Benzofuran on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Benzofuran is the heterocyclic compound consisting of fused benzene and furan rings. This colourless liquid is a component of coal tar. Benzofuran is the structural nucleus (parent compound) of many related compounds with more complex structures. For example, psoralen is a benzofuran derivative that occurs in several plants.
 * Perkin rearrangement, where a coumarin is reacted with a hydroxide:
:
* Diels–Alder reaction of nitro vinyl furans with various dienophiles:
:
* Cycloisomerization of alkyne ortho-substituted phenols:
:
* Perkin rearrangement, where a coumarin is reacted with a hydroxide:
:
* Diels–Alder reaction of nitro vinyl furans with various dienophiles:
:
* Cycloisomerization of alkyne ortho-substituted phenols:
:
Production
Benzofuran is extracted from coal tar. It is also obtained by dehydrogenation of 2-ethyl phenol.Laboratory methods
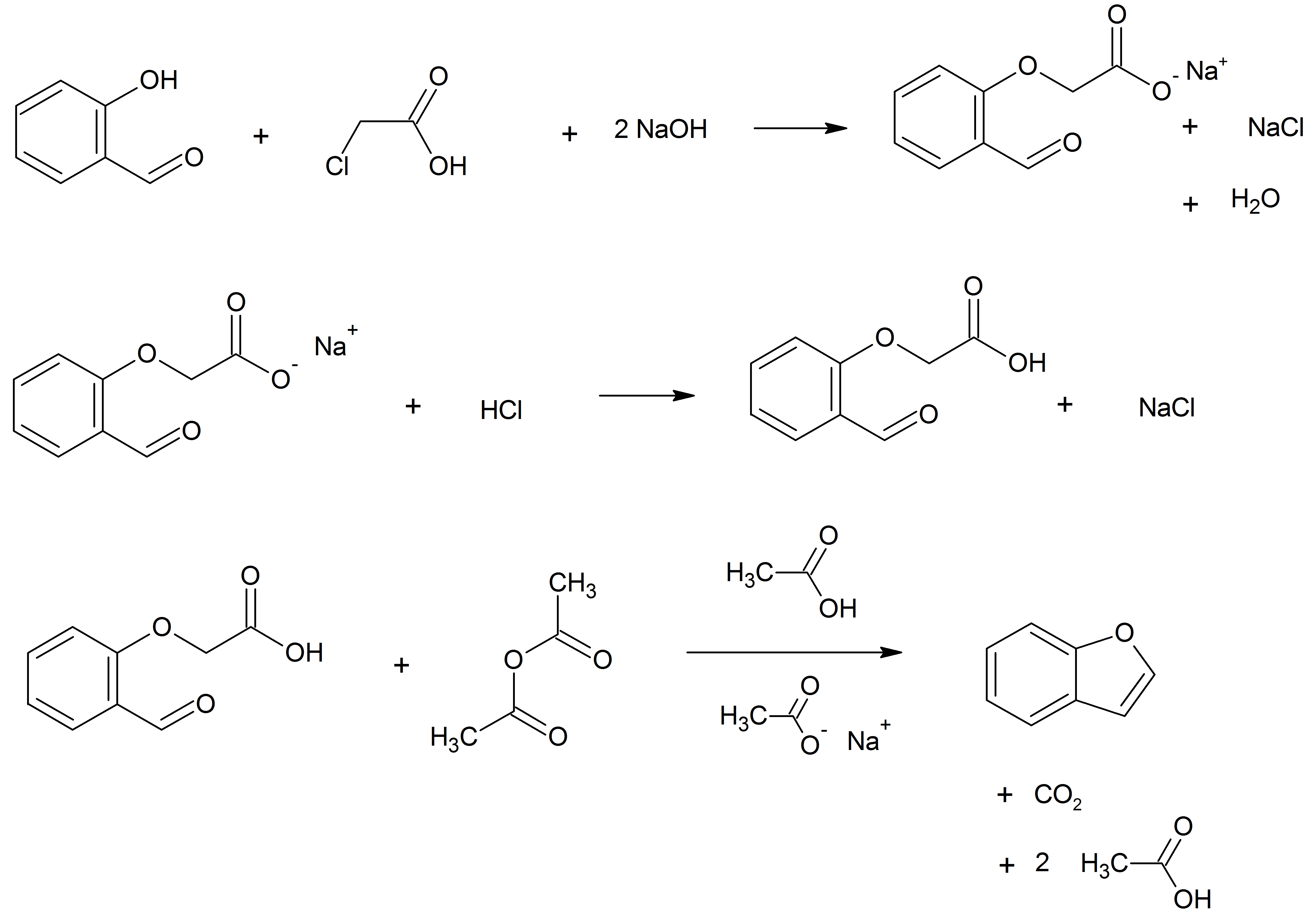
Benzofurans can be prepared by various methods in the laboratory. Notable examples include: *''O''-alkylation of salicylaldehyde with chloroacetic acid followed by dehydration (cyclication) of the resulting ether and decarboxylation. * Perkin rearrangement, where a coumarin is reacted with a hydroxide:
:
* Diels–Alder reaction of nitro vinyl furans with various dienophiles:
:
* Cycloisomerization of alkyne ortho-substituted phenols:
:
* Perkin rearrangement, where a coumarin is reacted with a hydroxide:
:
* Diels–Alder reaction of nitro vinyl furans with various dienophiles:
:
* Cycloisomerization of alkyne ortho-substituted phenols:
:
Related compounds
* Substituted benzofurans * Dibenzofuran, an analog with a second fused benzene ring. * Furan, an analog without the fused benzene ring. * Indole, an analog with a nitrogen instead of the oxygenatom
Atoms are the basic particles of the chemical elements. An atom consists of a atomic nucleus, nucleus of protons and generally neutrons, surrounded by an electromagnetically bound swarm of electrons. The chemical elements are distinguished fr ...
.
* Benzothiophene, an analog with a sulfur instead of the oxygen atom
Atoms are the basic particles of the chemical elements. An atom consists of a atomic nucleus, nucleus of protons and generally neutrons, surrounded by an electromagnetically bound swarm of electrons. The chemical elements are distinguished fr ...
.
* Isobenzofuran, the isomer with oxygen in the adjacent position.
* Aurone
* Thunberginol F
References
{{Authority control IARC Group 2B carcinogens Simple aromatic rings