|
Thomson MO5
The Thomson MO5 is a home computer introduced in France in June 1984 to compete against systems such as the ZX Spectrum and Commodore 64. It had a release price of 2390 FF. At the same time, Thomson also released the up-market Thomson TO7/70 machine. The MO5 was not sold in vast quantities outside France and was largely discontinued in favour of the improved Thomson MO6 in 1986. MO5s were used as educational tools in French schools for a period (see Computing for All, a French government plan to introduce computers to the country's pupils), and could be used as a "''nano-machine"'' terminal for the ''"Nanoréseau"'' educational network. The computer boots directly to the built-in Microsoft BASIC interpreter ( MO5 Basic 1.0). Specifications The Thomson MO5 runs on a Motorola 6809E processor clocked at 1 MHz and features 48 KB of RAM (16 KB used as video memory, 32 KB as free user RAM) and 16 KB of ROM (4 KB for the monitor and 12 KB f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
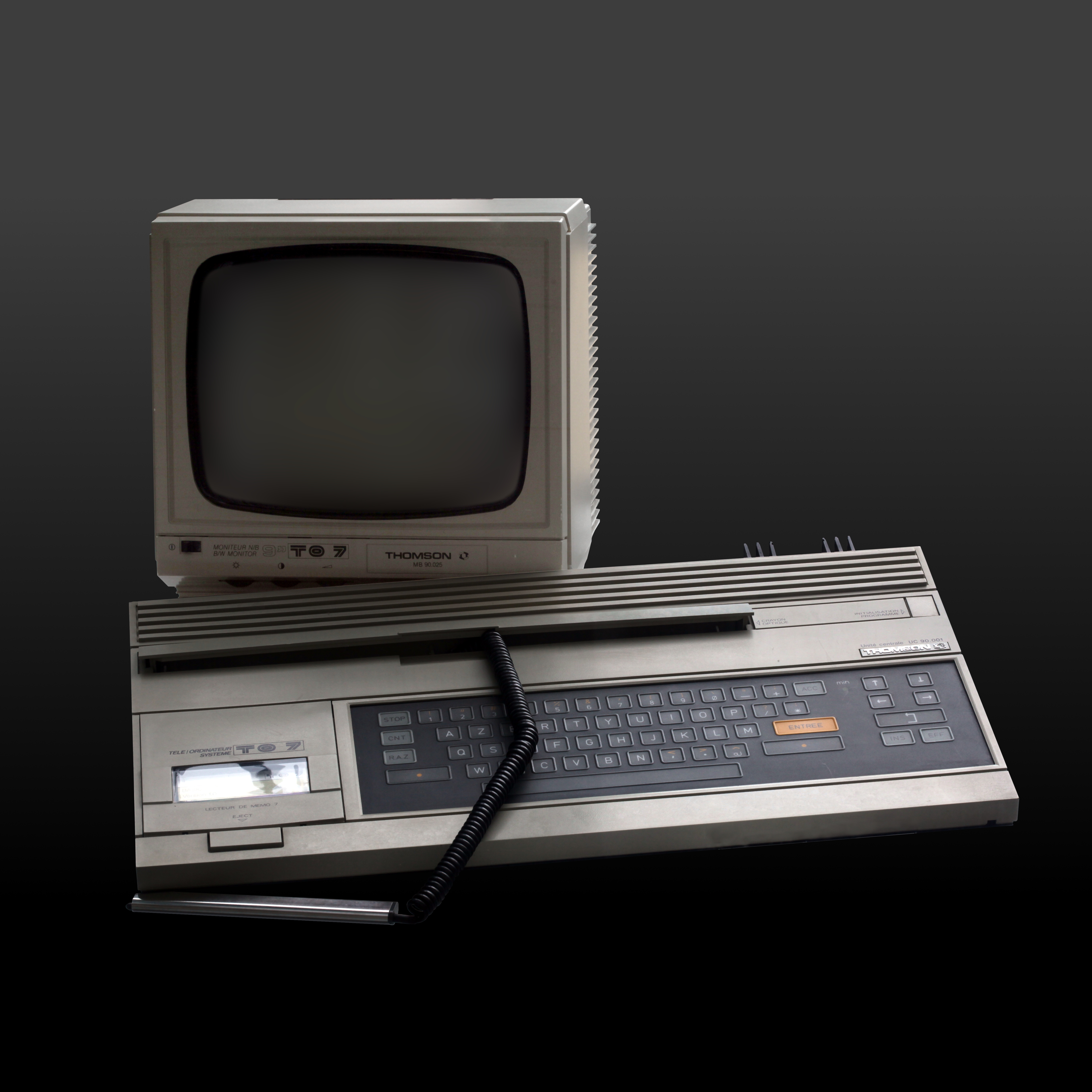
Thomson TO7/70
The Thomson TO7, also called ''Thomson 9000'' is a home computer introduced by Thomson SA in November 1982, with an original retail price of 3750 FF. By 1983 over 40000 units were produced. About 84 games were released for the TO7. The TO7 is built around a 1 MHz Motorola 6809 processor. ROM cartridges, designed as ''MEMO7'', can be introduced through a memory bay. The user interface uses Microsoft BASIC, included in the kit cartridge. The keyboard features a plastic membrane, and further user input is obtained through a lightpen. Cooling is provided by a rear radiator. A standard television can serve as a monitor using a RGB SCART (Peritel) connector, with a resolution of 320x200 (with 2 colors for each 8 x 1 pixels). The TO7 prototype, called Thomson T9000, was developed in 1980. The differences regarding the production model are a different startup menu and buggier BIOS. Specifications The Thomson TO7 runs on a Motorola 6809 processor clocked at 1 MHz and featu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomson SA
Vantiva SA (formerly Technicolor SA, Thomson SARL, Thomson SA, and Thomson Multimedia) is a French multinational corporation that provides technology products and services for the communication, media and entertainment industries. Headquartered in Paris, Vantiva also maintains offices in Rennes (France), Beijing (China), Seoul (South Korea), Chennai (India), Edegem (a suburb of Antwerp, Belgium), Norcross (U.S), and Manaus (Brazil). The company was originally known as Thomas Multimedia and rebranded as Technicolor SA on January 27, 2010, adopting the name of its U.S. film technology subsidiary. In September 2022, Technicolor Creative Studios was spun off as a separate entity (now known as Technicolor Group), and the remaining company rebranded as Vantiva. Vantiva is organized into three divisions: * Connected Home: Manufactures broadband modems and Android TV set-top boxes * HomeSight: Offers remote care and monitoring services in clients’ homes. * Smart Spaces: Provid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
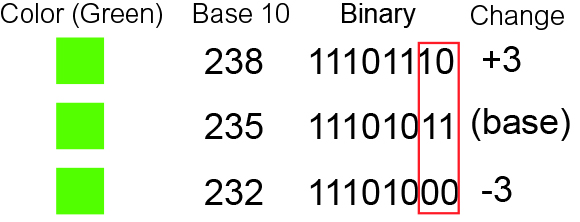
Bit Numbering
In computing, bit numbering is the convention used to identify the bit positions in a binary number. Bit significance and indexing In computing, the least significant bit (LSb) is the bit position in a binary integer representing the lowest-order place of the integer. Similarly, the most significant bit (MSb) represents the highest-order place of the binary integer. The LSb is sometimes referred to as the ''low-order bit''. Due to the convention in positional notation of writing less significant digits further to the right, the LSb also might be referred to as the ''right-most bit''. The MSb is similarly referred to as the ''high-order bit'' or ''left-most bit''. In both cases, the LSb and MSb correlate directly to the least significant digit and most significant digit of a decimal integer. Bit indexing correlates to the positional notation of the value in base 2. For this reason, bit index is not affected by how the value is stored on the device, such as the value's byte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AZERTY
AZERTY ( ) is a specific layout for the characters of the Latin alphabet on typewriter keys and computer keyboards. The layout takes its name from the first six letters to appear on the first row of alphabetical keys; that is, ( ). Like other European keyboard layouts, it is modelled on the English-language QWERTY layout. It is used in France and Belgium, though both countries have their own national variation on the layout. The competing layouts devised for French (e.g. the 1907 ZHJAY layout, Claude Marsan's 1976 layout, the 2002 Dvorak-fr, and the 2005 BÉPO layout) have obtained only limited recognition, although the latter has been included in the 2019 French keyboard layout standard. History The AZERTY layout appeared in France in the last decade of the 19th century as a variation on American QWERTY typewriters. Its exact origin is unknown. It was more successful than its contemporaries (e.g. the French ZHJAYS layout created by Albert Navarre in the early 20th cen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Modulator
Signal modulation is the process of varying one or more properties of a periodic waveform in electronics and telecommunication for the purpose of transmitting information. The process encodes information in form of the modulation or message signal onto a carrier signal to be transmitted. For example, the message signal might be an audio signal representing sound from a microphone, a video signal representing moving images from a video camera, or a digital signal representing a sequence of binary digits, a bitstream from a computer. This carrier wave usually has a much higher frequency than the message signal does. This is because it is impractical to transmit signals with low frequencies. Generally, receiving a radio wave requires a radio antenna with a length that is one-fourth of the wavelength of the transmitted wave. For low frequency radio waves, wavelength is on the scale of kilometers and building such a large antenna is not practical. Another purpose of modulation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Game Port
The game port is a device port that was found on IBM PC compatible and other computer systems throughout the 1980s and 1990s. It was the traditional connector for joystick input, and occasionally MIDI devices, until made obsolete by USB in the late 1990s. Originally located on a dedicated Game Control Adapter expansion card, the game port was later integrated with PC sound cards, and still later on the PC's motherboard. During the transition to USB, many input devices used the game port and a USB adapter dongle was included for systems without a game port. History Pre-IBM game ports At the time IBM was developing its game port, there was no industry standard for controller ports, although the Atari joystick port was close. It was introduced in 1977 with the Atari Video Computer System, and was later used on the VIC-20 (1980), Commodore 64 (1982), and Amstrad's PC1512 (1986). In contrast with the IBM design, the Atari port was primarily designed for digital inputs (includ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
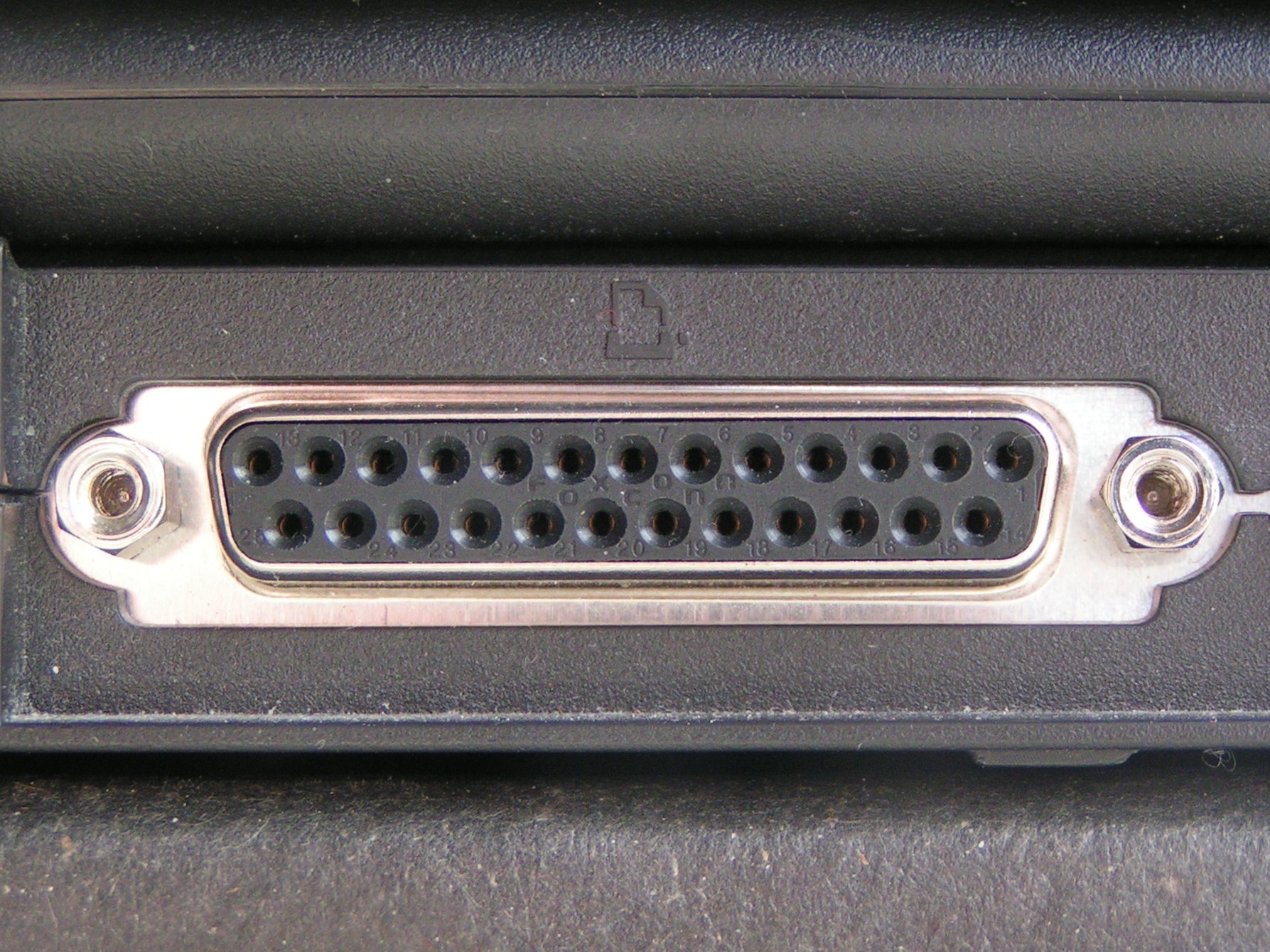
Parallel Port
In computing, a parallel port is a type of interface found on early computers ( personal and otherwise) for connecting peripherals. The name refers to the way the data is sent; parallel ports send multiple bits of data at once (parallel communication), as opposed to serial communication, in which bits are sent one at a time. To do this, parallel ports require multiple data lines in their cables and port connectors and tend to be larger than contemporary serial ports, which only require one data line. There are many types of parallel ports, but the term has become most closely associated with the printer port or Centronics port found on most personal computers from the 1970s through the 2000s. It was an industry ''de facto'' standard for many years, and was finally standardized as IEEE 1284 in the late 1990s, which defined the Enhanced Parallel Port (EPP) and Extended Capability Port (ECP) bi-directional versions. Today, the parallel port interface is virtually non ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
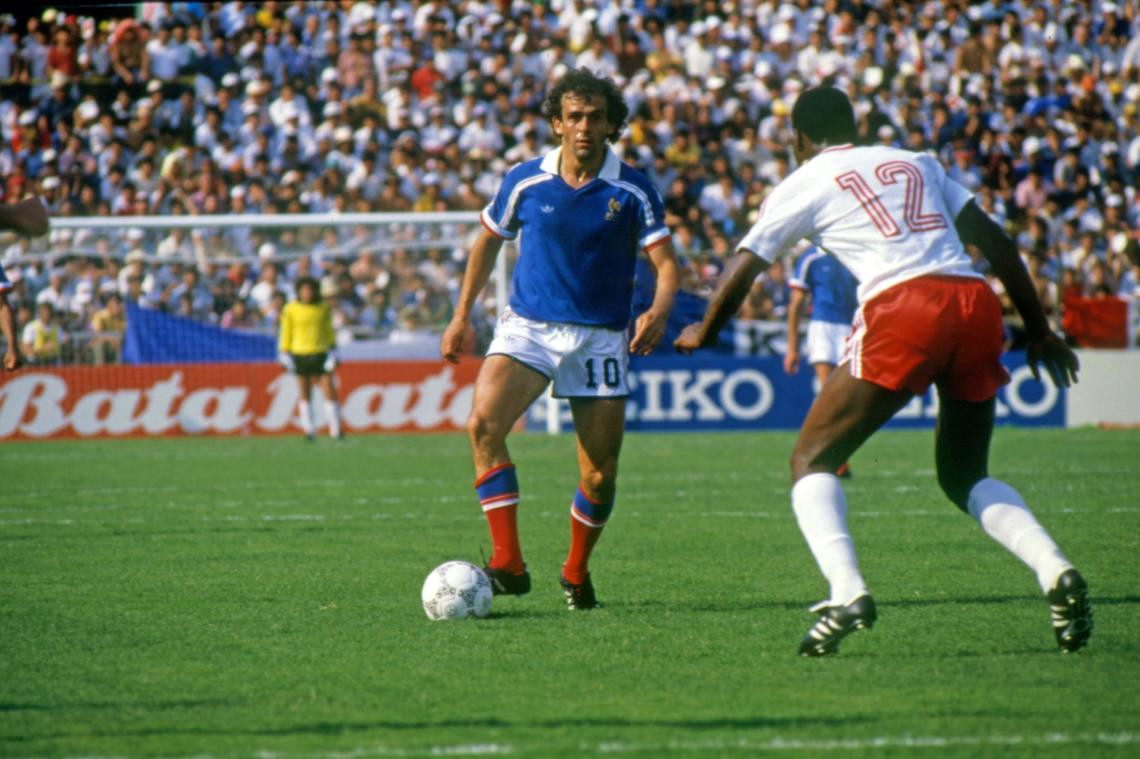
Michel Platini
Michel François Platini (; born 21 June 1955) is a French association football, football Administrator (business), administrator and former player and manager. Regarded as one of the greatest footballers of all time, Platini won the Ballon d'Or three times in a row, in 1983, 1984 and 1985, and came seventh in the FIFA Player of the Century#FIFA Magazine and Grand Jury vote, FIFA Player of the Century vote. In recognition of his achievements, he was named a Knight of the Legion of Honour in 1985 and became an Officer in 1998. As the president of UEFA in 2015 he was banned from involvement in football under FIFA's organisation, over ethics violations. The ban lasted until 2023. During his career, Platini played for the clubs AS Nancy, Nancy, AS Saint-Étienne, Saint-Étienne, and Juventus FC, Juventus. Nicknamed ''Le Roi'' (The King) for his ability and leadership, he was a prolific goalscorer; he won the Capocannoniere, Serie A ''capocannoniere'' award three consecutive times be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomson MO5 édition Platini! (9368426935)
Thomson may refer to: Names * Thomson (surname), a list of people with this name and a description of its origin * Thomson baronets, four baronetcies created for persons with the surname Thomson Businesses and organizations * SGS-Thomson Microelectronics, an electronics manufacturer * Various travel subsidiaries of TUI Group: ** Thomson Airways (now TUI Airways), a UK-based airline ** Thomson Cruises (now Marella Cruises), a UK-based cruise line ** Thomson Travel (now TUI UK), a UK-based travel company ** Thomsonfly, a former UK airline, formerly Britannia Airways * Thomson Directories, local business search company and publisher of: ** Thomson Local, the UK business directory * Thomson Multimedia, former name of Technicolor SA, a French multinational corporation * Thomson Reuters, Canadian media and information services company ** Thomson Corporation, former name of the company prior to its 2008 merger with Reuters ** Thomson Financial, former business division of Thoms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
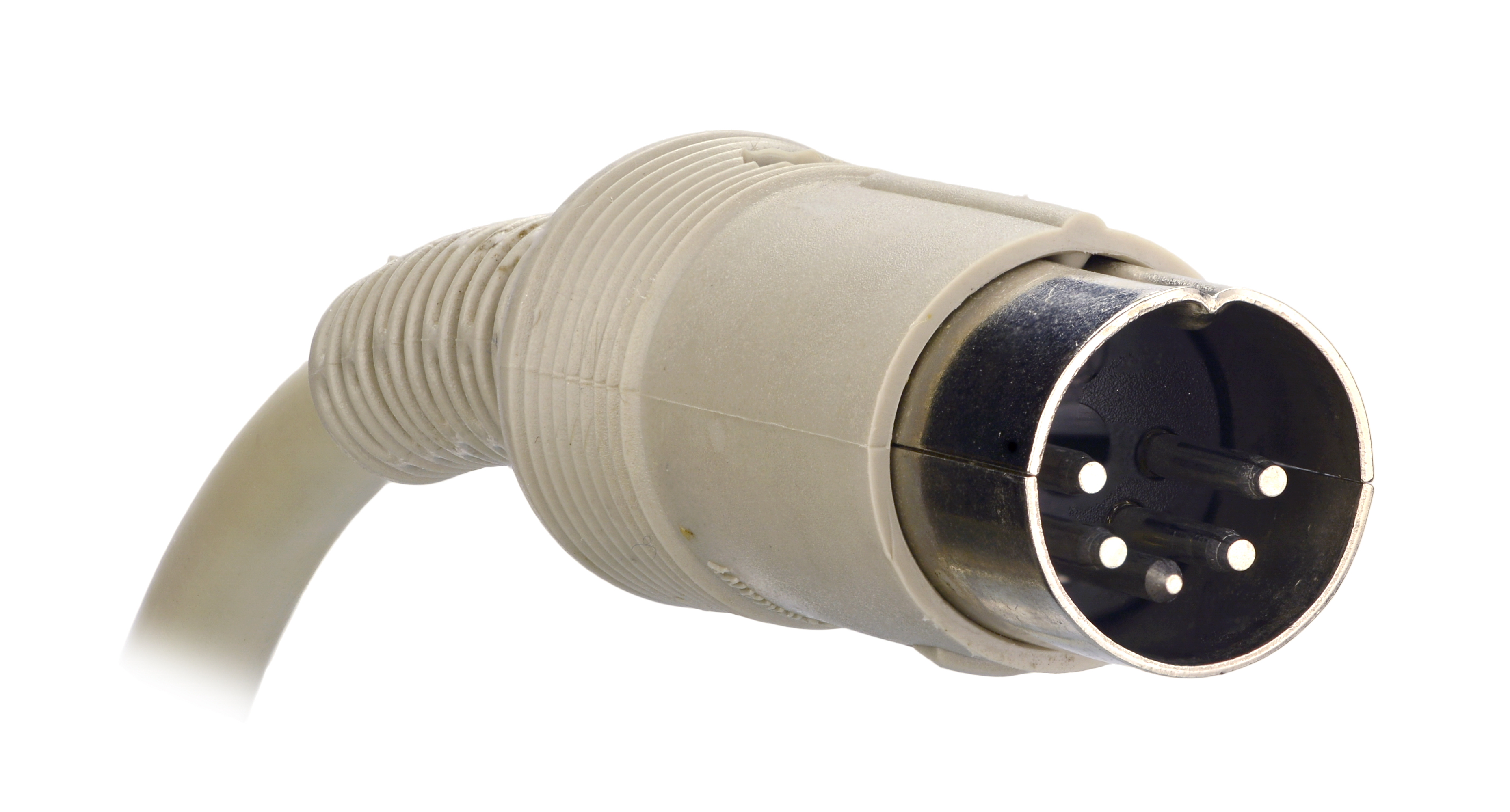
DIN Connector
The DIN connector is an electrical signal connector that was standardized by the (DIN), the German Institute for Standards, in the mid 1950s, initially with three pins for mono, but when stereo connections and gear appeared in the late 1950s, versions with five pins or more were made. The male DIN connectors (plugs) feature a 13.2 mm diameter metal shield with a notch that sets the orientation in which plug and socket can mate. The range of DIN connectors, different only in the configuration of the pins, has been standardized as DIN 41524 / IEC/DIN EN 60130-9 (3-pin at 90° and 5-pin at 45°); DIN 45322 (5-pin and 6-pin at 60°); DIN 45329 / IEC/DIN EN 60130–9 (7-pin at 45°); and DIN 45326 / IEC/DIN EN 60130-9 (8-pin at 45°). In consumer electronics, the cylindrical connectors were adopted for analog audio signals. Some DIN connectors have been used in analog video applications, for power connections, and for digital interfaces, such as the MIDI (DIN 41524), the IBM ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Square Wave (waveform)
A square wave is a non-sinusoidal waveform, non-sinusoidal periodic waveform in which the amplitude alternates at a steady frequency between fixed minimum and maximum values, with the same duration at minimum and maximum. In an ideal square wave, the transitions between minimum and maximum are instantaneous. The square wave is a special case of a pulse wave which allows arbitrary durations at minimum and maximum amplitudes. The ratio of the high period to the total period of a pulse wave is called the duty cycle. A true square wave has a 50% duty cycle (equal high and low periods). Square waves are often encountered in electronics and signal processing, particularly digital electronics and digital signal processing. Its stochastic counterpart is a two-state trajectory. Origin and uses Square waves are universally encountered in digital switching circuits and are naturally generated by binary (two-level) logic devices. They are used as timing references or "clock signa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1-bit DAC
A 1-bit DAC (sometimes called Bitstream converter by Philips) is a consumer electronics marketing term describing an oversampling digital-to-analog converter (DAC) that uses a digital noise shaping delta-sigma modulator operating at many multiples of the sampling frequency that outputs to an ''actual'' 1-bit DAC (which could be fully differential to minimize crosstalk). The combination can have high signal-to-noise and hence an equivalent effective number of bits as a DAC with a larger number of bits (usually 16-20). The advantages of this type of converter are high linearity combined with low cost, owed to the fact that most of the processing takes place in the digital domain, which helps relax the requirements for the subsequent analog low-pass filter (for anti-aliasing image frequencies and suppressing high-frequency noise-shaping noise). For these reasons, this design is very popular in digital consumer electronics (CD/DVD players, set-top boxes and the like). While single-bi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |