|
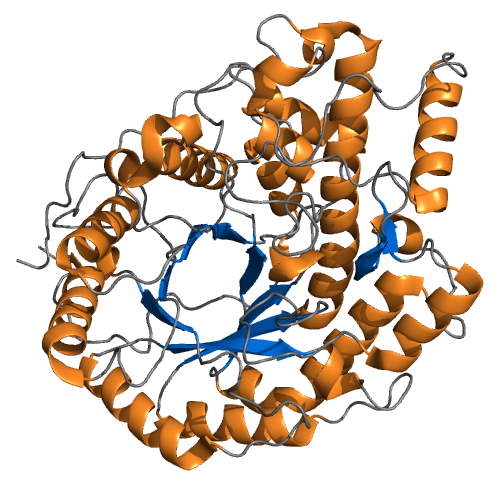
Sucrase-isomaltase
Sucrase-isomaltase is a bifunctional glucosidase (sugar-digesting enzyme) located on the brush border of the small intestine, encoded by the human gene ''SI''. It is a dual-function enzyme with two GH31 domains, one serving as the isomaltase, the other as a sucrose alpha-glucosidase. It has preferential expression in the apical membranes of enterocytes. The enzyme’s purpose is to digest dietary carbohydrates such as starch, sucrose and isomaltose. By further processing the broken-down products, energy in the form of ATP can be generated. Structure Sucrase-isomaltase consists of two enzymatic subunits: sucrase and isomaltase. The subunits originate from a polypeptide precursor, pro-SI. By heterodimerizing the two subunits, the sucrase-isomaltase complex is formed. The enzyme is anchored in the intestinal brush border membrane by a hydrophobic segment located near the N-terminus of the isomaltase subunit. Before the enzyme is anchored to the membrane, pro-SI is mannose-rich an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sucrose Intolerance
Sucrose intolerance or genetic sucrase-isomaltase deficiency (GSID) is the condition in which sucrase-isomaltase, an enzyme needed for proper metabolism of sucrose (sugar) and starch (e.g., grains), is not produced or the enzyme produced is either partially functional or non-functional in the small intestine. All GSID patients lack fully functional sucrase, while the isomaltase activity can vary from minimal functionality to almost normal activity. The presence of residual isomaltase activity may explain why some GSID patients are better able to tolerate starch in their diet than others with GSID. Signs and symptoms The presentation is as follows: * Abdominal cramps and bloating * Diarrhea and constipation * Vomiting * Hypoglycemia and headaches * Poor weight gain and growth * Upper respiratory tract and viral diseases * Anxiety and heart palpitations * Excess gas production Cause Sucrose intolerance can be caused by genetic mutations in which both parents must contain this gene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glucosidase
Glucosidases are the glycoside hydrolase enzymes categorized under the EC number 3.2.1. Function Alpha-glucosidases are enzymes involved in breaking down complex carbohydrates such as starch and glycogen into their monomers. They catalyze the cleavage of individual glucosyl residues from various glycoconjugates including alpha- or beta-linked polymers of glucose. This enzyme convert complex sugars into simpler ones. Members Different sources include different members in this class. Members marked with a "#" are considered by MeSH to be glucosidases. Clinical significance Alpha-glucosidases are targeted by alpha-glucosidase inhibitors such as acarbose and miglitol to control diabetes mellitus type 2 Type 2 diabetes (T2D), formerly known as adult-onset diabetes, is a form of diabetes mellitus that is characterized by high blood sugar, insulin resistance, and relative lack of insulin. Common symptoms include increased thirst, frequent .... See also * DNA glyc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
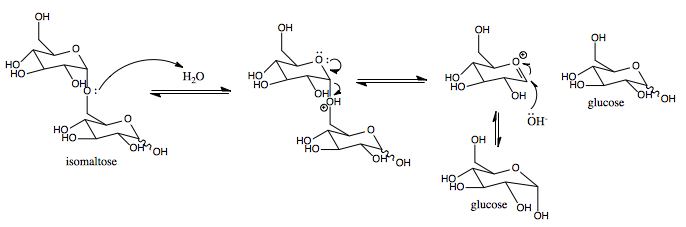
Isomaltase
Isomaltase () is an enzyme that breaks the bonds linking saccharides, which cannot be broken by amylase or maltase. It digests polysaccharides at the alpha 1-6 linkages. Its substrate, alpha-limit dextrin, is a product of amylopectin digestion that retains its 1-6 linkage (its alpha 1-4 linkages having already been broken down by amylase). The product of the enzymatic digestion of alpha-limit dextrin by isomaltase is maltose. Isomaltase helps amylase to digest alpha-limit dextrin to produce maltose. The human sucrase-isomaltase is a dual-function enzyme with two GH31 domains, one serving as the isomaltase, the other as a sucrose alpha-glucosidase. Nomenclature The list of enzymes, systematic name of sucrase-isomaltase is oligosaccharide 6-alpha-glucohydrolase. This enzyme is also known as: * Sucrase-alpha-dextrinase * oligo-1,6-glucosidase, * limit dextrin, * so maltase, * exo-oligo-1,6-glucosidase, * dextrin 6alpha-glucanohydrolase, * alpha-limit dextrin, * dextrin 6-gl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sucrase
Sucrases are digestive enzymes that catalyze the hydrolysis of sucrose to its component monosaccharides, fructose and glucose. One form, sucrase-isomaltase, is secreted in the small intestine on the brush border. The enzyme invertase, which occurs more commonly in plants, fungi and bacteria, also hydrolyzes sucrose (and other fructosides) but by a different mechanism: it is a fructosidase, whereas sucrase is a glucosidase. Types * is sucrase-isomaltase * is sucrose alpha-glucosidase Physiology Sucrose intolerance (also known as congenital sucrase-isomaltase deficiency (CSID), genetic sucrase-isomaltase deficiency (GSID), or sucrase-isomaltase deficiency) occurs when sucrase is not being secreted in the small intestine. With sucrose intolerance, the result of consuming sucrose is excess gas production and often diarrhea and malabsorption. Lactose intolerance is a similar condition that reflects an individual's inability to hydrolyze the disaccharide lactose. Sucrase is secret ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) is a type of cancer that affects the blood and bone marrow. In CLL, the bone marrow makes too many lymphocytes, which are a type of white blood cell. In patients with CLL, B cell lymphocytes can begin to collect in their blood, spleen, lymph nodes, and bone marrow. These cells do not function well and crowd out healthy blood cells. CLL is divided into two main types: # Slow-growing CLL (indolent CLL) # Fast-growing CLL Many people do not have any symptoms when they are first diagnosed. Those with symptoms (about 5-10% of patients with CLL) may experience the following: * Fevers * Fatigue * Night sweats * Unexplained weight loss * Loss of appetite * Painless lymph node swelling * Splenomegaly, Enlargement of the spleen, and/or * A anemia, low red blood cell count (anemia). These symptoms may worsen over time. While the exact cause of CLL is unknown, having a family member with CLL increases one's risk of developing the disease. Environmental ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acarbose
Acarbose ( INN) is an anti-diabetic drug used to treat diabetes mellitus type 2 and, in some countries, prediabetes. It is a generic sold in Europe and China as Glucobay ( Bayer AG), in North America as Precose ( Bayer Pharmaceuticals), and in Canada as Prandase ( Bayer AG). Acarbose is a starch blocker. It works by inhibiting alpha glucosidase, an intestinal enzyme that releases glucose from larger carbohydrates such as starch and sucrose. It is composed of an acarviosin moiety with a maltose at the reducing terminus. It can be degraded by a number of gut bacteria. Acarbose is cheap and popular in China, but not in the U.S. One physician explains that use in the U.S. is limited because it is not potent enough to justify the side effects of diarrhea and flatulence. However, a large study concluded in 2013 that "acarbose is effective, safe and well tolerated in a large cohort of Asian patients with type 2 diabetes." A possible explanation for the differing opinions is an obs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleophile
In chemistry, a nucleophile is a chemical species that forms bonds by donating an electron pair. All molecules and ions with a free pair of electrons or at least one pi bond can act as nucleophiles. Because nucleophiles donate electrons, they are Lewis bases. ''Nucleophilic'' describes the affinity of a nucleophile to bond with positively charged Atomic nucleus, atomic nuclei. Nucleophilicity, sometimes referred to as nucleophile strength, refers to a substance's nucleophilic character and is often used to compare the affinity of atoms. Neutral nucleophilic reactions with solvents such as Alcohol (chemistry), alcohols and water are named solvolysis. Nucleophiles may take part in nucleophilic substitution, whereby a nucleophile becomes attracted to a full or partial positive charge, and nucleophilic addition. Nucleophilicity is closely related to basicity. The difference between the two is, that basicity is a thermodynamic property (i.e. relates to an equilibrium state), but nucleop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydroxyl
In chemistry, a hydroxy or hydroxyl group is a functional group with the chemical formula and composed of one oxygen atom covalently bonded to one hydrogen atom. In organic chemistry, alcohols and carboxylic acids contain one or more hydroxy groups. Both the negatively charged anion , called hydroxide, and the neutral radical , known as the hydroxyl radical, consist of an unbonded hydroxy group. According to IUPAC definitions, the term ''hydroxyl'' refers to the hydroxyl radical () only, while the functional group is called a ''hydroxy group''. Properties Water, alcohols, carboxylic acids, and many other hydroxy-containing compounds can be readily deprotonated due to a large difference between the electronegativity of oxygen (3.5) and that of hydrogen (2.1). Hydroxy-containing compounds engage in intermolecular hydrogen bonding increasing the electrostatic attraction between molecules and thus to higher boiling and melting points than found for compounds that lack thi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen Bonds
In chemistry, a hydrogen bond (H-bond) is a specific type of molecular interaction that exhibits partial covalent character and cannot be described as a purely electrostatic force. It occurs when a hydrogen (H) atom, covalently bonded to a more electronegative donor atom or group (Dn), interacts with another electronegative atom bearing a lone pair of electrons—the hydrogen bond acceptor (Ac). Unlike simple dipole–dipole interactions, hydrogen bonding arises from charge transfer (nB → σ*AH), orbital interactions, and quantum mechanical delocalization, making it a resonance-assisted interaction rather than a mere electrostatic attraction. The general notation for hydrogen bonding is Dn−H···Ac, where the solid line represents a polar covalent bond, and the dotted or dashed line indicates the hydrogen bond. The most frequent donor and acceptor atoms are nitrogen (N), oxygen (O), and fluorine (F), due to their high electronegativity and ability to engage in stronger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
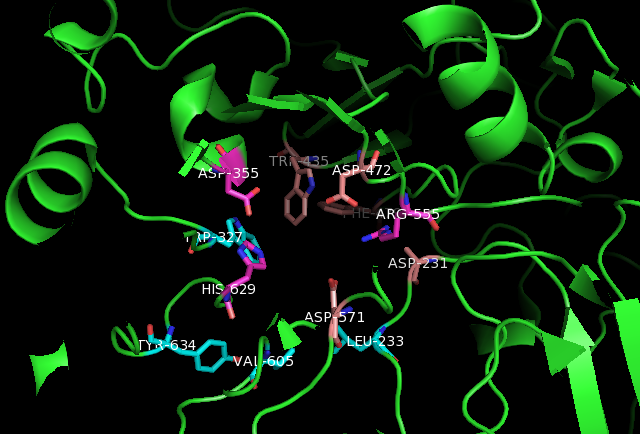
SI Active Site
The International System of Units, internationally known by the abbreviation SI (from French ), is the modern form of the metric system and the world's most widely used system of measurement. It is the only system of measurement with official status in nearly every country in the world, employed in science, technology, industry, and everyday commerce. The SI system is coordinated by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures, which is abbreviated BIPM from . The SI comprises a coherent system of units of measurement starting with seven base units, which are the second (symbol s, the unit of time), metre (m, length), kilogram (kg, mass), ampere (A, electric current), kelvin (K, thermodynamic temperature), mole (mol, amount of substance), and candela (cd, luminous intensity). The system can accommodate coherent units for an unlimited number of additional quantities. These are called coherent derived units, which can always be represented as products of powers of the base u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Active Site
In biology and biochemistry, the active site is the region of an enzyme where substrate molecules bind and undergo a chemical reaction. The active site consists of amino acid residues that form temporary bonds with the substrate, the ''binding site'', and residues that catalyse a reaction of that substrate, the ''catalytic site''. Although the active site occupies only ~10–20% of the volume of an enzyme, it is the most important part as it directly catalyzes the chemical reaction. It usually consists of three to four amino acids, while other amino acids within the protein are required to maintain the tertiary structure of the enzymes. Each active site is evolved to be optimised to bind a particular substrate and catalyse a particular reaction, resulting in high specificity. This specificity is determined by the arrangement of amino acids within the active site and the structure of the substrates. Sometimes enzymes also need to bind with some cofactors to fulfil their functio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |