|
Toxication
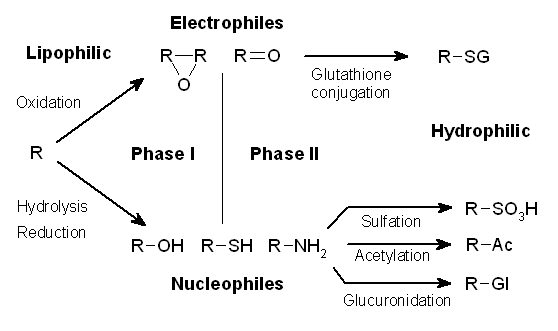
Toxication, toxification or toxicity exaltation is the conversion of a chemical compound into a more toxic form in living organisms or in substrates such as soil or water. The conversion can be caused by enzyme, enzymatic metabolism in the organisms, as well as by abiotic chemical reactions. While the parent drug is usually less active, both the parent drug and its metabolite can be chemically active and cause toxicity, leading to mutagenesis, teratogenesis, and carcinogenesis. Different classes of enzymes, such as P450 monooxygenases, epoxide hydrolase, or acetyltransferases can catalyze the process in the cell, mostly in the liver. Parent non-toxic chemicals are generally referred to as ''protoxins''. While toxication is generally undesirable, in certain cases it is required for the ''in vivo'' conversion of a prodrug to a metabolite with desired pharmacological or toxicological activity. Codeine is an example of a prodrug, metabolized in the body to the active compounds morphine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water
Water is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is a transparent, tasteless, odorless, and Color of water, nearly colorless chemical substance. It is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living organisms (in which it acts as a solvent). It is vital for all known forms of life, despite not providing food energy or organic micronutrients. Its chemical formula, , indicates that each of its molecules contains one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms, connected by covalent bonds. The hydrogen atoms are attached to the oxygen atom at an angle of 104.45°. In liquid form, is also called "water" at standard temperature and pressure. Because Earth's environment is relatively close to water's triple point, water exists on Earth as a solid, a liquid, and a gas. It forms precipitation in the form of rain and aerosols in the form of fog. Clouds consist of suspended droplets of water and ice, its solid state. When finely divided, crystalline ice ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methanol
Methanol (also called methyl alcohol and wood spirit, amongst other names) is an organic chemical compound and the simplest aliphatic Alcohol (chemistry), alcohol, with the chemical formula (a methyl group linked to a hydroxyl group, often abbreviated as MeOH). It is a light, Volatility (chemistry), volatile, colorless and flammable liquid with a distinctive alcoholic odor similar to that of ethanol (potable alcohol), but is more acutely toxic than the latter. Methanol acquired the name wood alcohol because it was once produced through destructive distillation of wood. Today, methanol is mainly produced industrially by hydrogenation of carbon monoxide. Methanol consists of a methyl group linked to a polar hydroxyl group. With more than 20 million tons produced annually, it is used as a Precursor (chemistry), precursor to other commodity chemicals, including formaldehyde, acetic acid, methyl tert-butyl ether, methyl ''tert''-butyl ether, methyl benzoate, anisole, peroxyacids, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drug Metabolism
Drug metabolism is the metabolic breakdown of drugs by living organisms, usually through specialized enzymatic systems. More generally, xenobiotic metabolism (from the Greek xenos "stranger" and biotic "related to living beings") is the set of metabolic pathways that modify the chemical structure of xenobiotics, which are compounds foreign to an organism's normal biochemistry, such as any drug or poison. These pathways are a form of biotransformation present in all major groups of organisms and are considered to be of ancient origin. These reactions often act to detoxify poisonous compounds (although in some cases the intermediates in xenobiotic metabolism can themselves cause toxic effects). The study of drug metabolism is the object of pharmacokinetics. Metabolism is one of the stages (see ADME) of the drug's transit through the body that involves the breakdown of the drug so that it can be excreted by the body. The metabolism of pharmaceutical drugs is an important as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Codeine
Codeine is an opiate and prodrug of morphine mainly used to treat pain, coughing, and diarrhea. It is also commonly used as a recreational drug. It is found naturally in the sap of the opium poppy, ''Papaver somniferum''. It is typically used to treat mild to moderate degrees of pain. Greater benefit may occur when combined with paracetamol (acetaminophen) or a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) such as aspirin or ibuprofen. Evidence does not support its use for acute cough suppression in children. In Europe, it is not recommended as a cough medicine for those under 12 years of age. It is generally taken by mouth. It typically starts working after half an hour, with maximum effect at two hours. Its effects last for about four to six hours. Codeine exhibits abuse potential similar to other opioid medications, including a risk of addiction and overdose. Common side effects include nausea, vomiting, constipation, itchiness, lightheadedness, and drowsiness. Serious ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toxicity
Toxicity is the degree to which a chemical substance or a particular mixture of substances can damage an organism. Toxicity can refer to the effect on a whole organism, such as an animal, bacteria, bacterium, or plant, as well as the effect on a substructure of the organism, such as a cell (biology), cell (cytotoxicity) or an organ such as the liver (hepatotoxicity). Sometimes the word is more or less synonymous with poison#Poisoning, poisoning in everyday usage. A central concept of toxicology is that the effects of a toxicant are Dose (biochemistry), dose-dependent; even water can lead to water intoxication when taken in too high a dose, whereas for even a very toxic substance such as snake venom there is a dose below which there is no detectable toxic effect. Toxicity is species-specific, making cross-species analysis problematic. Newer paradigms and metrics are evolving to bypass animal testing, while maintaining the concept of toxicity endpoints. Etymology In Ancient G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Compound
A chemical compound is a chemical substance composed of many identical molecules (or molecular entities) containing atoms from more than one chemical element held together by chemical bonds. A molecule consisting of atoms of only one element is therefore not a compound. A compound can be transformed into a different substance by a chemical reaction, which may involve interactions with other substances. In this process, bonds between atoms may be broken or new bonds formed or both. There are four major types of compounds, distinguished by how the constituent atoms are bonded together. Molecular compounds are held together by covalent bonds; ionic compounds are held together by ionic bonds; intermetallic compounds are held together by metallic bonds; coordination complexes are held together by coordinate covalent bonds. Non-stoichiometric compounds form a disputed marginal case. A chemical formula specifies the number of atoms of each element in a compound molecule, usin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Troleandomycin
Troleandomycin (TAO for short) is a macrolide antibiotic. It was sold in Italy (branded Triocetin) and Turkey (branded Tekmisin). It is no longer sold in Italy as of 2018. The drug's mode of action is to bind to the ribosome, specifically in the tunnel through which the newly formed peptide egresses, thereby halting protein synthesis. Troleandomycin is a CYP3A4 inhibitor that may cause drug interaction In pharmaceutical sciences, drug interactions occur when a drug's mechanism of action is affected by the concomitant administration of substances such as foods, beverages, or other drugs. A popular example of drug–food interaction is the effect ...s. References CYP3A4 inhibitors Macrolide antibiotics Epoxides Spiro compounds Acetate esters {{antibiotic-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
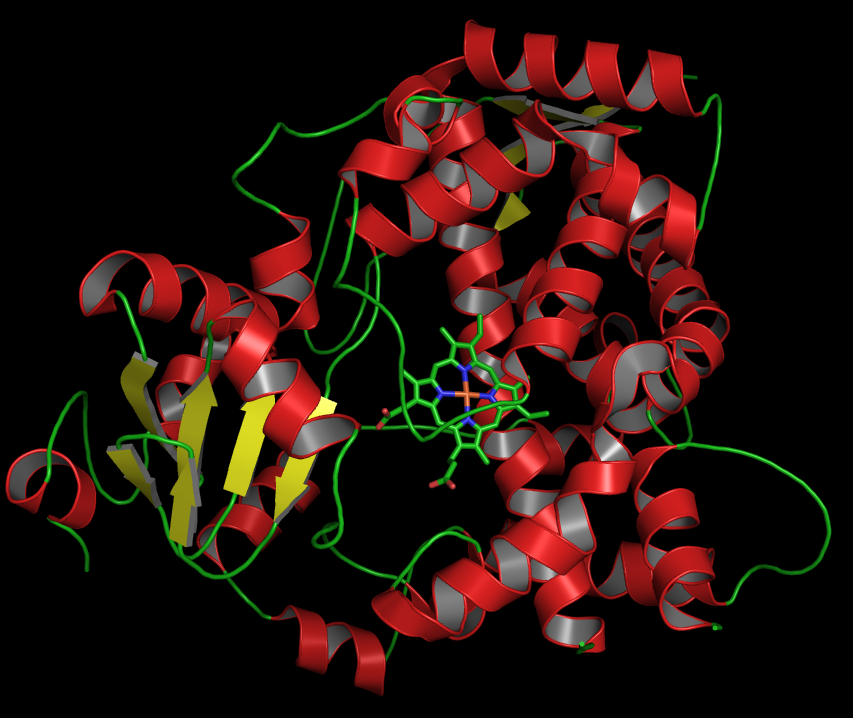
CYP3A
Cytochrome P450, family 3, subfamily A, also known as CYP3A, is a human gene locus. A homologous locus is found in mice. These genes encode monooxygenases which catalyze many reactions involved in the synthesis of cholesterol, steroids and other lipids as well as drug metabolism. The CYP3A locus includes all the known members of the 3A subfamily of the cytochrome P450 superfamily of genes. The CYP3A cluster consists of four genes: * CYP3A4, * CYP3A5, * CYP3A7, and * CYP3A43. The region also contains four pseudogenes: * , * , * , and * . as well as several extra exons which may or may not be included in transcripts produced from this region. Previously another CYP3A member, CYP3A3, was thought to exist; however, it is now thought that this sequence represents a transcript variant of CYP3A4. Structure Structurally, the key to the CYP3A enzyme’s large range of activity is the heme cofactor and the P450 protein fold, an oxidation reaction through molecular oxygen and NADPH. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hepatotoxicity
Hepatotoxicity (from ''hepatic toxicity'') implies chemical-driven liver damage. Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) is a cause of acute and chronic liver disease caused specifically by medications and the most common reason for a drug to be withdrawn from the market after approval. The liver plays a central role in transforming and clearing chemicals and is susceptible to the toxicity from these agents. Certain medicinal agents, when taken in overdoses (e.g. acetaminophen, paracetamol) and sometimes even when introduced within therapeutic ranges (e.g. halothane), may injure the organ. Other chemical agents, such as those used in laboratories and industries, natural chemicals (e.g., alpha-amanitin), and herbal remedies (two prominent examples being kava, though the causal mechanism is unknown, and comfrey, through pyrrolizidine alkaloid content) can also induce hepatotoxicity. Chemicals that cause liver injury are called hepatotoxins. More than 900 drugs have been implicated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flucloxacillin
Flucloxacillin, also known as floxacillin, is an antibiotic used to treat skin infections, external ear infections, infections of leg ulcers, diabetic foot infections, and infection of bone. It may be used together with other medications to treat pneumonia, and endocarditis. It may also be used prior to surgery to prevent ''Staphylococcus'' infections. It is not effective against methicillin-resistant ''Staphylococcus aureus'' (MRSA). It is taken by mouth or given by injection into a vein or muscle. Common side effects include an upset stomach. Other side effects may include muscle or joint pains, shortness of breath, and liver problems. It appears to be safe during pregnancy and breastfeeding. It should not be used in those who are allergic to penicillin. It is a narrow-spectrum beta-lactam antibiotic of the penicillin class. It is similar in effect to cloxacillin and dicloxacillin, being active against penicillinase forming bacteria. Flucloxacillin was patented in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
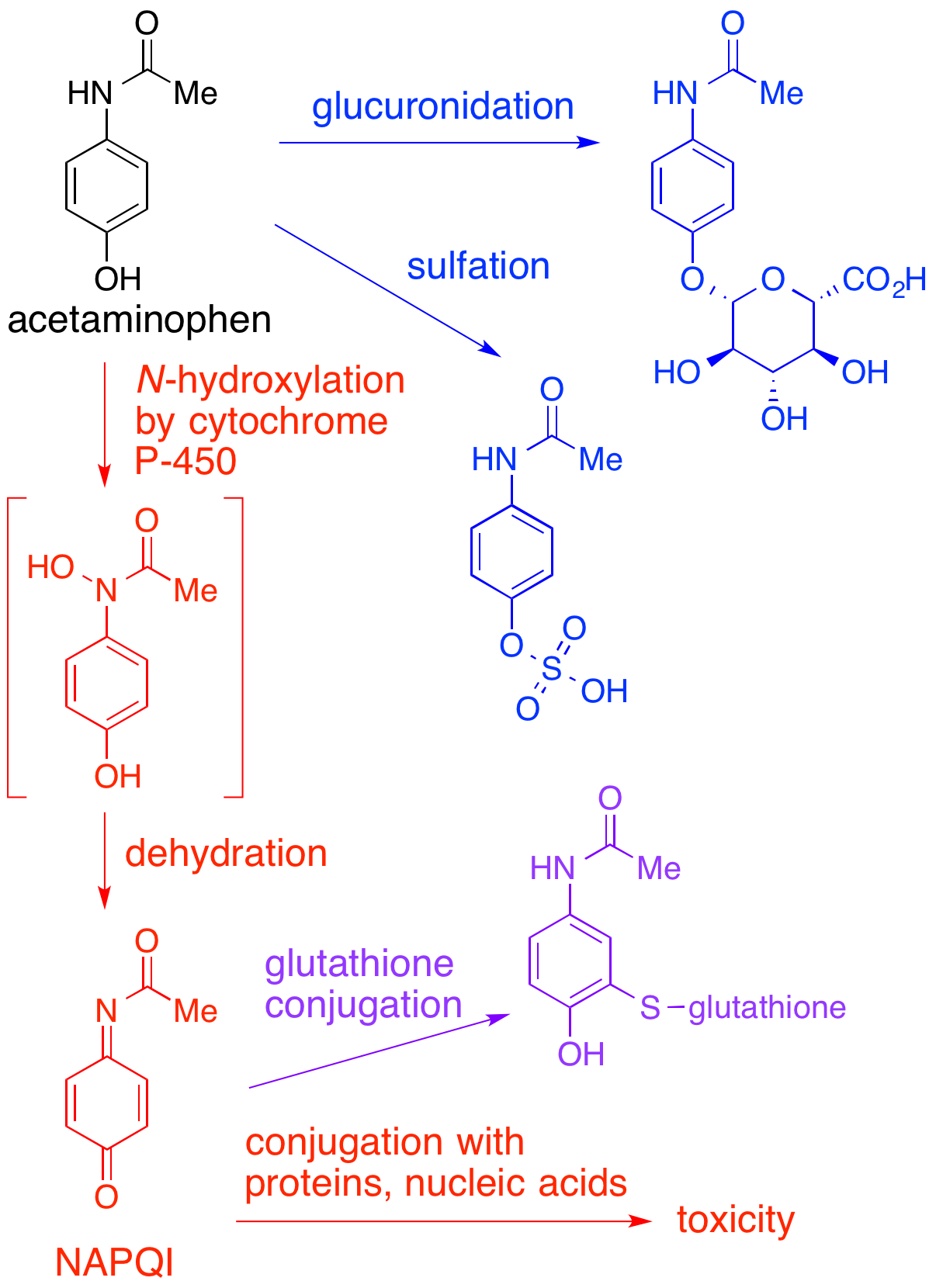
NAPQI
NAPQI, also known as NAPBQI or ''N''-acetyl-''p''-benzoquinone imine, is a toxic byproduct produced during the xenobiotic metabolism of the analgesic paracetamol (acetaminophen). It is normally produced only in small amounts, and then almost immediately detoxified in the liver. However, under some conditions in which NAPQI is not effectively detoxified (usually in the case of paracetamol overdose), it causes severe damage to the liver. This becomes apparent 3–4 days after ingestion and may result in death from fulminant liver failure several days after the overdose. Metabolism In adults, the primary metabolic pathway for paracetamol is glucuronidation. This yields a relatively non-toxic metabolite, which is excreted into bile and passed out of the body. A small amount of the drug is metabolized via the cytochrome P-450 pathway (to be specific, CYP3A4 and CYP2E1) into NAPQI, which is extremely toxic to liver tissue, as well as being a strong biochemical oxidizer. In an av ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Troglitazone
Troglitazone is an antidiabetic and anti-inflammatory drug, and a member of the drug class of the thiazolidinediones. It was prescribed for people with diabetes mellitus type 2. It was patented in 1983 and approved for medical use in 1997. It was subsequently withdrawn. Mechanism of action Troglitazone, like the other thiazolidinediones ( pioglitazone and rosiglitazone), works by activating peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs). Troglitazone is a ligand to both PPARα and – more strongly – PPARγ. Troglitazone also contains an α-Tocopherol moiety, potentially giving it vitamin E-like activity in addition to its PPAR activation. It has been shown to reduce inflammation. Troglitazone use was associated with a decrease of nuclear factor kappa-B (NF-κB) and a concomitant increase in its inhibitor (IκB). NFκB is an important cellular transcription regulator for the immune response. History Troglitazone was developed by Daiichi Sankyo (Japan). In t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |