|
Heterocycle
A heterocyclic compound or ring structure is a cyclic compound that has atoms of at least two different elements as members of its ring(s). Heterocyclic organic chemistry is the branch of organic chemistry dealing with the synthesis, properties, and applications of organic heterocycles. Examples of heterocyclic compounds include all of the nucleic acids, the majority of drugs, most biomass (cellulose and related materials), and many natural and synthetic dyes. More than half of known compounds are heterocycles. 59% of US FDA-approved drugs contain nitrogen heterocycles. Classification The study of organic heterocyclic chemistry focuses especially on organic unsaturated derivatives, and the preponderance of work and applications involves unstrained organic 5- and 6-membered rings. Included are pyridine, thiophene, pyrrole, and furan. Another large class of organic heterocycles refers to those fused to benzene rings. For example, the fused benzene derivatives of p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyridine
Pyridine is a basic (chemistry), basic heterocyclic compound, heterocyclic organic compound with the chemical formula . It is structurally related to benzene, with one methine group replaced by a nitrogen atom . It is a highly flammable, weakly alkaline, water-miscible liquid with a distinctive, unpleasant fish-like smell. Pyridine is colorless, but older or impure samples can appear yellow, due to the formation of extended, unsaturated Polymer, polymeric chains, which show significant electrical conductivity. The pyridine ring occurs in many important compounds, including agrochemicals, pharmaceuticals, and vitamins. Historically, pyridine was produced from coal tar. As of 2016, it is synthesized on the scale of about 20,000 tons per year worldwide. Properties Physical properties Pyridine is diamagnetism, diamagnetic. Its critical point (thermodynamics), critical parameters are: pressure 5.63 MPa, temperature 619 K and volume 248 cm3/mol. In the temperatur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indole
Indole is an organic compound with the formula . Indole is classified as an aromatic heterocycle. It has a bicyclic structure, consisting of a six-membered benzene ring fused to a five-membered pyrrole ring. Indoles are derivatives of indole where one or more of the hydrogen atoms have been replaced by substituent groups. Indoles are widely distributed in nature, most notably as amino acid tryptophan and neurotransmitter serotonin. General properties and occurrence Indole is a solid at room temperature. It occurs naturally in human feces and has an intense fecal odor. At very low concentrations, however, it has a flowery smell, and is a constituent of many perfumes. It also occurs in coal tar. It has been identified in cannabis. It is the main volatile compound in stinky tofu. When indole is a substituent on a larger molecule, it is called an ''indolyl group'' by systematic nomenclature. Indole undergoes electrophilic substitution, mainly at position 3 (see diagram in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyridine
Pyridine is a basic (chemistry), basic heterocyclic compound, heterocyclic organic compound with the chemical formula . It is structurally related to benzene, with one methine group replaced by a nitrogen atom . It is a highly flammable, weakly alkaline, water-miscible liquid with a distinctive, unpleasant fish-like smell. Pyridine is colorless, but older or impure samples can appear yellow, due to the formation of extended, unsaturated Polymer, polymeric chains, which show significant electrical conductivity. The pyridine ring occurs in many important compounds, including agrochemicals, pharmaceuticals, and vitamins. Historically, pyridine was produced from coal tar. As of 2016, it is synthesized on the scale of about 20,000 tons per year worldwide. Properties Physical properties Pyridine is diamagnetism, diamagnetic. Its critical point (thermodynamics), critical parameters are: pressure 5.63 MPa, temperature 619 K and volume 248 cm3/mol. In the temperatur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piperidine
Piperidine is an organic compound with the molecular formula (CH2)5NH. This heterocyclic amine consists of a six-membered ring containing five methylene bridges (–CH2–) and one amine bridge (–NH–). It is a colorless liquid with an odor described as objectionable, typical of amines. The name comes from the genus name '' Piper'', which is the Latin word for pepper. Although piperidine is a common organic compound, it is best known as a representative structure element within many pharmaceuticals and alkaloids, such as natural-occurring solenopsins. Production Piperidine was first reported in 1850 by the Scottish chemist Thomas Anderson and again, independently, in 1852 by the French chemist Auguste Cahours, who named it. Both of them obtained piperidine by reacting piperine with nitric acid. Industrially, piperidine is produced by the hydrogenation of pyridine, usually over a molybdenum disulfide catalyst: : C5H5N + 3 H2 → C5H10NH Pyridine can also be reduce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyrrole
Pyrrole is a heterocyclic, aromatic, organic compound, a five-membered ring with the formula . It is a colorless volatile liquid that darkens readily upon exposure to air. Substituted derivatives are also called pyrroles, e.g., ''N''-methylpyrrole, . Porphobilinogen, a trisubstituted pyrrole, is the biosynthetic precursor to many natural products such as heme. Pyrroles are components of more complex macrocycles, including the porphyrinogens and products derived therefrom, including porphyrins of heme, the chlorins, bacteriochlorins, and chlorophylls. Properties, structure, bonding Pyrrole is a colorless volatile liquid that darkens readily upon exposure to air, and is usually purified by distillation immediately before use. Pyrrole has a nutty odor. Pyrrole is a 5-membered aromatic heterocycle, like furan and thiophene. Unlike furan and thiophene, it has a dipole in which the positive end lies on the side of the heteroatom, with a dipole moment of 1.58 D. In CDCl3, it ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
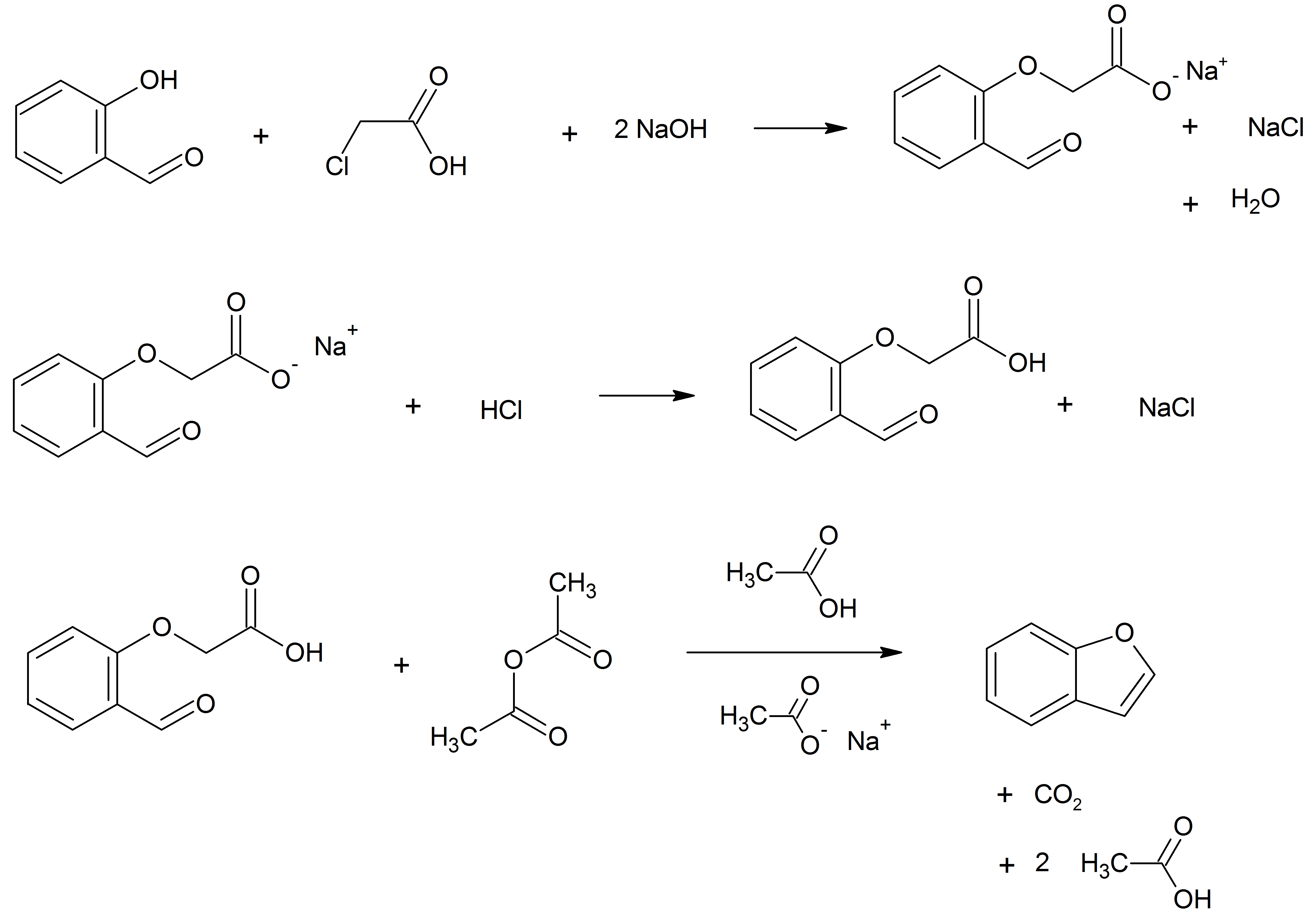
Benzofuran
Benzofuran is the heterocyclic compound consisting of fused benzene and furan rings. This colourless liquid is a component of coal tar. Benzofuran is the structural nucleus (parent compound) of many related compounds with more complex structures. For example, psoralen is a benzofuran derivative that occurs in several plants. Production Benzofuran is extracted from coal tar. It is also obtained by dehydrogenation of 2-ethyl phenol. Laboratory methods Benzofurans can be prepared by various methods in the laboratory. Notable examples include: *''O''-alkylation of salicylaldehyde with chloroacetic acid followed by dehydration (cyclication) of the resulting ether and decarboxylation. * Perkin rearrangement, where a coumarin is reacted with a hydroxide: : * Diels–Alder reaction of nitro vinyl furans with various dienophiles: : * Cycloisomerization of alkyne ortho-substituted phenols: : Related compounds * Substituted benzofurans * Dibenzofuran, an analog w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclic Compound
A cyclic compound (or ring compound) is a term for a compound in the field of chemistry in which one or more series of atoms in the compound is connected to form a ring. Rings may vary in size from three to many atoms, and include examples where all the atoms are carbon (i.e., are carbocycles), none of the atoms are carbon (inorganic cyclic compounds), or where both carbon and non-carbon atoms are present ( heterocyclic compounds with rings containing both carbon and non-carbon). Depending on the ring size, the bond order of the individual links between ring atoms, and their arrangements within the rings, carbocyclic and heterocyclic compounds may be aromatic or non-aromatic; in the latter case, they may vary from being fully saturated to having varying numbers of multiple bonds between the ring atoms. Because of the tremendous diversity allowed, in combination, by the valences of common atoms and their ability to form rings, the number of possible cyclic structures, even of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Chemistry
Organic chemistry is a subdiscipline within chemistry involving the science, scientific study of the structure, properties, and reactions of organic compounds and organic matter, organic materials, i.e., matter in its various forms that contain carbon atoms.Clayden, J.; Greeves, N. and Warren, S. (2012) ''Organic Chemistry''. Oxford University Press. pp. 1–15. . Study of structure determines their structural formula. Study of properties includes Physical property, physical and Chemical property, chemical properties, and evaluation of Reactivity (chemistry), chemical reactivity to understand their behavior. The study of organic reactions includes the organic synthesis, chemical synthesis of natural products, drugs, and polymers, and study of individual organic molecules in the laboratory and via theoretical (in silico) study. The range of chemicals studied chemistry includes hydrocarbons (compounds containing only carbon and hydrogen) as well as compounds based on carbon, but a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Borazine
Borazine, also known as borazole, inorganic benzene, is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula B3H6N3. In this cyclic compound, the three BH units and three NH units alternate. The compound is isoelectronic and isostructural with benzene. For this reason borazine is sometimes referred to as “inorganic benzene”. Like benzene, borazine is a colourless liquid with an aromatic odor. Synthesis The compound was reported in 1926 by the chemists Alfred Stock and Erich Pohland by a reaction of diborane with ammonia. Borazine can be synthesized by treating diborane and ammonia in a 1:2 ratio at 250–300 °C with a conversion of 50%. :3 B2H6 + 6 NH3 → 2 B3H6N3 + 12 H2 An alternative more efficient route begins with sodium borohydride and ammonium sulfate: :6 NaBH4 + 3 (NH4)2SO4 → 2 B3N3H6 + 3 Na2SO4 + 18 H2 In a two-step process to borazine, boron trichloride is first converted to trichloroborazine: :3 BCl3 + 3 NH4Cl → Cl3B3H3N3 + 9 HCl The B-Cl bonds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethers
In organic chemistry, ethers are a class of compounds that contain an ether group, a single oxygen atom bonded to two separate carbon atoms, each part of an organyl group (e.g., alkyl or aryl). They have the general formula , where R and R′ represent the organyl groups. Ethers can again be classified into two varieties: if the organyl groups are the same on both sides of the oxygen atom, then it is a simple or symmetrical ether, whereas if they are different, the ethers are called mixed or unsymmetrical ethers. A typical example of the first group is the solvent and anaesthetic diethyl ether, commonly referred to simply as "ether" (). Ethers are common in organic chemistry and even more prevalent in biochemistry, as they are common linkages in carbohydrates and lignin. Structure and bonding Ethers feature bent linkages. In dimethyl ether, the bond angle is 111° and C–O distances are 141 pm. The barrier to rotation about the C–O bonds is low. The bonding of oxygen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dibenzothiophene
Dibenzothiophene (DBT, diphenylene sulfide) is the organosulfur compound consisting of two benzene rings fused to a central thiophene ring. It has the chemical formula C12H8S. It is a colourless solid that is chemically somewhat similar to anthracene. This tricyclic heterocycle, and especially its disubstituted derivative 4,6-dimethyldibenzothiophene are problematic impurities in petroleum. Synthesis and reactions Dibenzothiophene is prepared by the reaction of biphenyl with sulfur dichloride in the presence of aluminium chloride. Reduction with lithium Lithium (from , , ) is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol Li and atomic number 3. It is a soft, silvery-white alkali metal. Under standard temperature and pressure, standard conditions, it is the least dense metal and the ... results in scission of one C-S bond. With butyllithium, this heterocycle undergoes stepwise lithiation at the 4-position. S-oxidation with peroxides gives the sulfoxide. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |