|
Desmoplakin
Desmoplakin is a protein in humans that is encoded by the ''DSP'' gene. Desmoplakin is a critical component of desmosome structures in cardiac muscle and epidermal cells, which function to maintain the structural integrity at adjacent cell contacts. In cardiac muscle, desmoplakin is localized to intercalated discs which mechanically couple cardiac cells to function in a coordinated syncytial structure. Mutations in desmoplakin have been shown to play a role in dilated cardiomyopathy and arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy, where it may present with acute myocardial injury; striate palmoplantar keratoderma, Carvajal syndrome and paraneoplastic pemphigus. Structure Desmoplakin exists as two predominant isoforms; the first, known as "DPII", has molecular weight 260.0 kDa (2272 amino acids) and the second, known as "DPI", has molecular weight 332.0 kDa (2871 amino acids). These isoforms are identical except for the shorter rod domain in DPII. DPI is the predomi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Desmosome - 2
A desmosome (; "binding body"), also known as a macula adherens (plural: maculae adherentes) (Latin for ''adhering spot''), is a cell structure specialized for cell-to-cell adhesion. A type of junctional complex, they are localized spot-like adhesions randomly arranged on the lateral sides of plasma membranes. Desmosomes are one of the stronger cell-to-cell adhesion types and are found in tissue that experience intense mechanical stress, such as cardiac muscle tissue, bladder tissue, gastrointestinal mucosa, and epithelia. Structure Desmosomes are composed of desmosome-intermediate filament complexes (DIFCs), a network of cadherin proteins, linker proteins and intermediate filaments. The DIFCs can be broken into three regions: the extracellular core region ("desmoglea"), the outer dense plaque (ODP), and the inner dense plaque (IDP). The extracellular core region, approximately 34 nm in length, contains desmoglein and desmocollin, which are in the cadherin family of cell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
JUP (gene)
Plakoglobin, also known as junction plakoglobin or gamma-catenin, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''JUP'' gene. Plakoglobin is a member of the catenin protein family and homologous to β-catenin. Plakoglobin is a cytoplasmic component of desmosomes and adherens junctions structures located within intercalated discs of cardiac muscle that function to anchor sarcomeres and join adjacent cells in cardiac muscle. Mutations in plakoglobin are associated with arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia. Structure Human plakoglobin is 81.7 kDa in molecular weight and 745 amino acids long. The ''JUP'' gene contains 13 exons spanning 17 kb on chromosome 17q21. Plakoglobin is a member of the catenin family, since it contains a distinct repeating amino acid motif called the armadillo repeat. Plakoglobin is highly similar to β-catenin; both have 12 armadillo repeats as well as N-terminal and C-terminal globular domains of unknown structure. Plakoglobin was originally identifi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
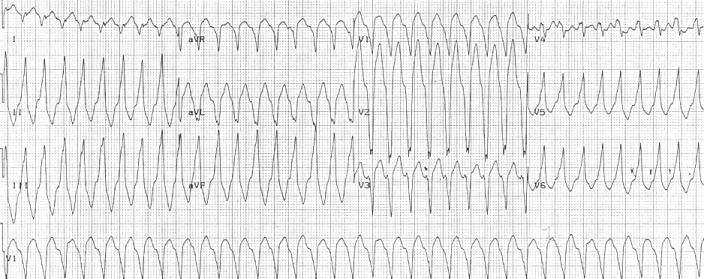
Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy
Arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy (ACM) is an inherited heart disease. ACM is caused by genetic defects of parts of the cardiac muscle known as desmosomes, areas on the surface of muscle cells which link them together. The desmosomes are composed of several proteins, and many of those proteins can have harmful mutations. ARVC can also develop in intense endurance training, endurance athletes in the absence of desmosomal abnormalities. Exercise-induced ARVC is possibly a result of excessive right ventricular wall stress during high intensity exercise. The disease is a type of Ischemia, non-ischemic cardiomyopathy that primarily involves the Ventricle (heart), right ventricle, though cases of exclusive left ventricular disease have been reported. It is characterized by hypokinesia, hypokinetic areas involving the free wall of the ventricle, with fibrofatty replacement of the myocardium, with associated Heart arrhythmia, arrhythmias often originating in the right ventricle. The nomenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paraneoplastic Pemphigus
Paraneoplastic pemphigus (PNP) is an autoimmune disorder stemming from an underlying tumor. It is hypothesized that antigens associated with the tumor trigger an immune response resulting in blistering of the skin and mucous membranes. While patients with malignant and benign tumors are both at risk, malignancy is associated with high mortality rates (near 90%). Current treatment focuses on general wound healing and administering corticosteroids, which has not demonstrated a high success rate. Recent research developments aim to treat the underlying tumor in order to alleviate the symptoms of PNP. Signs and symptoms While the presence of lesions is the denominator among patients with PNP, the characteristics of the lesions differ. The five clinical presentations of lesions associated with PNP include: * "Pemphigus-like": Flaccid blister (discrete), crusts over the raw exuding skin lesions * "Pemphigoid-like": Tense blister(s) on brick red erythema * "Erythema multiforme-like": Sev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Desmin
Desmin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''DES'' gene. Desmin is a muscle-specific, type III intermediate filament that integrates the sarcolemma, Z disk, and nuclear membrane in sarcomeres and regulates sarcomere architecture. Structure Desmin is a 53.5 kD protein composed of 470 amino acids, encoded by the human ''DES'' gene located on the long arm of chromosome 2. There are three major domains to the desmin protein: a conserved alpha helix rod, a variable non alpha helix head, and a carboxy-terminal tail. Desmin, as all intermediate filaments, shows no polarity when assembled. The rod domain consists of 308 amino acids with parallel alpha helical coiled coil dimers and three linkers to disrupt it. The rod domain connects to the head domain. The head domain 84 amino acids with many arginine, serine, and aromatic residues is important in filament assembly and dimer-dimer interactions. The tail domain is responsible for the integration of filaments and intera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intermediate Filament
Intermediate filaments (IFs) are cytoskeleton, cytoskeletal structural components found in the cells of vertebrates, and many invertebrates. Homologues of the IF protein have been noted in an invertebrate, the cephalochordate ''Branchiostoma''. Intermediate filaments are composed of a family of related proteins sharing common structural and sequence features. Initially designated 'intermediate' because their average diameter (10 Nanometre, nm) is between those of narrower microfilaments (actin) and wider myosin filaments found in muscle cells, the diameter of intermediate filaments is now commonly compared to actin microfilaments (7 nm) and microtubules (25 nm). Animal intermediate filaments are subcategorized into six types based on similarities in amino acid sequence and protein structure. Most types are cytoplasmic, but one type, Type V is a nuclear lamin. Unlike microtubules, IF distribution in cells shows no good correlation with the distribution of either ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Striate Palmoplantar Keratoderma
Palmoplantar keratodermas are a heterogeneous group of skin disorders characterized by abnormal thickening (scleroderma) of the stratum corneum of the palms and soles. Autosomal recessive, dominant, X-linked, and acquired forms have all been described in medical literature. Types Clinically, three distinct patterns of palmoplantar keratoderma may be identified: diffuse, focal, and punctate. Diffuse Diffuse palmoplantar keratoderma is a type of palmoplantar keratoderma that is characterized by an even, thick, symmetric hyperkeratosis over the whole of the palm and sole, usually evident at birth or in the first few months of life. Restated, diffuse palmoplantar keratoderma is an autosomal dominant disorder in which hyperkeratosis is confined to the palms and soles. The two major types can have a similar clinical appearance: * ''Diffuse epidermolytic palmoplantar keratoderma'' (also known as "Palmoplantar keratoderma cum degeneratione granulosa Vörner", "Vörner's epidermo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intercalated Disc
Intercalated discs or lines of Eberth are microscopic identifying features of cardiac muscle. Cardiac muscle consists of individual heart muscle cells (cardiomyocytes) connected by intercalated discs to work as a single functional Syncytium#Cardiac muscle, syncytium. By contrast, skeletal muscle consists of multinucleated muscle fibers and exhibits no intercalated discs. Intercalated discs support synchronized contraction of cardiac tissue in a wave-like pattern so that the heart can work like a pump. They occur at the Z line of the sarcomere and can be visualized easily when observing a longitudinal section of the tissue. Structure Intercalated discs are complex structures that connect adjacent cardiac muscle cells. The three types of cell junction recognised as making up an intercalated disc are desmosomes, Fascia adherens, fascia adherens junctions, and gap junctions. * Fascia adherens are anchoring sites for actin, and connect to the closest sarcomere. * Desmosomes prevent se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SH3 Domain
The SRC Homology 3 Domain (or SH3 domain) is a small protein domain of about 60 amino acid residues. Initially, SH3 was described as a conserved sequence in the viral adaptor protein v-Crk. This domain is also present in the molecules of phospholipase and several cytoplasmic tyrosine kinases such as Abl and Src. It has also been identified in several other protein families such as: PI3 Kinase, Ras GTPase-activating protein, CDC24 and cdc25. SH3 domains are found in proteins of signaling pathways regulating the cytoskeleton, the Ras protein, and the Src kinase and many others. The SH3 proteins interact with adaptor proteins and tyrosine kinases. Interacting with tyrosine kinases, SH3 proteins usually bind far away from the active site. Approximately 300 SH3 domains are found in proteins encoded in the human genome. In addition to that, the SH3 domain was responsible for controlling protein-protein interactions in the signal transduction pathways and regulating the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiomyocyte
Cardiac muscle (also called heart muscle or myocardium) is one of three types of vertebrate muscle tissues, the others being skeletal muscle and smooth muscle. It is an involuntary, striated muscle that constitutes the main tissue of the wall of the heart. The cardiac muscle (myocardium) forms a thick middle layer between the outer layer of the heart wall (the pericardium) and the inner layer (the endocardium), with blood supplied via the coronary circulation. It is composed of individual cardiac muscle cells joined by intercalated discs, and encased by collagen fibers and other substances that form the extracellular matrix. Cardiac muscle contracts in a similar manner to skeletal muscle, although with some important differences. Electrical stimulation in the form of a cardiac action potential triggers the release of calcium from the cell's internal calcium store, the sarcoplasmic reticulum. The rise in calcium causes the cell's myofilaments to slide past each other in a p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
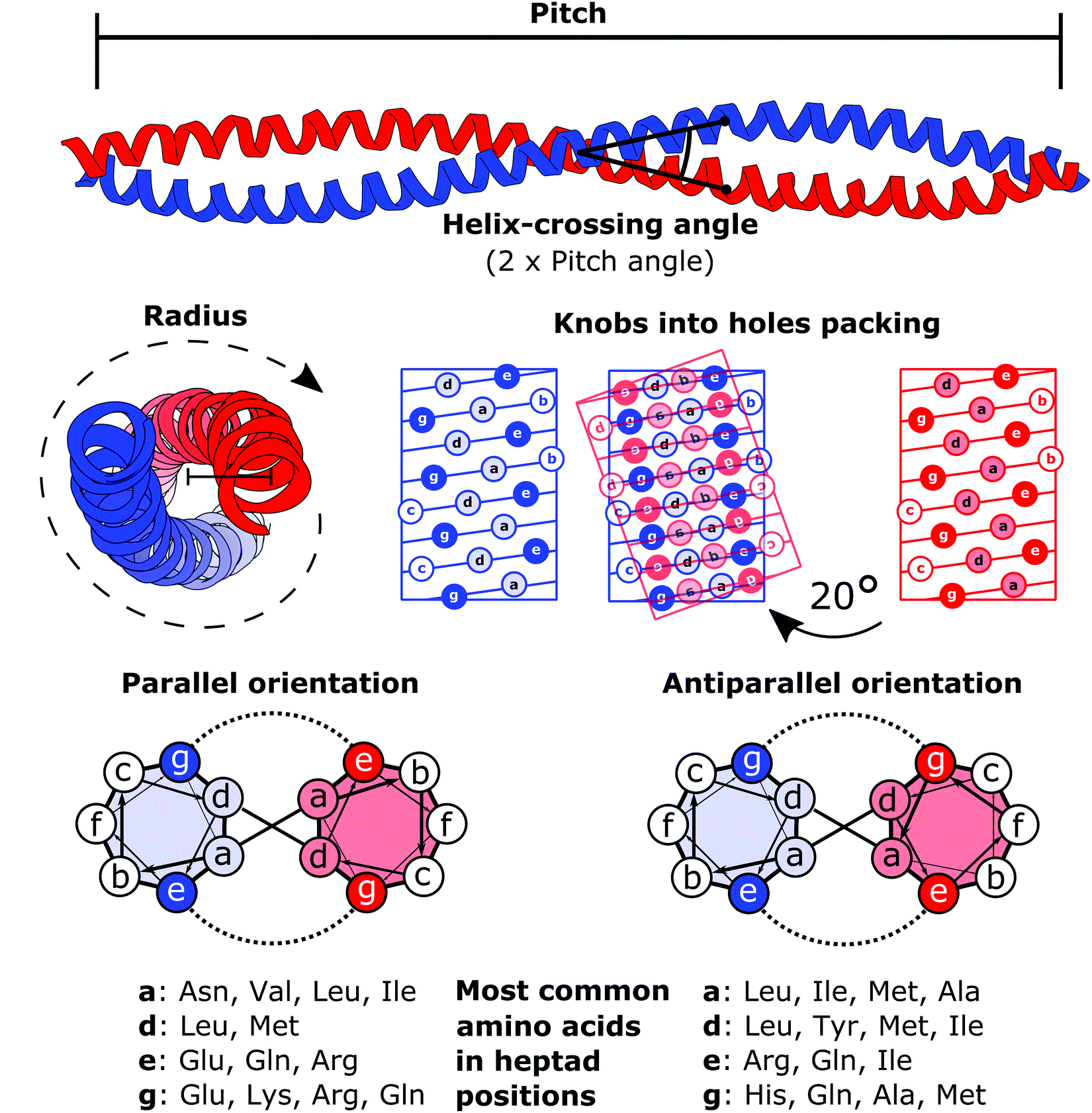
Coiled-coil
A coiled coil is a structural motif in proteins in which two to seven alpha-helices are coiled together like the strands of a rope. ( Dimers and trimers are the most common types.) They have been found in roughly 5-10% of proteins and have a variety of functions. They are one of the most widespread motifs found in protein-protein interactions. To aid protein study, several tools have been developed to predict coiled-coils in protein structures. Many coiled coil-type proteins are involved in important biological functions, such as the regulation of gene expression — e.g., transcription factors. Notable examples are the oncoproteins c-Fos and c-Jun, as well as the muscle protein tropomyosin. Discovery The possibility of coiled coils for α-keratin was initially somewhat controversial. Linus Pauling and Francis Crick independently came to the conclusion that this was possible at about the same time. In the summer of 1952, Pauling visited the laboratory in England where Cric ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |