermediate filaments are subcategorized into six types based on similarities in amino acid sequence and protein structure. Most types are cytoplasmic, but one type, Type V is a nuclear lamin. Unlike microtubules, IF distribution in cells shows no good correlation with the distribution of either ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |