Xikang on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
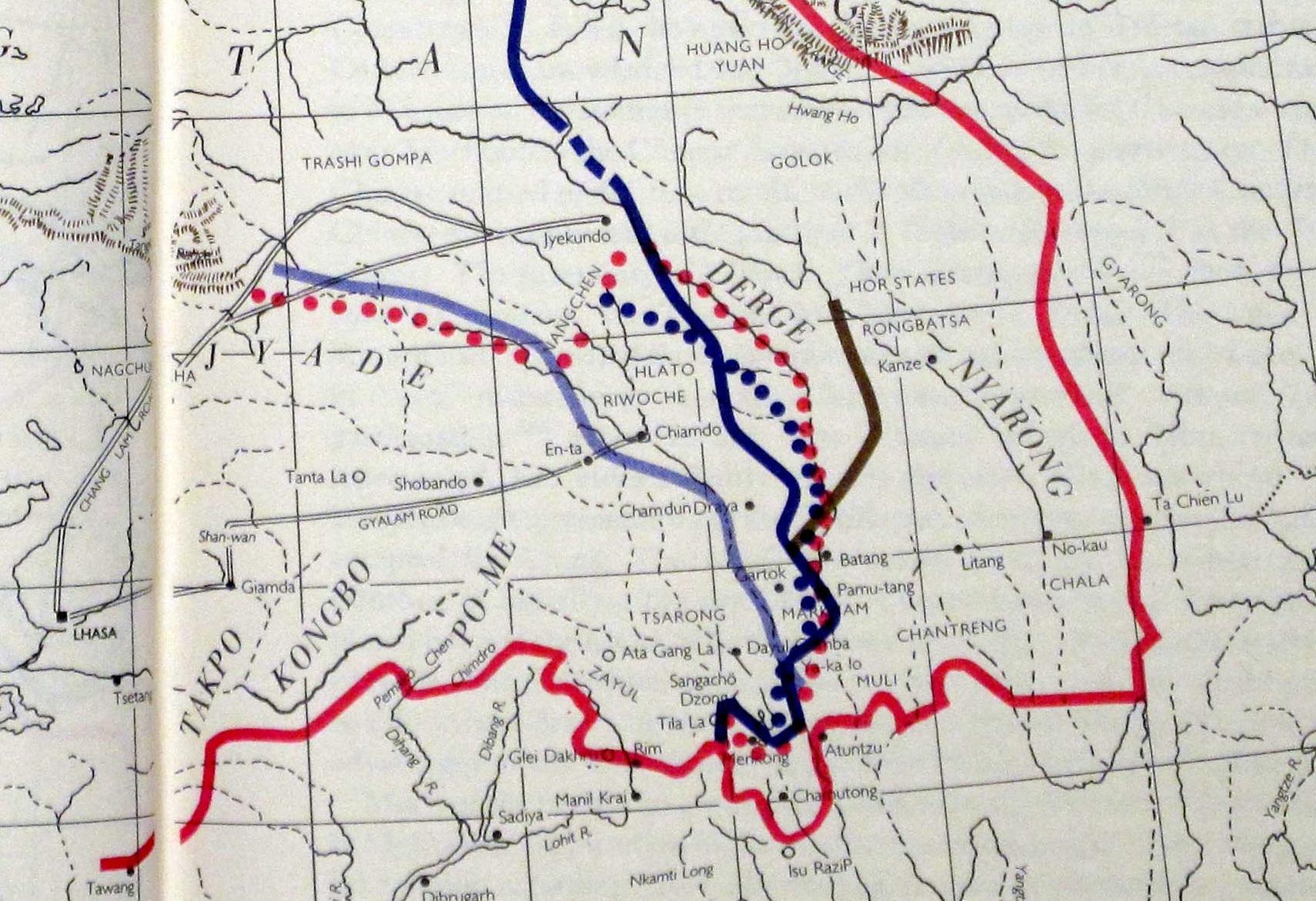 Following the 1905 Batang uprising, Qing China appointed Zhao Erfeng as the Imperial Commissioner for the Sichuan-Yunnan Frontier. Zhao reduced all the autonomous native states in both the western and eastern Kham by 1910 and converted them into Chinese districts governed by magistrates. He signed an agreement with the Tibetan government setting the border between China and Tibet at Gyamda. This paved the way for the formation of a Xikang province, proposed by Zhang's successor Fu Songmu.
Following the Wuchang Uprising in October 1911, which led to the downfall of the
Following the 1905 Batang uprising, Qing China appointed Zhao Erfeng as the Imperial Commissioner for the Sichuan-Yunnan Frontier. Zhao reduced all the autonomous native states in both the western and eastern Kham by 1910 and converted them into Chinese districts governed by magistrates. He signed an agreement with the Tibetan government setting the border between China and Tibet at Gyamda. This paved the way for the formation of a Xikang province, proposed by Zhang's successor Fu Songmu.
Following the Wuchang Uprising in October 1911, which led to the downfall of the
Xikang (formerly romanized as Sikang or Hsikang, or 'Kham to the west f Sichuan">Sichuan.html" ;"title="f Sichuan">f Sichuan) was a nominal province
formed by the Republic of China (1912–1949)">Republic of China
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia. The main geography of Taiwan, island of Taiwan, also known as ''Formosa'', lies between the East China Sea, East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocea ...
in 1939 on the initiative of prominent Sichuan
Sichuan is a province in Southwestern China, occupying the Sichuan Basin and Tibetan Plateau—between the Jinsha River to the west, the Daba Mountains to the north, and the Yunnan–Guizhou Plateau to the south. Its capital city is Cheng ...
warlord Liu Wenhui and retained by the early China, People's Republic of China. The former territory of Xikang is now divided between the Tibet Autonomous Region (TAR) and Sichuan, Sichuan province.
The idea behind Xikang province was to form a single unified province for the entire Kham
Kham (; ) is one of the three traditional Tibet, Tibetan regions, the others being Domey also known as Amdo in the northeast, and Ü-Tsang in central Tibet. The official name of this Tibetan region/province is Dotoe (). The original residents of ...
region under direct Chinese administration, in effect annexing the western Kham region that was then under Tibetan control. Kham was entirely populated by Tibetan people called Khampas. The then-independent Tibet
Tibet (; ''Böd''; ), or Greater Tibet, is a region in the western part of East Asia, covering much of the Tibetan Plateau and spanning about . It is the homeland of the Tibetan people. Also resident on the plateau are other ethnic groups s ...
controlled the portion of Kham west of the Upper Yangtze River.
The nominal Xikang province also included in the south the Assam Himalayan region (Arunachal Pradesh
Arunachal Pradesh (; ) is a States and union territories of India, state in northeast India. It was formed from the North-East Frontier Agency (NEFA) region, and India declared it as a state on 20 February 1987. Itanagar is its capital and la ...
) that Tibet had recognised as a part of British India
The provinces of India, earlier presidencies of British India and still earlier, presidency towns, were the administrative divisions of British governance in South Asia. Collectively, they have been called British India. In one form or another ...
by the 1914 McMahon Line agreement.
The eastern part of the province was inhabited by a number of different ethnic groups, such as Han Chinese
The Han Chinese, alternatively the Han people, are an East Asian people, East Asian ethnic group native to Greater China. With a global population of over 1.4 billion, the Han Chinese are the list of contemporary ethnic groups, world's la ...
, Yi, Qiang people and Tibetan, then known as ''Chuanbian'' (), a special administrative region of the Republic of China. In 1939, it became the new Xikang province with the additional territories belonging to Tibetan and British control added in. It was taken over by Chinese communist forces in 1949.
The provincial capital of Xikang was Kangding from 1939 to 1951 and Ya'an from 1951 to 1955. The province had a population of 3.4 million in 1954. In 1955, its eastern half was merged into Sichuan, and its western half came under the administration of the TAR preparatory committee.
Overview
The idea of "Xikang" was to construct an independent province of China for the entireKham
Kham (; ) is one of the three traditional Tibet, Tibetan regions, the others being Domey also known as Amdo in the northeast, and Ü-Tsang in central Tibet. The official name of this Tibetan region/province is Dotoe (). The original residents of ...
region, which would be separate from Tibet
Tibet (; ''Böd''; ), or Greater Tibet, is a region in the western part of East Asia, covering much of the Tibetan Plateau and spanning about . It is the homeland of the Tibetan people. Also resident on the plateau are other ethnic groups s ...
as well as Sichuan
Sichuan is a province in Southwestern China, occupying the Sichuan Basin and Tibetan Plateau—between the Jinsha River to the west, the Daba Mountains to the north, and the Yunnan–Guizhou Plateau to the south. Its capital city is Cheng ...
. Even though it was defined in regulations and sketched out on maps, only the eastern Kham region was ever under the control of the Republic of China
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia. The main geography of Taiwan, island of Taiwan, also known as ''Formosa'', lies between the East China Sea, East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocea ...
.
History
 Following the 1905 Batang uprising, Qing China appointed Zhao Erfeng as the Imperial Commissioner for the Sichuan-Yunnan Frontier. Zhao reduced all the autonomous native states in both the western and eastern Kham by 1910 and converted them into Chinese districts governed by magistrates. He signed an agreement with the Tibetan government setting the border between China and Tibet at Gyamda. This paved the way for the formation of a Xikang province, proposed by Zhang's successor Fu Songmu.
Following the Wuchang Uprising in October 1911, which led to the downfall of the
Following the 1905 Batang uprising, Qing China appointed Zhao Erfeng as the Imperial Commissioner for the Sichuan-Yunnan Frontier. Zhao reduced all the autonomous native states in both the western and eastern Kham by 1910 and converted them into Chinese districts governed by magistrates. He signed an agreement with the Tibetan government setting the border between China and Tibet at Gyamda. This paved the way for the formation of a Xikang province, proposed by Zhang's successor Fu Songmu.
Following the Wuchang Uprising in October 1911, which led to the downfall of the Qing dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing, was a Manchu-led Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China and an early modern empire in East Asia. The last imperial dynasty in Chinese history, the Qing dynasty was preceded by the ...
, the region subdued by Frontier Commissioners was established as the Chuanbian Special Administrative District () by the newly founded Republic of China.
In June 1930, eastern Kham (later Xikang) was invaded by the army of Tibet, precipitating the Sino-Tibetan War. With the district locked in internal struggles, no reinforcements were sent to support the Sichuan
Sichuan is a province in Southwestern China, occupying the Sichuan Basin and Tibetan Plateau—between the Jinsha River to the west, the Daba Mountains to the north, and the Yunnan–Guizhou Plateau to the south. Its capital city is Cheng ...
ese troops stationed here. As a result, the Tibetan army captured Garzê and Xinlong Counties without encountering much resistance. When a negotiated ceasefire failed, Tibetan forces expanded the war, attempting to capture parts of southern Qinghai province. In March 1932, their force invaded Qinghai but was defeated by the local Hui warlord Ma Bufang in July, who routed the Tibetan army and drove it back to this district.
The Hui army captured counties that had fallen into the hands of the Tibetan army since 1919. Their victories threatened the supply lines of the Tibetan forces in Garzê and Xinlong. As a result, part of the Tibetan army was forced to withdraw.
In 1932 Liu Wenhui in cooperation with the Qinghai army, sent out a brigade
A brigade is a major tactical military unit, military formation that typically comprises three to six battalions plus supporting elements. It is roughly equivalent to an enlarged or reinforced regiment. Two or more brigades may constitute ...
to attack the Tibetan troops in Garzê and Xinlong, eventually occupying them, Dêgê and other counties east of the Jinshajiang River. The 1934 Khamba Rebellion led by the Pandatsang family broke out against the Tibetan government in Lhasa. The Khampa revolutionary leader Pandatsang Rapga was involved.
In January 1939, the ''Chuanbian Special Administrative District'' officially became a province of the Republic, the Hsikang Province. Kesang Tsering was sent by the Chinese to Batang to take control of Xikang, where he formed a local government. He was sent there for the purpose of propagating the Three Principles of the People to the Khampa.
In 1949, the People's Liberation Army
The People's Liberation Army (PLA) is the military of the Chinese Communist Party (CCP) and the People's Republic of China (PRC). It consists of four Military branch, services—People's Liberation Army Ground Force, Ground Force, People's ...
took control of Xikang. In 1955, western Xikang was merged into Sichuan
Sichuan is a province in Southwestern China, occupying the Sichuan Basin and Tibetan Plateau—between the Jinsha River to the west, the Daba Mountains to the north, and the Yunnan–Guizhou Plateau to the south. Its capital city is Cheng ...
, and eastern Xikang came under the administration of the Preparatory Committee for the Tibet Autonomous Region.
Administrative divisions
1939–1950
1950–1955
List of governors
Chairperson of the Provincial Government
Xikang CCP Committee Secretary
People's Government Chairperson/Governor
See also
* *Kham
Kham (; ) is one of the three traditional Tibet, Tibetan regions, the others being Domey also known as Amdo in the northeast, and Ü-Tsang in central Tibet. The official name of this Tibetan region/province is Dotoe (). The original residents of ...
References
Bibliography
* * * * * * {{Authority control 1930s in Tibet 1939 establishments in Asia 20th-century establishments in Tibet Provinces of the Republic of China (1912–1949) Former provinces of China Tibet 1950 disestablishments in China