|
Thionamide
A thioamide (rarely, thionamide, but also known as thiourylenes) is a functional group with the general structure , where are any groups (typically organyl groups or hydrogen). Analogous to amides, thioamides exhibit greater multiple bond character along the C-N bond, resulting in a larger rotational barrier. Synthesis Thioamides are typically prepared by treating amides with phosphorus sulfides such as phosphorus pentasulfide, a reaction first described in the 1870s. An alternative to P2S5 is its more soluble analogue Lawesson's reagent. The Willgerodt-Kindler reaction can give benzylthioamides via an analogous process. These transformations can be seen in the synthesis of tolrestat. : The reaction of nitriles with hydrogen sulfide also affords thioamides: : Imidoyl chlorides react with hydrogen sulfide to produce thioamides. : Reactions A well-known thioamide is thioacetamide, which is used as a source of the sulfide ion. Thioamides are precursors to heterocycles. Such a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thioamides
A thioamide (rarely, thionamide, but also known as thiourylenes) is a functional group with the general structure , where are any groups (typically organyl groups or hydrogen). Analogous to amides, thioamides exhibit greater multiple bond character along the C-N bond, resulting in a larger rotational barrier. Synthesis Thioamides are typically prepared by treating amides with phosphorus sulfides such as phosphorus pentasulfide, a reaction first described in the 1870s. An alternative to P2S5 is its more soluble analogue Lawesson's reagent. The Willgerodt-Kindler reaction can give benzylthioamides via an analogous process. These transformations can be seen in the synthesis of tolrestat. : The reaction of nitriles with hydrogen sulfide also affords thioamides: : Imidoyl chlorides react with hydrogen sulfide to produce thioamides. : Reactions A well-known thioamide is thioacetamide, which is used as a source of the sulfide ion. Thioamides are precursors to heterocycles. S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organyl
In organic and organometallic chemistry, an organyl group (commonly denoted by the letter " R") is an organic substituent with one (sometimes more) free valence electron(s) at a carbon atom.. The term is often used in chemical patent literature to protect claims over a broad scope. Examples * Acetonyl group * Acyl group (e.g. acetyl group, benzoyl group) * Alkyl group (e.g., methyl group, ethyl group) * Alkenyl group (e.g., vinyl group, allyl group) * Alkynyl group ( propargyl group) * Benzyloxycarbonyl group (Cbz) * '' tert'' -butoxycarbonyl group (Boc) * Carboxyl group In organic chemistry, a carboxylic acid is an organic acid that contains a carboxyl group () attached to an R-group. The general formula of a carboxylic acid is often written as or , sometimes as with R referring to an organyl group (e.g. ... References Functional groups {{organic-chem-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heterocycle
A heterocyclic compound or ring structure is a cyclic compound that has atoms of at least two different elements as members of its ring(s). Heterocyclic organic chemistry is the branch of organic chemistry dealing with the synthesis, properties, and applications of organic heterocycles. Examples of heterocyclic compounds include all of the nucleic acids, the majority of drugs, most biomass (cellulose and related materials), and many natural and synthetic dyes. More than half of known compounds are heterocycles. 59% of US FDA-approved drugs contain nitrogen heterocycles. Classification The study of organic heterocyclic chemistry focuses especially on organic unsaturated derivatives, and the preponderance of work and applications involves unstrained organic 5- and 6-membered rings. Included are pyridine, thiophene, pyrrole, and furan. Another large class of organic heterocycles refers to those fused to benzene rings. For example, the fused benzene derivatives of p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colloid
A colloid is a mixture in which one substance consisting of microscopically dispersed insoluble particles is suspended throughout another substance. Some definitions specify that the particles must be dispersed in a liquid, while others extend the definition to include substances like aerosols and gels. The term colloidal suspension refers unambiguously to the overall mixture (although a narrower sense of the word '' suspension'' is distinguished from colloids by larger particle size). A colloid has a dispersed phase (the suspended particles) and a continuous phase (the medium of suspension). The dispersed phase particles have a diameter of approximately 1 nanometre to 1 micrometre. Some colloids are translucent because of the Tyndall effect, which is the scattering of light by particles in the colloid. Other colloids may be opaque or have a slight color. Colloidal suspensions are the subject of interface and colloid science. This field of study began in 1845 by Franc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
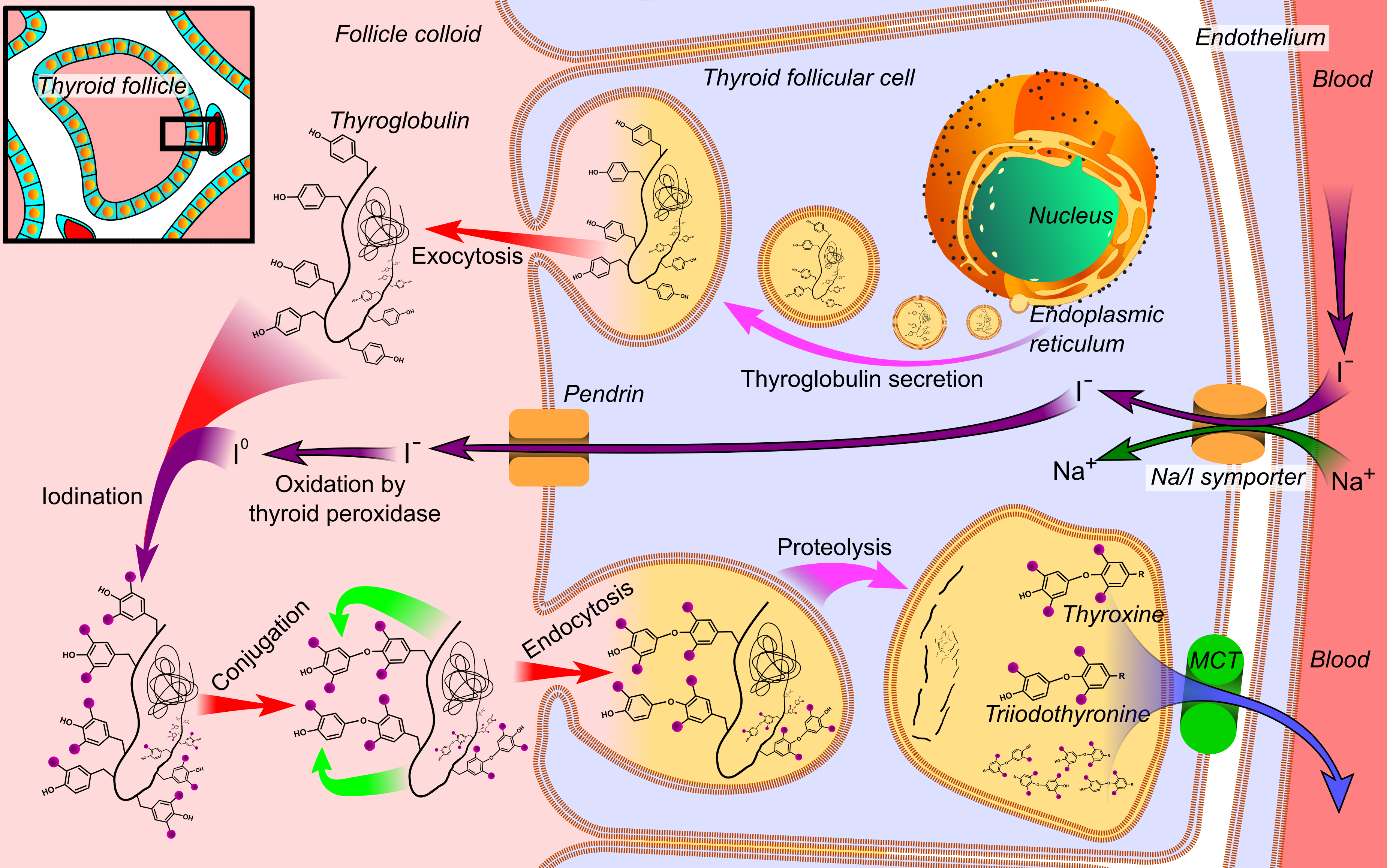
Thyroxine
Thyroxine, also known as T4, is a hormone produced by the thyroid gland. It is the primary form of thyroid hormone found in the blood and acts as a prohormone of the more active thyroid hormone, triiodothyronine (T3). Thyroxine and its active metabolites are essential for regulating metabolic rate, supporting heart and muscle function, promoting brain development, and maintaining bone health. Regulation Thyroxine has a half-life of approximately one week and hence maintains relatively stable blood levels. Its production and release are controlled through a complex feedback loop involving the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, and thyroid gland. This regulatory system ensures that optimal hormone levels are maintained. Biosynthesis Thyroxine biosynthesis is a multi-step process that occurs in follicular cell within the thyroid gland. The synthesis of thyroxine requires adequate iodine supply and appropriate hormonal control. The process begins with the active uptake o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triiodothyronine
Triiodothyronine, also known as T3, is a thyroid hormone. It affects almost every physiological process in the body, including growth and development, metabolism, body temperature, and heart rate. Production of T3 and its prohormone thyroxine (T4) is activated by thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), which is released from the anterior pituitary gland. This pathway is part of a closed-loop feedback process: Elevated concentrations of T3, and T4 in the blood plasma inhibit the production of TSH in the anterior pituitary gland. As concentrations of these hormones decrease, the anterior pituitary gland increases production of TSH, and by these processes, a feedback control system stabilizes the level of thyroid hormones in the bloodstream. At the cellular level, T3 is the body's more active and potent thyroid hormone. T3 helps deliver oxygen and energy to all of the body's cells, its effects on target tissues being roughly four times more potent than those of T4. Of the thyroid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thyroid
The thyroid, or thyroid gland, is an endocrine gland in vertebrates. In humans, it is a butterfly-shaped gland located in the neck below the Adam's apple. It consists of two connected lobes. The lower two thirds of the lobes are connected by a thin band of tissue called the isthmus (: isthmi). Microscopically, the functional unit of the thyroid gland is the spherical thyroid follicle, lined with follicular cells (thyrocytes), and occasional parafollicular cells that surround a lumen containing colloid. The thyroid gland secretes three hormones: the two thyroid hormones triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4)and a peptide hormone, calcitonin. The thyroid hormones influence the metabolic rate and protein synthesis and growth and development in children. Calcitonin plays a role in calcium homeostasis. Secretion of the two thyroid hormones is regulated by thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), which is secreted from the anterior pituitary gland. TSH is regulated by thy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thyroid Peroxidase
Thyroid peroxidase, also called thyroperoxidase (TPO), thyroid specific peroxidase or iodide peroxidase, is an enzyme expressed mainly in the thyroid where it is secreted into colloid. Thyroid peroxidase oxidizes iodide ions to form iodine atoms for addition onto tyrosine residues on thyroglobulin for the production of thyroxine (T4) or triiodothyronine (T3), the thyroid hormones. In humans, thyroperoxidase is encoded by the ''TPO'' gene. Function Inorganic iodine enters the body primarily as iodide, I−. After entering the thyroid follicle (or thyroid follicular cell) via a Na+/I− symporter (NIS) on the basolateral side, iodide is shuttled across the apical membrane into the colloid via pendrin after which thyroid peroxidase oxidizes iodide to atomic iodine (I) or iodinium (I+). The chemical reactions catalyzed by thyroid peroxidase occur on the outer apical membrane surface and are mediated by hydrogen peroxide. The "organification of iodine", the incorporation of iodine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bioavailability
In pharmacology, bioavailability is a subcategory of absorption and is the fraction (%) of an administered drug that reaches the systemic circulation. By definition, when a medication is administered intravenously, its bioavailability is 100%. However, when a medication is administered via routes other than intravenous, its bioavailability is lower due to intestinal epithelium absorption and first-pass metabolism. Thereby, mathematically, bioavailability equals the ratio of comparing the area under the plasma drug concentration curve versus time (AUC) for the extravascular formulation to the AUC for the intravascular formulation. AUC is used because AUC is proportional to the dose that has entered the systemic circulation. Bioavailability of a drug is an average value; to take population variability into account, deviation range is shown as ±. To ensure that the drug taker who has poor absorption is dosed appropriately, the bottom value of the deviation range is employed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Structure Activity Relationship
A structure is an arrangement and organization of interrelated elements in a material object or system, or the object or system so organized. Material structures include man-made objects such as buildings and machines and natural objects such as biological organisms, minerals and chemicals. Abstract structures include data structures in computer science and musical form. Types of structure include a hierarchy (a cascade of one-to-many relationships), a network featuring many-to-many links, or a lattice featuring connections between components that are neighbors in space. Load-bearing Buildings, aircraft, skeletons, anthills, beaver dams, bridges and salt domes are all examples of load-bearing structures. The results of construction are divided into buildings and non-building structures, and make up the infrastructure of a human society. Built structures are broadly divided by their varying design approaches and standards, into categories including building structures, arch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isostere
Classical Isosteres are molecules or ions with similar shape and often electronic properties. Many definitions are available. but the term is usually employed in the context of bioactivity and drug development. Such biologically-active compounds containing an isostere is called a bioisostere. This is frequently used in drug design: the bioisostere will still be recognized and accepted by the body, but its functions there will be altered as compared to the parent molecule. History and additional definitions Non-classical isosteres do not obey the above classifications, but they still produce similar biological effects in vivo. Non-classical isosteres may be made up of similar atoms, but their structures do not follow an easily definable set of rules. The isostere concept was formulated by Irving Langmuir in 1919, and later modified by Grimm. Hans Erlenmeyer extended the concept to biological systems in 1932.Mukesh Doble, Anil Kumar Kruthiventi, Vilas Gajanan. ''Biotransformations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |