|
Xikang
Xikang (also Sikang or Hsikang) was a nominal province formed by the Republic of China in 1939 on the initiative of prominent Sichuan warlord Liu Wenhui and continued by the early People's Republic of China. Thei idea was to form a single unified province for the entire Kham region under direct Chinese administration, in effect annexing the western Kham region that was then under Tibetan control. Kham was entirely populated by Tibetan people called Khampas. The then independent Tibet controlled the portion of Kham west of the Upper Yangtze River. The nominal Xikang province also included in the south the Assam Himalayan region (Arunachal Pradesh) that Tibet had recognised as a part of British India by the 1914 McMahon Line agreement. The eastern part of the province was inhabited by a number of different ethnic groups, such as Han Chinese, Yi, Qiang people and Tibetan, then known as ''Chuanbian'' (), a special administrative region of the Republic of China. In 1939, it bec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
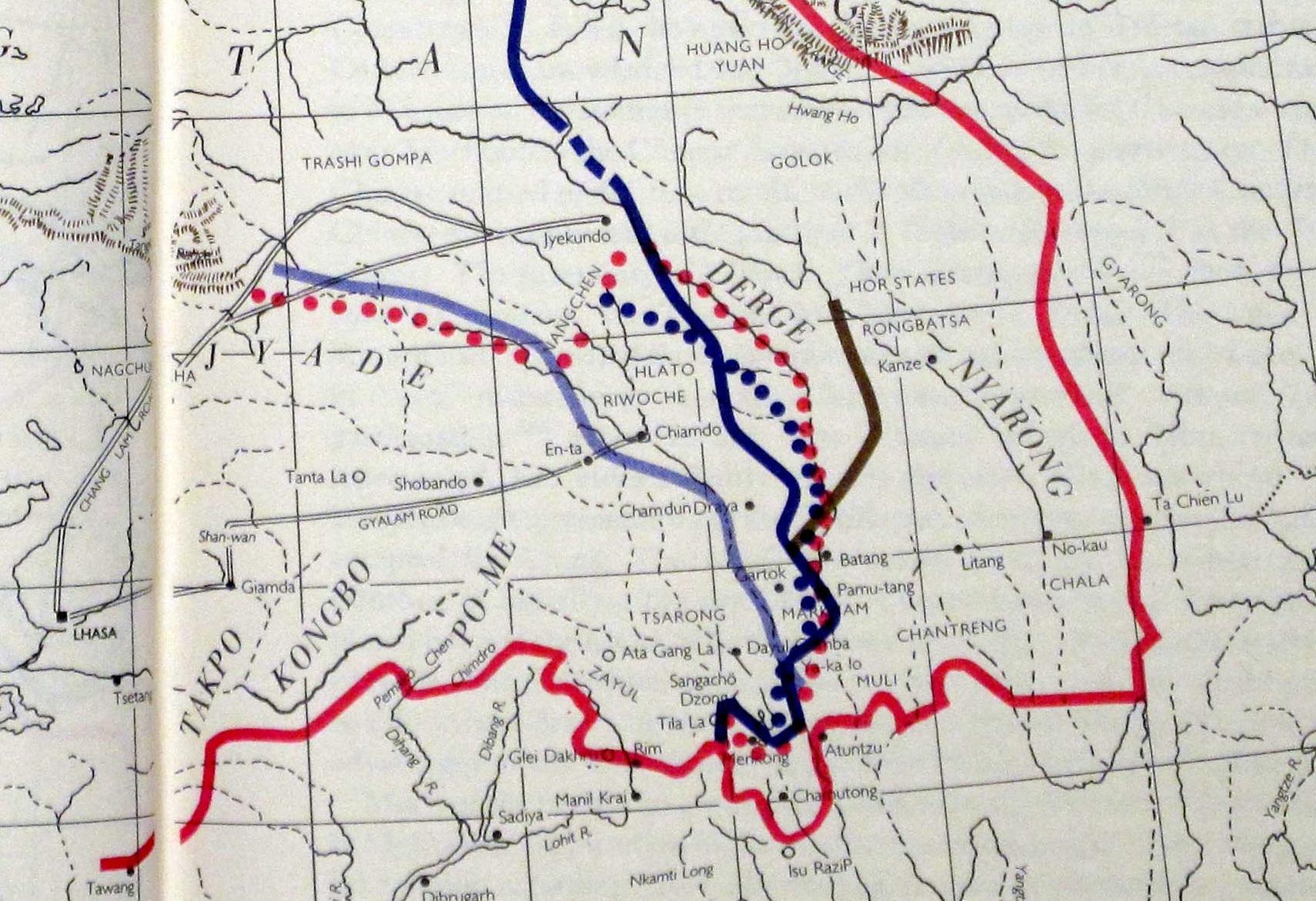
Xikang Province In 1950 CIA Map Of Tibet
Xikang (also Sikang or Hsikang) was a nominal province formed by the Republic of China in 1939 on the initiative of prominent Sichuan warlord Liu Wenhui and continued by the early People's Republic of China. Thei idea was to form a single unified province for the entire Kham region under direct Chinese administration, in effect annexing the western Kham region that was then under Tibetan control. Kham was entirely populated by Tibetan people called Khampas. The then independent Tibet controlled the portion of Kham west of the Upper Yangtze River. The nominal Xikang province also included in the south the Assam Himalayan region (Arunachal Pradesh) that Tibet had recognised as a part of British India by the 1914 McMahon Line agreement. The eastern part of the province was inhabited by a number of different ethnic groups, such as Han Chinese, Yi, Qiang people and Tibetan, then known as ''Chuanbian'' (), a special administrative region of the Republic of China. In 1939, it became ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liu Wenhui
Liu Wenhui (; 1895 – 24 June 1976) was a Chinese general and warlord of Sichuan province ( Sichuan clique). At the beginning of his career, he was aligned with the Kuomintang (KMT), commanding the Sichuan-Xikang Defence Force from 1927 to 1929. The western part of Sichuan province was then known as Xikang. Bordering Tibet, the region had a mixed population of Tibetans and Han Chinese. In 1949 he defected to the Communist forces of Mao Zedong, and went on to hold high office in the new People's Republic of China, serving as Minister of Forestry (1959–1967), member of the National People's Congress, member of the National Committee of the Chinese People's Political Consultative Conference, and member of the Central Committee of the Revolutionary Committee of the Chinese Kuomintang. Military career and Republic of China Liu Wenhui was born in 1895 in Dayi County, Sichuan, and studied at the Baoding Military Academy, graduating in 1916.Wang Chengbin (editor-in-chief) "Republic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khampa (people)
Kham (; ) is one of the three traditional Tibetan regions, the others being Amdo in the northeast, and Ü-Tsang in central Tibet. The original residents of Kham are called Khampas (), and were governed locally by chieftains and monasteries. Kham presently covers a land area distributed between five regions in China, most of it in Tibet Autonomous Region and Sichuan, with smaller portions located within Qinghai, Gansu and Yunnan provinces. Densely forested with grass plains, its convergence of six valleys and four rivers supported independent Kham polities of Tibetan warrior kingdoms together with Tibetan Buddhist monastic centers.Jann Ronis"An Overview of Kham (Eastern Tibet) Historical Polities" The University of Virginia The early trading route between Central Tibet and China traveled through Kham, and Kham is said to be the inspiration for Shangri-La in James Hilton's novel. Settled as Tibet's eastern frontier in the 7th century, King Songtsen Gampo built temples along its e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kham
Kham (; ) is one of the three traditional Tibetan regions, the others being Amdo in the northeast, and Ü-Tsang in central Tibet. The original residents of Kham are called Khampas (), and were governed locally by chieftains and monasteries. Kham presently covers a land area distributed between five regions in China, most of it in Tibet Autonomous Region and Sichuan, with smaller portions located within Qinghai, Gansu and Yunnan provinces. Densely forested with grass plains, its convergence of six valleys and four rivers supported independent Kham polities of Tibetan warrior kingdoms together with Tibetan Buddhist monastic centers.Jann Ronis"An Overview of Kham (Eastern Tibet) Historical Polities" The University of Virginia The early trading route between Central Tibet and China traveled through Kham, and Kham is said to be the inspiration for Shangri-La in James Hilton's novel. Settled as Tibet's eastern frontier in the 7th century, King Songtsen Gampo built temples along its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sino-Tibetan War
The Sino-Tibetan War (, lit. Kham–Tibet dispute) was a war that began in 1930 when the Tibetan Army under the 13th Dalai Lama responded to the attempted seizure of a monastery. Chinese-administered eastern Kham region (later called Xikang), and the Yushu region in Qinghai, over disputes regarding monasteries. Ma clique warlord Ma Bufang secretly sent a telegram to Sichuan warlord Liu Wenhui and the leader of the Republic of China, Chiang Kai-shek, suggesting a joint attack on the Tibetan forces. Their armies rapidly overwhelmed and defeated the Tibetan Army. Background The roots of the conflict lay in three areas: first, the disputed border between Tibetan government territory and the territory of the Republic of China, with the Tibetan government in principle claiming areas inhabited by Tibetans in neighboring Chinese provinces (Qinghai, Sichuan) which were in fact ruled by Chinese warlords loosely aligned with the Republic; second, the tense relationship between the 13 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sichuan
Sichuan (; zh, c=, labels=no, ; zh, p=Sìchuān; alternatively romanized as Szechuan or Szechwan; formerly also referred to as "West China" or "Western China" by Protestant missions) is a province in Southwest China occupying most of the Sichuan Basin and the easternmost part of the Tibetan Plateau between the Jinsha River on the west, the Daba Mountains in the north and the Yungui Plateau to the south. Sichuan's capital city is Chengdu. The population of Sichuan stands at 83 million. Sichuan neighbors Qinghai to the northwest, Gansu to the north, Shaanxi to the northeast, Chongqing to the east, Guizhou to the southeast, Yunnan to the south, and the Tibet Autonomous Region to the west. In antiquity, Sichuan was the home of the ancient states of Ba and Shu. Their conquest by Qin strengthened it and paved the way for Qin Shi Huang's unification of China under the Qin dynasty. During the Three Kingdoms era, Liu Bei's state of Shu was based in Sichuan. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Provinces Of China
The provincial level administrative divisions () are the highest-level administrative divisions of China. There are 34 such divisions claimed by the People's Republic of China, classified as 23 provinces (), five autonomous regions, four municipalities and two special administrative regions. The political status of Taiwan Province along with a small fraction of Fujian Province remain in dispute; those are under separate rule by the Republic of China, which is usually referred to as "Taiwan". Every province on Mainland China (including the island province of Hainan) has a Chinese Communist Party (CCP) provincial committee (), headed by a secretary (). The Committee Secretary is effectively in charge of the province, rather than the governor of the provincial government. The same arrangement exists for the autonomous regions and municipalities. Types of provincial level divisions Province The government of each standard province () is nominally led by a provincial co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Special Administrative Regions Of China
The special administrative regions (SAR) of the People's Republic of China are one of the provincial-level administrative divisions of the People's Republic of China directly under the control of its Central People's Government (State Council), being integral areas of the country. As a region, they possess the highest degree of autonomy from China. However, despite the relative autonomy that the Central People's Government offers the special administrative regions, the National People's Congress remains capable of enforcing laws for the special administrative regions. The legal basis for the establishment of SARs, unlike the other administrative divisions of China, is provided for by Article 31, rather than Article 30, of the Constitution of the People's Republic of China of 1982. Article 31 reads: "The state may establish special administrative regions when necessary. The systems to be instituted in special administrative regions shall be prescribed by law enacted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ya'an
Ya'an (, Tibetan: Yak-Nga ) is a prefecture-level city in the western part of Sichuan province, China, located just below the Tibetan Plateau. The city is home to Sichuan Agricultural University, the only 211 Project university and the largest regional comprehensive university in Ya'an. As of the 2020 Chinese census, Ya'an has a population of 1,434,603. History Previously known as Yazhou-fu, the city is first mentioned during the Zhou Dynasty (1122-255 BCE). It served as a county seat during the Qin and Han Dynasties, but was subsequently taken by nomadic tribes. After being reintegrated into the Chinese Empire in the late 5th century, it was made the seat of the ''Ya Prefecture'' in 604. The modern Ya'an county was established in 1912. It became the provincial capital of Xikang province in 1951, but has been a municipality under the administration of Sichuan province since 1955, when Xikang province was merged and became a part of Sichuan province. The first giant panda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chamdo Region
Chamdo Region or Qamdo Region () was a province-level area of the People's Republic of China comprising most of the western Kham region of traditional Tibet, where the Khampa, a subgroup of the Tibetan people, live. Chamdo split from Xikang Province in 1950 after the Battle of Chamdo. Chamdo was merged into Tibet Autonomous Region in 1965. Administrative divisions 1950–1956 See also * Xikang Province * Kham Region * Chamdo Chamdo, officially Qamdo () and also known in Chinese as Changdu, is a prefecture-level city in the eastern part of the Tibet Autonomous Region, China. Its seat is the town of Chengguan in Karuo District. Chamdo is Tibet's third largest city ... Prefecture-level City References 1950 establishments in China Former provinces of China Kham Chamdo 1956 disestablishments in China {{PRChina-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tibet
Tibet (; ''Böd''; ) is a region in East Asia, covering much of the Tibetan Plateau and spanning about . It is the traditional homeland of the Tibetan people. Also resident on the plateau are some other ethnic groups such as Monpa people, Monpa, Tamang people, Tamang, Qiang people, Qiang, Sherpa people, Sherpa and Lhoba peoples and now also considerable numbers of Han Chinese and Hui people, Hui settlers. Since Annexation of Tibet by the People's Republic of China, 1951, the entire plateau has been under the administration of the People's Republic of China, a major portion in the Tibet Autonomous Region, and other portions in the Qinghai and Sichuan provinces. Tibet is the highest region on Earth, with an average elevation of . Located in the Himalayas, the highest elevation in Tibet is Mount Everest, Earth's highest mountain, rising 8,848.86 m (29,032 ft) above sea level. The Tibetan Empire emerged in the 7th century. At its height in the 9th century, the Tibet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Republic Of China (1912–1949)
The Republic of China (ROC), between 1912 and 1949, was a sovereign state recognised as the official designation of China when it was based on Mainland China, prior to the relocation of its central government to Taiwan as a result of the Chinese Civil War. At a population of 541 million in 1949, it was the world's most populous country. Covering , it consisted of 35 provinces, 1 special administrative region, 2 regions, 12 special municipalities, 14 leagues, and 4 special banners. The People's Republic of China (PRC), which rules mainland China today, considers ROC as a country that ceased to exist since 1949; thus, the history of ROC before 1949 is often referred to as Republican Era () of China. The ROC, now based in Taiwan, today considers itself a continuation of the country, thus calling the period of its mainland governance as the Mainland Period () of the Republic of China in Taiwan. The Republic was declared on 1 January 1912 after the Xinhai Revolution, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |