|
Emperor Antoku
was the 81st emperor of Japan, according to the traditional order of succession. His reign spanned the years from 1180 through 1185. During this time, the Imperial family was involved in a bitter struggle between warring clans. Minamoto no Yoritomo with his cousin Minamoto no Yoshinaka, led a force from the Minamoto clan against the Taira, who controlled the emperor. During the climactic sea Battle of Dan-no-ura in April 1185, Antoku's grandmother Taira no Tokiko took him and plunged with him into the water in the Shimonoseki Straits, drowning the child emperor rather than allowing him to be captured by the opposing forces. The conflict between the clans led to numerous legends and tales. The story of Emperor Antoku and his mother's family became the subject of the Kamakura period epic poem ''The Tale of the Heike'' (Heike is an alternative reading of the Japanese characters for "House of the Taira"). Antoku's tomb is said to be located in a number of places around western ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emperor Of Japan
The Emperor of Japan is the monarch and the head of the Imperial Family of Japan. Under the Constitution of Japan, he is defined as the symbol of the Japanese state and the unity of the Japanese people, and his position is derived from "the will of the people with whom resides sovereign power". Imperial Household Law governs the line of imperial succession. The emperor is immune from prosecution by the Supreme Court of Japan. He is also the head of the Shinto religion. In Japanese, the emperor is called , literally "Emperor of heaven or " Heavenly Sovereign". The Japanese Shinto religion holds him to be the direct descendant of the sun goddess Amaterasu. The emperor is also the head of all national Japanese orders, decorations, medals, and awards. In English, the use of the term for the emperor was once common but is now considered obsolete. The Imperial House of Japan, known by their name the Yamato Dynasty, is amongst the oldest in the world, with its historical ori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
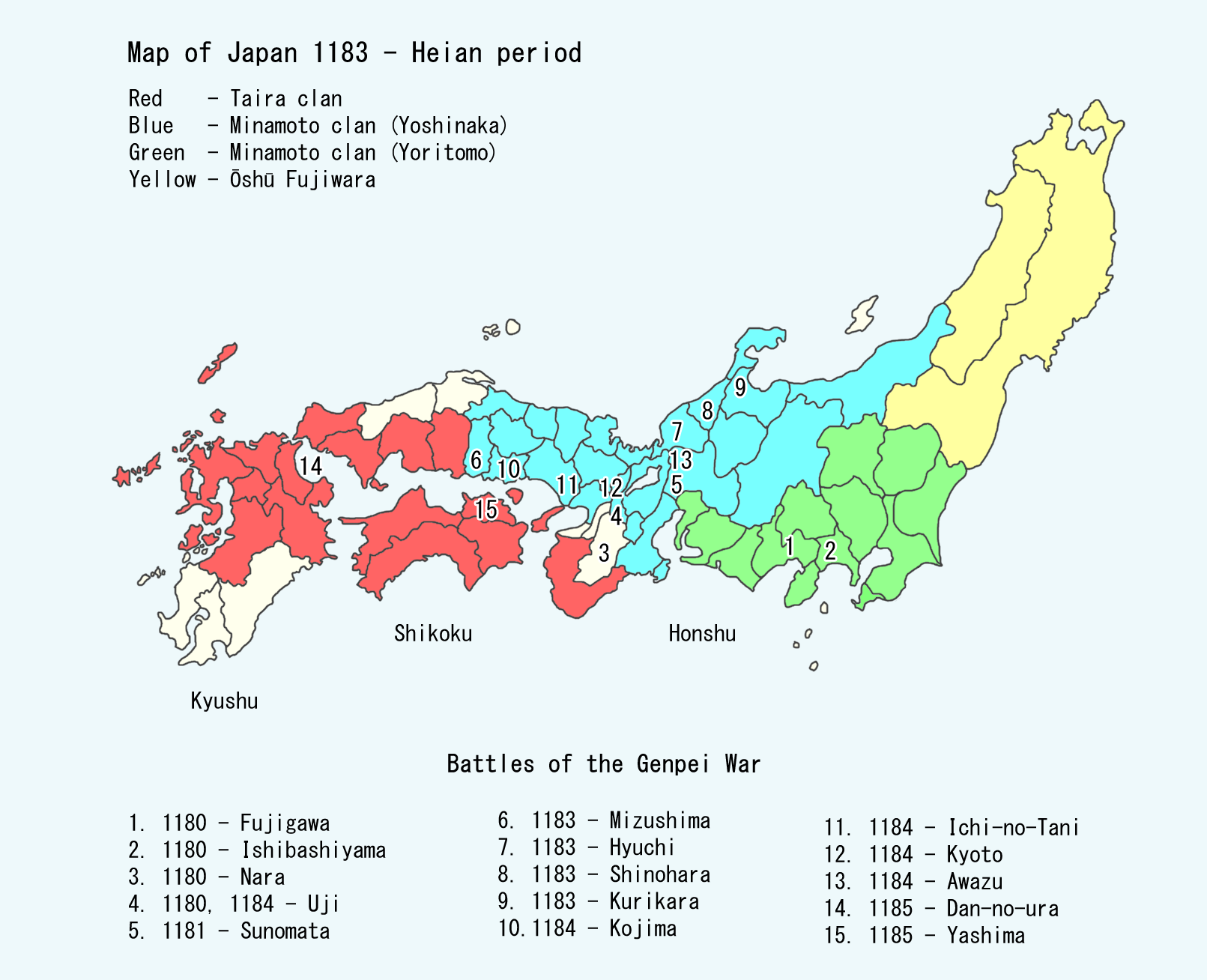
Kamakura Period
The is a period of Japanese history that marks the governance by the Kamakura shogunate, officially established in 1192 in Kamakura by the first '' shōgun'' Minamoto no Yoritomo after the conclusion of the Genpei War, which saw the struggle between the Taira and Minamoto clans. The period is known for the emergence of the samurai, the warrior caste, and for the establishment of feudalism in Japan. During the early Kamakura period, the shogunate continued warfare against the Northern Fujiwara which was only defeated in 1189. Then, the authority to the Kamakura rulers waned in the 1190s and power was transferred to the powerful Hōjō clan in the early 13th century with the head of the clan as regent ( Shikken) under the shogun which became a powerless figurehead. The later Kamakura period saw the invasions of the Mongols in 1274 and again in 1281. To reduce the amount of chaos, the Hōjō rulers decided to decentralize power by allowing two imperial lines – Northern and Sout ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jishō
was a after ''Angen'' and before '' Yōwa''. This period spanned the years from August 1177 through July 1181. The reigning emperors were and . Change of era * 1177 : The new era name was created to mark an event or a number of events. The previous era ended and a new one commenced in ''Angen'' 3, on the 4th day of the 8th month of 1177. Events of the ''Jishō'' era * 1177 (''Jishō 1, 28th day of the 4th month''): A great fire in the capital was spread by high winds; and the palace was reduced to cinders. * 1178 (''Jishō 2, 12th day of the 11th month''): Emperor Takakura's consort, Tokuko, gives birth to an infant who will become Emperor Antoku.Kitagawa, H. (1975). ''The Tale of the Heike'', p. 784. * 1180 (''Jisho 4, 21st day of the 2nd month''): Emperor Takakura abdicates. * 1180 (''Jishō 4, 21st day of the 4th month''): In the 12th year of Takakura''-tennō''s reign (高倉天皇12年), the emperor was forced to abdicate; and the succession (''senso'') was received by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crown Prince
A crown prince or hereditary prince is the heir apparent to the throne in a royal or imperial monarchy. The female form of the title is crown princess, which may refer either to an heiress apparent or, especially in earlier times, to the wife of the person styled crown prince. ''Crown prince'' as a descriptive term has been used throughout history for the prince who is first-in-line to a throne and is expected to succeed (i.e. the heir apparent), barring any unforeseen future event preventing this. In certain monarchies, a more specific substantive title may be accorded and become associated with the position of ''heir apparent'' (e.g. Prince of Wales in the United Kingdom or Prince of Asturias in the Spain, Kingdom of Spain). In these monarchies, the term crown prince may be used less often than the substantive title (or never). Until the late twentieth century, no modern monarchy adopted a system whereby females would be guaranteed to succeed to the throne (i.e. absolute pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taira No Kasemori
The Taira was one of the four most important clans that dominated Japanese politics during the Heian, Kamakura and Muromachi Periods of Japanese history – the others being the Fujiwara, the Tachibana, and the Minamoto. The clan is divided into four major groups, named after the emperor they descended from: Kanmu Heishi, Ninmyō Heishi, Montoku Heishi, and Kōkō Heishi. The clan is commonly referred to as or , using the character's On'yomi for ''Taira'', while means " clan", and is used as a suffix for "extended family". History Along with the Minamoto, Taira was one of the honorary surnames given by the emperors of the Heian Period (794–1185 CE) to their children and grandchildren who were not considered eligible for the throne. The clan was founded when the Imperial Court grew too large, and the emperor ordered that the descendants of previous emperors from several generations ago would no longer be princes, but would instead be given noble surnames and rank ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
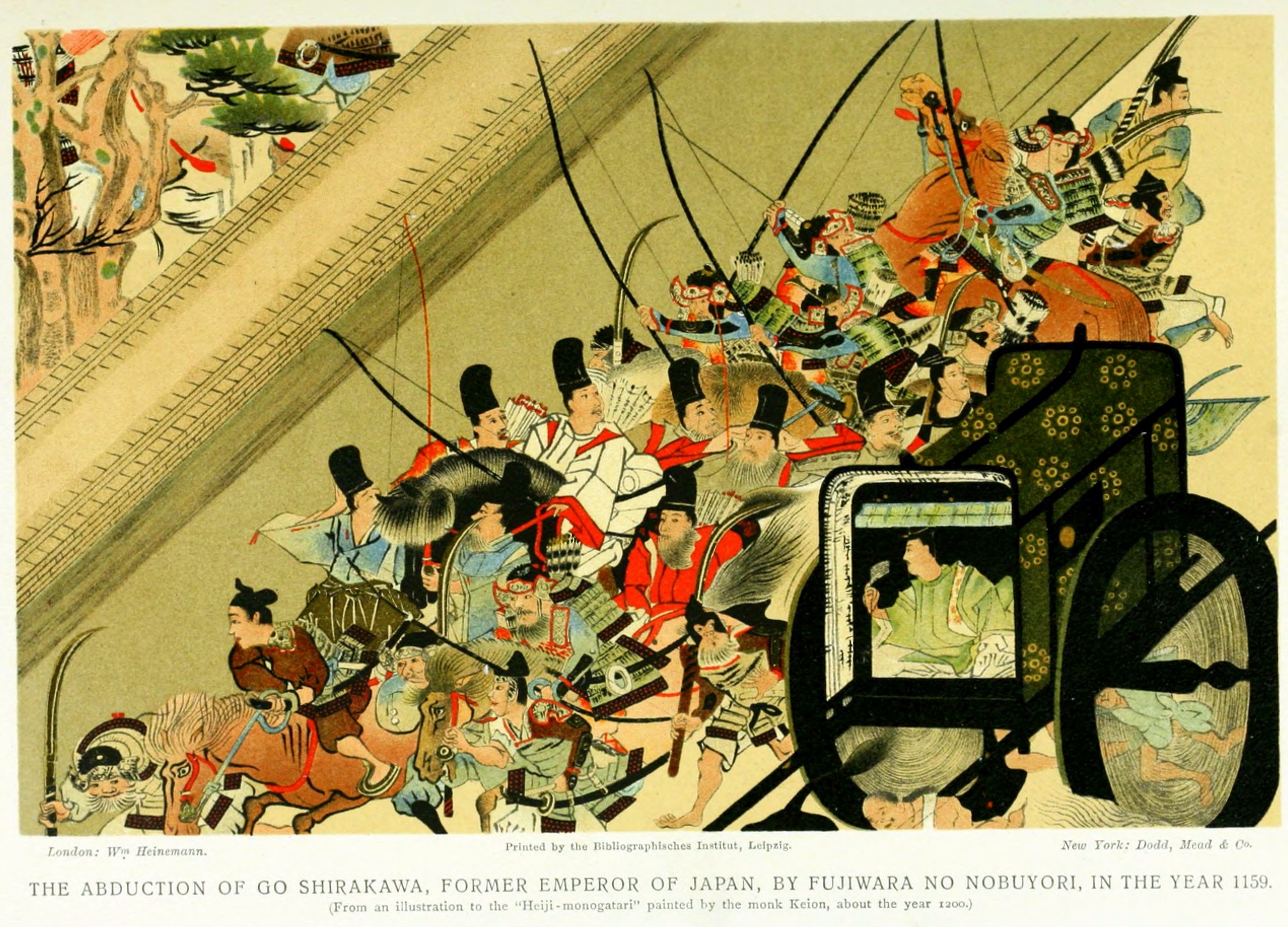
Emperor Go-Shirakawa
was the 77th emperor of Japan, according to the traditional order of succession. His de jure reign spanned the years from 1155 through 1158, though arguably he effectively maintained imperial power for almost thirty-seven years through the ''insei'' system – scholars differ as to whether his rule can be truly considered part of the ''insei'' system, given that the Hōgen Rebellion undermined the imperial position. However, it is broadly acknowledged that by politically outmaneuvering his opponents, he attained greater influence and power than the diminished authority of the emperor's position during this period would otherwise allow. Posthumously, this 12th-century sovereign was named after the 11th-century Emperor Shirakawa. ''Go-'' (後), translates literally as "later"; and thus, he is sometimes called the "Later Emperor Shirakawa", or in some older sources, may be identified as "Shirakawa, the second" or as "Shirakawa II". Unusually, the years of Go-Shirakawa's reign ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daijō Tennō
is a title for an Emperor of Japan who abdicates the Chrysanthemum Throne in favour of a successor. As defined in the Taihō Code, although retired, a ''Daijō Tennō'' could still exert power. The first such example is the Empress Jitō in the 7th century. A retired emperor sometimes entered the Buddhist monastic community, becoming a cloistered emperor. During late Heian period, cloistered emperors wielded power in a system known as cloistered rule. List A total of 64 Japanese emperors have abdicated. A list follows: Abdication during the Empire of Japan Emperor Kōmei and the Shōgun Commodore Matthew C. Perry and his squadron of what the Japanese dubbed "the Black Ships", sailed into the harbor at Edo (now known as Tokyo) in July 1853. Perry sought to open Japan to trade, and warned the Japanese of military consequences if they did not agree. During the crisis brought on by Perry's arrival, the Tokugawa shogunate took, for the first time in at least 250 years, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emperor Jomei
was the 34th emperor of Japan,Kunaichō 斉明天皇 (34)/ref> according to the traditional order of succession. Jomei's reign spanned the years from 629 through 641. Traditional narrative Before Jomei's ascension to the Chrysanthemum Throne, his personal name ('' imina'') was or . As emperor, his name would have been ''Okinagatarashihi Hironuka Sumeramikoto'' (息長足日広額天皇). He was a grandson of Emperor Bidatsu, both paternally and maternally. His father was Prince Oshisakanohikohito-no-Ōe, his mother was Princess Nukate-hime, who was a younger sister of his father. Events in Jomei's reign He succeeded his great aunt, Empress Suiko. Suiko did not make it clear who was to succeed her after her death. Before her death, she called Tamura and Prince Shōtoku's son, Prince Yamashiro-no-Ōe, and gave some brief advice to each of them. After her death the court was divided into two factions, each supporting one of the princes for the throne. Soga no Emishi, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chrysanthemum Throne
The is the throne of the Emperor of Japan. The term also can refer to very specific seating, such as the throne in the Shishin-den at Kyoto Imperial Palace. Various other thrones or seats that are used by the Emperor during official functions, such as those used in the Tokyo Imperial Palace or the throne used in the Speech from the Throne ceremony in the National Diet, are, however, not known as the "Chrysanthemum Throne". In a metonymic sense, the "Chrysanthemum Throne" also refers rhetorically to the head of state and the institution of the Japanese monarchy itself. History Japan is the oldest continuing hereditary monarchy in the world. In much the same sense as the British Crown, the Chrysanthemum Throne is an abstract metonymic concept that represents the monarch and the legal authority for the existence of the government. Unlike its British counterpart, the concepts of Japanese monarchy evolved differently before 1947 when there was, for example, no perceived separ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iwo Jima
Iwo Jima (, also ), known in Japan as , is one of the Japanese Volcano Islands and lies south of the Bonin Islands. Together with other islands, they form the Ogasawara Archipelago. The highest point of Iwo Jima is Mount Suribachi at high. Although south of the metropolis of Tokyo on the mainland, this island of 21 km2 (8 square miles) is administered as part of the Ogasawara Subprefecture of Tokyo. Since July 1944, when all the civilians were forcibly evacuated, the island has had a military-only population. The island was the location of the Battle of Iwo Jima between February 1945 and March 1945. This engagement saw some of the fiercest fighting of the Pacific War, with each side suffering over 20,000 casualties in the battle. The island became globally recognized when Joe Rosenthal, of the Associated Press, published his photograph '' Raising the Flag on Iwo Jima'', taken on Mount Suribachi. The US military occupied Iwo Jima until 1968, when it was returned to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |