|
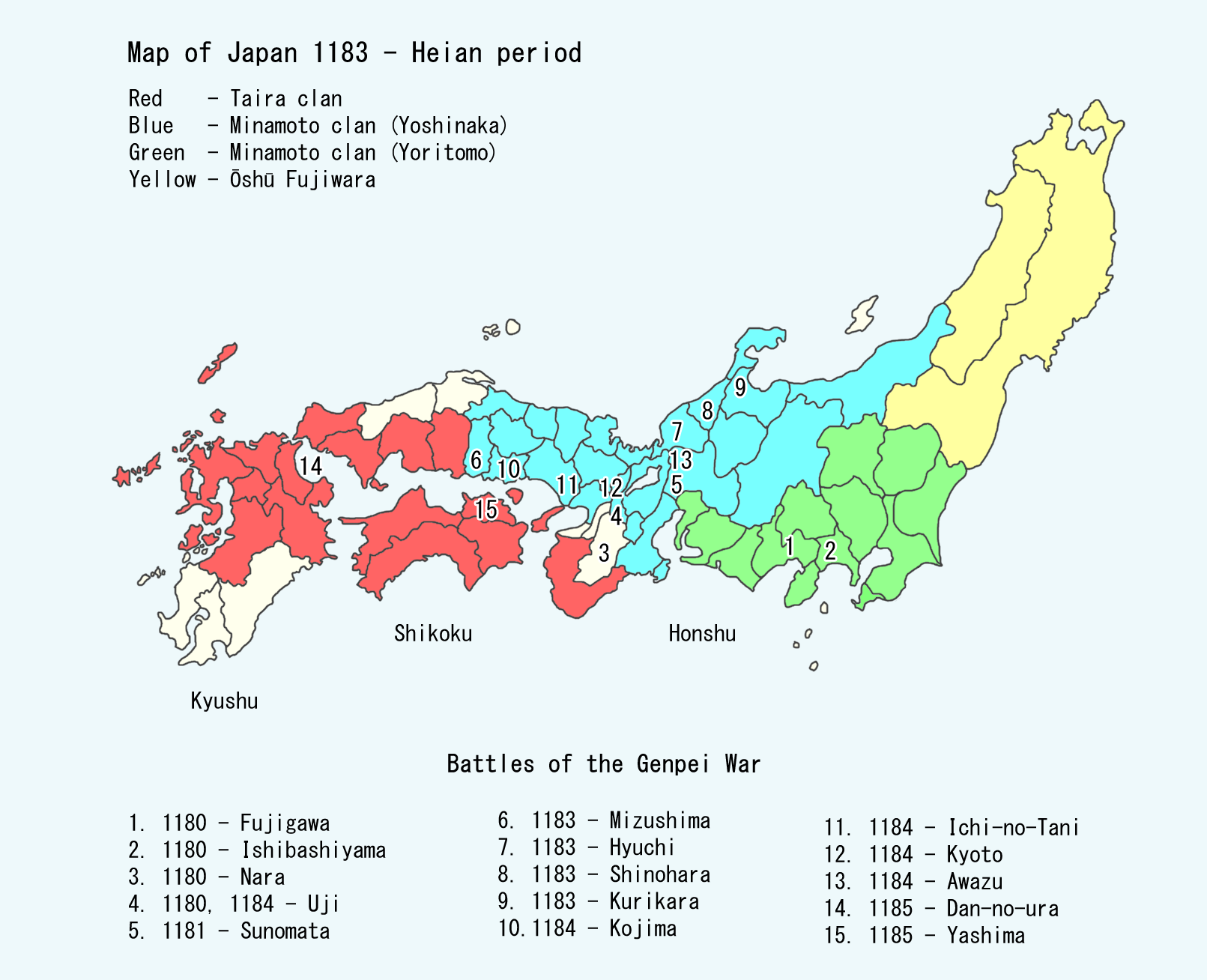
Taira Clan
The was one of the four most important Japanese clans, clans that dominated Japanese politics during the Heian period, Heian period of History of Japan, Japanese history – the others being the Minamoto clan, Minamoto, the Fujiwara clan, Fujiwara, and the Tachibana clan (kuge), Tachibana. The clan is divided into four major groups, named after the Emperor of Japan, emperors they descended from: Emperor Kanmu, Kanmu Heishi, Emperor Ninmyō, Ninmyō Heishi, Emperor Montoku, Montoku Heishi, and Emperor Kōkō, Kōkō Heishi, the most influential of which was the Kanmu Heishi line. In the twilight of the Heian period, the Taira controlled the boy emperor Emperor Antoku, Antoku (himself the grandson of the powerful ''Kugyō'' Taira no Kiyomori) and had effectively dominated the Imperial capital of Heian-kyō, Heian. However, they were opposed by their rivals the Minamoto clan (the Genji), which culminated in the Genpei War (1180–1185 AD). The five-year-long war concluded with a d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hitachi Province
was an old provinces of Japan, old province of Japan in the area of Ibaraki Prefecture.Louis Frédéric, Nussbaum, Louis-Frédéric. (2005). "''Hitachi fudoki''" in . It was sometimes called . Hitachi Province bordered on Shimōsa Province, Shimōsa (Lower Fusa Province, Fusa), Shimotsuke Province, Shimotsuke, and Mutsu Province, Mutsu (Iwase Province, Iwase -1718-, Iwashiro Province, Iwashiro -1869-, Iwaki Province (718), Iwaki -1718- and Iwaki Province (1868), -1869-) Provinces. Generally, its northern border was with Mutsu. History The ancient provincial capital (Hitachi Kokufu) and temple (Hitachi Kokubun-ji) were located near modern Ishioka, Ibaraki, Ishioka and have been excavated, while the chief shrine was further east at Kashima, Ibaraki, Kashima (Kashima Shrine). The province was established in the 7th century. In the Sengoku period the area was divided among several ''daimyōs'', but the chief castle was usually in the Mito Castle of the modern city of Mito, Ibar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adjectival Noun (Japanese)
In descriptions of the Japanese language, an adjectival noun, nominal adjective, copular noun, , quasi-adjective, pseudo-adjective, or ''na''-adjective, is a noun that can function as an adjective by taking the particle 〜な ''-na''. (In comparison, regular nouns can function adjectivally by taking the particle 〜の ''-no'', which is analyzed as the genitive case.) Adjectival nouns constitute one of several Japanese word classes that can be considered equivalent to adjectives. In their attributive function, Japanese adjectival nouns function similarly to English noun adjuncts, as in "''chicken'' soup" or "''winter'' coat" – in these cases, the nouns "chicken" and "winter" modify the nouns "soup" and "coat", respectively. Japanese adjectival nouns can also be used predicatively – in that use, they do not take the ''-na'' suffix, but normally combine with forms of the copular verb. Terminology The current term for the so-called "adjectival nouns" is . Here, ref ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taira No Kiyomori
was a military leader and '' kugyō'' of the late Heian period of Japan. He established the first samurai-dominated administrative government in the history of Japan. Early life Kiyomori was born in Japan, in 1118 as the first son of Taira no Tadamori. His mother, Gion no Nyogo, was wife of Tadamori and a palace servant according to '' The Tale of the Heike''. Family Father: Taira no TadamoriMother: Gion no Nyogo (d. 1147)Concubine(s): Taira no TokikoChildren: * Taira no Shigemori * Taira no Munemori * Taira no Tomomori * Taira no Tokuko * Taira no Shigehira Career After the death of his father in 1153, Kiyomori assumed control of the Taira clan and ambitiously entered the political realm, in which he had previously only held a minor post. Before that though, in 1156, he and Minamoto no Yoshitomo, head of the Minamoto clan, suppressed the rebels in the Hōgen Rebellion. This established the Taira and Minamoto as the top samurai clans in Kyoto. However, this ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kugyō
is the collective term for the very few most powerful men attached to the court of the Emperor of Japan in pre-Meiji eras. The term generally referred to the and court officials and denoted a court rank between First Rank and Third Rank under the '' Ritsuryō'' system, as opposed to the lower court nobility, thus being the collective term for the upper court nobility. However, later on some holders of the Fourth Rank were also included. In 1869, following the Meiji Restoration, the court nobility and daimyo were merged into a new peerage, the '' kazoku''. Overview The ''kugyō'' generally refers to two groups of court officials: * the ''Kō'' (公), comprising the Chancellor of the Realm, the Minister of the Left, and the Minister of the Right; and * the ''Kei'' (卿), comprising the Major Counsellor, the Middle Counsellor, and the Associate Counselors, who held the court rank of Third Rank or higher. History The ''kugyō'' originated from the Three Lords a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emperor Antoku
was the 81st emperor of Japan, according to the traditional order of succession. His reign spanned the years from 1180 through 1185. His death marked the end of the Heian period and the beginning of the Kamakura period. During this time, the Imperial family was involved in a bitter struggle between warring clans. Minamoto no Yoritomo with his cousin Minamoto no Yoshinaka, led a force from the Minamoto clan against the Taira, who controlled the emperor. During the climactic sea Battle of Dan-no-ura in April 1185, Antoku's grandmother Taira no Tokiko took him and plunged with him into the water in the Shimonoseki Straits, drowning the child emperor rather than allowing him to be captured by the opposing forces. This clash of clans led to numerous legends and tales. The story of Emperor Antoku and his mother's family became the subject of the Kamakura period epic poem ''The Tale of the Heike'' (Heike is an alternative reading of the Japanese characters for "House of the Taira"). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emperor Kōkō
was the 58th emperor of Japan,Imperial Household Agency (''Kunaichō'') 光孝天皇 (58)/ref> according to the traditional order of succession. Kōkō reigned from 884 to 887. Traditional narrative Before the emperor's ascension to the Chrysanthemum Throne, his name (''imina'') was or ''Komatsu-tei''. He would later be identified sometimes as "the Emperor of Komatsu". This resulted in the later Emperor Go-Komatsu adopting this name (''go-'' meaning "later", so "Later Emperor Komatsu" or "Emperor Komatsu II"). Tokiyasu ''Shinnō'' was the third son of Emperor Ninmyō. His mother was Fujiwara no Sawako. Kōkō had four Imperial consorts and 41 Imperial sons and daughters.Brown, p. 289. Events of Kōkō's life The first '' kampaku'' Fujiwara no Mototsune was influential in the process by which Kōkō became an emperor. At the time Emperor Yōzei was deposed, Prince Tokiyasu was already Governor of Hitachi and Chief Minister of Ceremonies (''Jibu-kyō'', 治部卿) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emperor Montoku
(August 827 – 7 October 858) was the 55th emperor of Japan,Imperial Household Agency (''Kunaichō'') 文徳天皇 (55)/ref> according to the traditional order of succession. Montoku's reign lasted from 850 to 858. Traditional narrative Before Montoku's ascension to the Chrysanthemum Throne, his personal name (''imina'') was . He was also known as ''Tamura-no-mikado''Varley, p. 165. or ''Tamura-tei''. He was the eldest son of Emperor Ninmyō. His mother was Empress Dowager Fujiwara no Junshi (also called the Gojō empress 五条后), daughter of the minister of the left, Fujiwara no Fuyutsugu. Montoku had six Imperial consorts and 29 Imperial children.Brown, p. 285. Events of Montoku's life * 6 May 850 ('' Kashō 3, 21st day of the 3rd month''): In the 17th year of Ninmyō''-tennō''s reign (仁明天皇十七年), the emperor died; and his eldest son received the succession (''senso''). * 850 (''Kashō 3, 4th month''): Emperor Montoku formally acceded to the throne (''s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emperor Ninmyō
was the 54th emperor of Japan, Emperor Ninmyō, Fukakusa Imperial Mausoleum, Imperial Household Agency according to the traditional order of succession. Ninmyō's reign lasted from 833 to 850, during the Heian period. Traditional narrative Ninmyō was the second son of Emperor Saga and the Empress Tachibana no Kachiko. His personal name (''imina'') was . After his death, he was given the title . Ninmyō had nine Empresses, Imperial consorts, and concubines (''kōi''); and the emperor had 24 Imperial sons and daughters. Brown and Ishida, p. 283. Emperor Ninmyō is traditionally venerated at his tomb; the Imperial Household Agency designates , in Fushimi-ku, Kyoto, as the location of Ninmyō's mausoleum. Events of Ninmyō's life Ninmyō ascended to the throne following the abdication of his uncle, Emperor Junna. * 6 January 823 (): Received the title of Crown Prince at the age of 14. * 22 March 833 (): In the 10th year of Emperor Junna's reign, the emperor abdicated; and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emperor Of Japan
The emperor of Japan is the hereditary monarch and head of state of Japan. The emperor is defined by the Constitution of Japan as the symbol of the Japanese state and the unity of the Japanese people, his position deriving from "the will of the people with whom resides sovereign power". The Imperial Household Law governs the line of Succession to the Japanese throne, imperial succession. Pursuant to his constitutional role as a national symbol, and in accordance with rulings by the Supreme Court of Japan, the emperor is personally sovereign immunity, immune from prosecution. By virtue of his position as the head of the Imperial House of Japan, Imperial House, the emperor is also recognized as the head of the Shinto religion, which holds him to be the direct descendant of the sun goddess Amaterasu. According to tradition, the office of emperor was created in the 7th century BC, but the first historically verifiable emperors appear around the 5th or 6th centuries Anno Domini, AD ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tachibana Clan (kuge)
The was one of the four most powerful ''kuge'' (court nobility) families in Japan's Nara period, Nara and early Heian periods—the other three were the Minamoto clan, Minamoto, the Fujiwara clan, Fujiwara, and the Taira clan, Taira. Members of the Tachibana family often held high court posts within the Daijō-kan (Ministry of State), most frequently ''Sadaijin'' (Minister of the Left). Like the other major families at court, they also constantly sought to increase and secure their power by marrying into the Imperial House of Japan, imperial family. However, as the Minamoto clan and the Fujiwara clan gained power over the course of the 9th and 10th centuries, the Tachibana were eclipsed and eventually became scattered across the country. Though serving in high government posts outside the capital, they were thus denied the degree of power and influence within the court at Kyoto (Heian-kyō) which they once enjoyed. The name of ''Tachibana'' was bestowed on Agata no Inukai no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fujiwara Clan
The was a powerful family of imperial regents in Japan, descending from the Nakatomi clan and, as legend held, through them their ancestral god Ame-no-Koyane. The Fujiwara prospered since ancient times and dominated the imperial court until the Meiji Restoration in 1868. They held the title of Ason. The abbreviated form is . The 8th century clan history states the following at the biography of the clan's patriarch, Fujiwara no Kamatari (614–669): "Kamatari, the Inner Palace Minister who was also called ‘Chūrō'',''’ was a man of the Takechi district of Yamato Province. His forebears descended from Ame no Koyane no Mikoto; for generations they had administered the rites for Heaven and Earth, harmonizing the space between men and the gods. Therefore, it was ordered their clan was to be called Ōnakatomi" The clan originated when the founder, Nakatomi no Kamatari (614–669) of the Nakatomi clan, was rewarded by Emperor Tenji with the honorific "Fujiwara"after the w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minamoto Clan
was a Aristocracy (class), noble surname bestowed by the Emperors of Japan upon members of the Imperial House of Japan, imperial family who were excluded from the List of emperors of Japan, line of succession and demoted into the ranks of Nobility, the nobility since 814."...the Minamoto (1192-1333)". ''Warrior Rule in Japan'', page 11. Cambridge University Press. Several noble lines were bestowed the surname, the most notable of which was the Seiwa Genji, whose descendants established the Kamakura shogunate, Kamakura and Ashikaga shogunate, Ashikaga Shogun, shogunates following the Heian era. The Minamoto was one of the four great Japanese clans, clans that dominated Japanese politics during the Heian period, Heian period in History of Japan, Japanese history—the other three were the Fujiwara clan, Fujiwara, the Taira clan, Taira, and the Tachibana clan (kuge), Tachibana. In the late Heian period, Minamoto rivalry with the Taira culminated in the Genpei War (1180–1185 AD). T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |