|
Tatsienlu
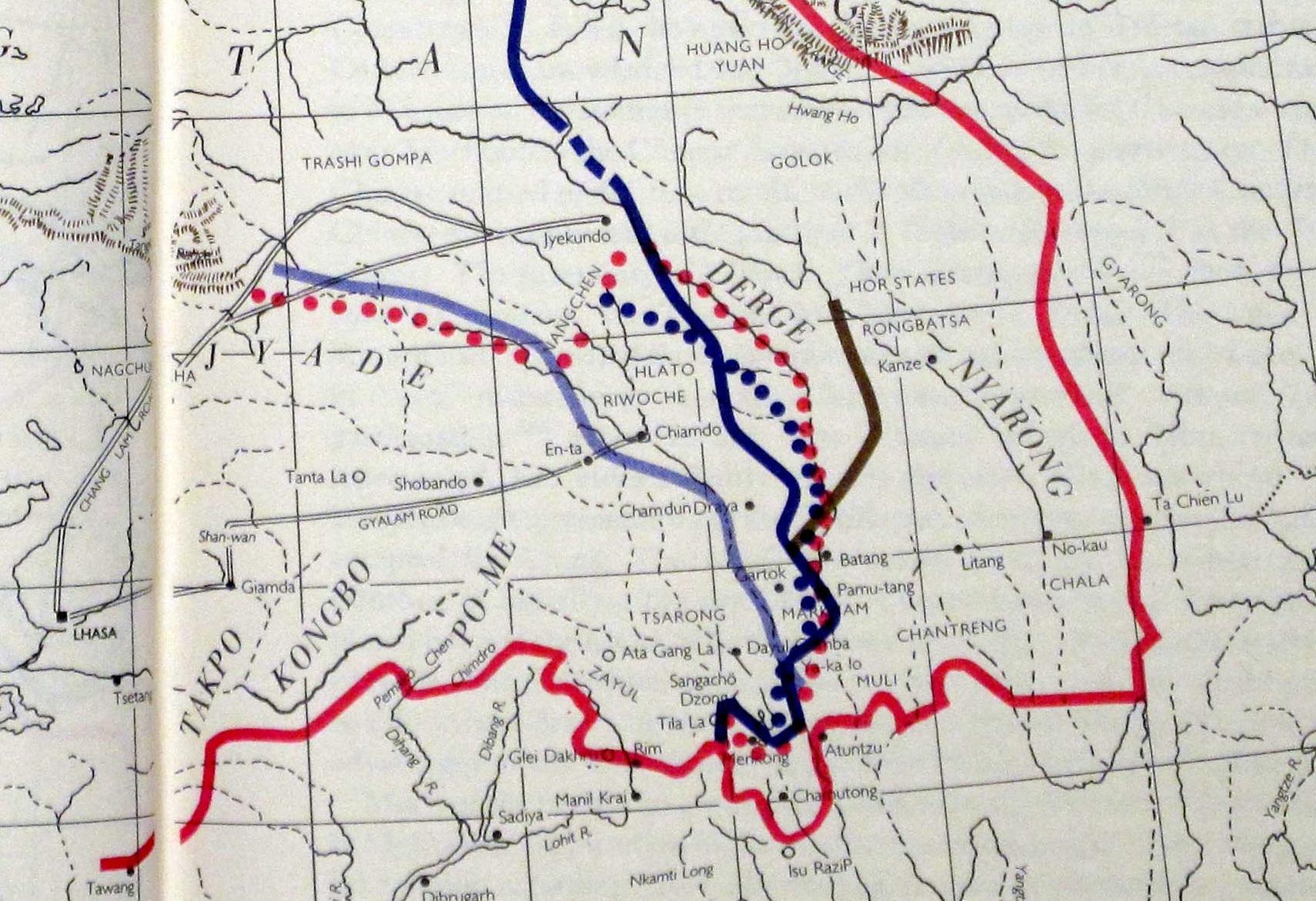
Kangding ( zh, c=康定), also known as Dartsedo (), is a county-level city and the seat of Garzê Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture in Sichuan province of Southwest China. Kangding is on the bank of the Dadu River and has been considered the historical border between the Kham region of Tibet and the Sichuan region. Kangding's urban center is called Lucheng, which has around 134,000 inhabitants. Names Historically, the urban center was known in Chinese as ''Dajianlu'' ( zh, c=打箭炉, also transliterated ''Tachienlu'' or ''Tatsienlu'') from the Chinese transliteration of the Tibetan name ''Dartsedo'' or ''Darzêdo''. History Kangding was on the historical border between Tibet and China. From Kangding to the west lies Tibetan civilization, whereas to the east are Han cultural areas. It was the capital of the Kingdom of Chakla. During its history, Kangding has witnessed many conflicts between Tibetan and Han polities. Kangding was for many centuries an important trading city where ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lucheng, Kangding
Lucheng Subdistrict is one of two subdistricts of Kangding city in Garzê Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture in western Sichuan Province, China. Lucheng Subdistrict serves as the seat of the Kangding city government. As of 2010, the subdistrict has a population of 41,399 people. Administrative divisions The subdistrict is divided into four neighborhood committees and ten village committees. Transport * China National Highway 318 See also * List of township-level divisions of Sichuan This is a list of Administrative divisions of the People's Republic of China#Township level, township-level divisions in the province of Sichuan, China, People's Republic of China (PRC). Bazhong Bazhou District * Eight Townships of China, ... References Further reading *Dorje, Gyurme (1999). ''Footprint Tibet Handbook with Bhutan''. 2nd Edition. Footprint Handbooks, Bath, England. . * Forbes, Andrew; Henley, David (2011). ''China's Ancient Tea Horse Road''. Chiang Mai: Cognoscenti Book ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dartsedo
Kangding ( zh, c=康定), also known as Dartsedo (), is a county-level city and the seat of Garzê Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture in Sichuan province of Southwest China. Kangding is on the bank of the Dadu River and has been considered the historical border between the Kham region of Tibet and the Sichuan region. Kangding's urban center is called Lucheng, which has around 134,000 inhabitants. Names Historically, the urban center was known in Chinese as ''Dajianlu'' ( zh, c=打箭炉, also transliterated ''Tachienlu'' or ''Tatsienlu'') from the Chinese transliteration of the Tibetan name ''Dartsedo'' or ''Darzêdo''. History Kangding was on the historical border between Tibet and China. From Kangding to the west lies Tibetan civilization, whereas to the east are Han cultural areas. It was the capital of the Kingdom of Chakla. During its history, Kangding has witnessed many conflicts between Tibetan and Han polities. Kangding was for many centuries an important trading city where ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
County-level City
A county-level city () is a County-level divisions of China, county-level administrative division of the China, People's Republic of China. County-level cities have judiciary, judicial but no legislature, legislative rights over their own local ordinance, local law and are usually governed by Administrative divisions of China#Prefectural level (2nd), prefecture-level divisions, but a few are governed directly by Administrative divisions of China#Provincial level (1st), province-level divisions. A county-level city is a "city" () and "county" () that have been merged into one unified jurisdiction. As such, it is simultaneously a city, which is a municipal entity, and a county, which is an administrative division of a prefecture. Most county-level cities were created in the 1980s and 1990s by replacing denser populated Counties of China, counties. County-level cities are not "city, cities" in the strictest sense of the word, since they usually contain rural areas many times the size ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brick Tea
Compressed tea, called tea bricks, tea cakes or tea lumps, and tea nuggets according to the shape and size, are blocks of whole or finely ground black tea, green tea, or post-fermented tea leaves that have been packed in molds and pressed into block form. This was the most commonly produced and used form of tea in ancient China prior to the Ming Dynasty. Although tea bricks are less commonly produced in modern times, many post-fermented teas, such as '' pu-erh'', are still commonly found in bricks, discs, and other pressed forms. Tea bricks can be made into beverages like tea or eaten as food, and were also used in the past as a form of currency. Production In ancient China, compressed teas were usually made with thoroughly dried and ground tea leaves that were pressed into various bricks or other shapes, although partially dried and whole leaves were also used. Some tea bricks were also mixed with binding agents such as flour, blood, or manure to better preserve thei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1959 Tibetan Uprising
The 1959 Tibetan uprising or Lhasa uprising began on 10 March 1959 as a series of protests in the Tibetan capital of Lhasa, fueled by fears that the Chinese government planned to arrest the Dalai Lama. Over the next ten days, the demonstrations evolved from expressions of support for the 14th Dalai Lama to demands for independence and the reversal of the 1951 Chinese annexation of Tibet. After protesters acquired weapons, the Chinese People's Liberation Army (PLA) shelled protesters in the Dalai Lama's summer palace and deployed tanks to suppress the demonstrations. Bloody fighting continued for the next three days while the Dalai Lama escaped to India. Thousands of Tibetans were killed during the 1959 uprising, but the exact number is disputed. Earlier in 1956, armed conflict between Tibetan guerrillas and the PLA started in the Kham and Amdo regions, which had been subjected to socialist reform. The guerrilla warfare later spread to other areas of Tibet and lasted throug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jasper Becker
Jasper Martin Becker (born 19 May 1956) is a British author, commentator, and journalist who has spent two decades as a foreign correspondent, mostly in China. Journalism In 1995, he joined the staff of the Hong Kong–based ''South China Morning Post''. He was later promoted to the senior position of Beijing bureau chief, which meant he was in charge of all mainland content. In 2002, he lost his job, in an experience he writes about in a ''Washington Post'' column headlined "Why I Was Fired in Hong Kong." Given his often critical views of China, his abrupt removal was considered by some to be a sign of deteriorating press freedoms in Hong Kong. Becker's dismissal for "insubordination" was widely reported in the international media. He was fired after commenting that the paper was restricting his reporting and downplaying coverage on AIDS and labour disturbances on the Mainland. Publications Becker's books include: * ''The Lost Country: Mongolia Revealed'' (1992) * '' Hung ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laogai
''Laogai'' (), short for ''laodong gaizao'' (), which means reform through labor, is a criminal justice system involving the use of penal labor and prison farms in the People's Republic of China (PRC). ''Láogǎi'' is different from ''láojiào'', or re-education through labor, which was the abolished administrative detention system for people who were not criminals but had committed Misdemeanor, minor offenses, and was intended to "reform offenders into law-abiding citizens". Persons who were detained in the ''laojiao'' were detained in facilities that were separate from those which comprised the general prison system of the ''laogai''. Both systems, however, were based on penal labor. Some writers have likened the ''laogai'' to Slavery in China, slavery. History Maoist era During the 1950s and 1960s, Chinese prisons, which were similar to organized factories, contained large numbers of people who were considered too critical of the government or "counter-revolution ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xikang
Xikang (formerly romanized as Sikang or Hsikang, or 'Kham to the west f Sichuan) was a nominal province formed by the Republic of China (1912–1949)">Republic of China in 1939 on the initiative of prominent Sichuan warlord Liu Wenhui and retained by the early China, People's Republic of China. The former territory of Xikang is now divided between the Tibet Autonomous Region (TAR) and Sichuan, Sichuan province. The idea behind Xikang province was to form a single unified province for the entire Kham region under direct Chinese administration, in effect annexing the western Kham region that was then under Tibetan control. Kham was entirely populated by Tibetan people called Khampas. The then-independent Tibet controlled the portion of Kham west of the Upper Yangtze River. The nominal Xikang province also included in the south the Assam Himalayan region (Arunachal Pradesh) that Tibet had recognised as a part of British India by the 1914 McMahon Line agreement. The easter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Republic Of China (1912–1949)
The Republic of China (ROC) began on 1 January 1912 as a sovereign state in mainland China following the 1911 Revolution, which overthrew the Manchu people, Manchu-led Qing dynasty and ended China's imperial China, imperial history. From 1927, the Kuomintang (KMT) Northern expedition, reunified the country and initially ruled it as a one-party state with Nanjing as the national capital. In 1949, Nationalist government, the KMT-led government was defeated in the Chinese Civil War and lost control of the mainland to the Chinese Communist Party (CCP). The CCP Proclamation of the People's Republic of China, established the People's Republic of China (PRC) while the ROC was forced to Retreat of the government of the Republic of China to Taiwan, retreat to Taiwan; the ROC retains control over the Taiwan Area, and political status of Taiwan, its political status remains disputed. The ROC is recorded as a founding member of both the League of Nations and the United Nations, and previous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dorris Shelton Still
Dorris Evangeline Shelton Still (25 August 1904 – 29 April 1997 p. 352) was an American author. She wrote the book ''Sue in Tibet'', a semi-biographical work about growing up in . She was born in Kangding, in the region of Tibet. Biography She was the eldest daughter of Albert Shelton (1875–1 ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |