|
Sucrase
Sucrases are digestive enzymes that catalyze the hydrolysis of sucrose to its component monosaccharides, fructose and glucose. One form, sucrase-isomaltase, is secreted in the small intestine on the brush border. The enzyme invertase, which occurs more commonly in plants, fungi and bacteria, also hydrolyzes sucrose (and other fructosides) but by a different mechanism: it is a fructosidase, whereas sucrase is a glucosidase. Types * is sucrase-isomaltase * is sucrose alpha-glucosidase Physiology Sucrose intolerance (also known as congenital sucrase-isomaltase deficiency (CSID), genetic sucrase-isomaltase deficiency (GSID), or sucrase-isomaltase deficiency) occurs when sucrase is not being secreted in the small intestine. With sucrose intolerance, the result of consuming sucrose is excess gas production and often diarrhea and malabsorption. Lactose intolerance is a similar condition that reflects an individual's inability to hydrolyze the disaccharide lactose. Sucrase is secret ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sucrose Intolerance
Sucrose intolerance or genetic sucrase-isomaltase deficiency (GSID) is the condition in which sucrase-isomaltase, an enzyme needed for proper metabolism of sucrose (sugar) and starch (e.g., grains), is not produced or the enzyme produced is either partially functional or non-functional in the small intestine. All GSID patients lack fully functional sucrase, while the isomaltase activity can vary from minimal functionality to almost normal activity. The presence of residual isomaltase activity may explain why some GSID patients are better able to tolerate starch in their diet than others with GSID. Signs and symptoms The presentation is as follows: * Abdominal cramps and bloating * Diarrhea and constipation * Vomiting * Hypoglycemia and headaches * Poor weight gain and growth * Upper respiratory tract and viral diseases * Anxiety and heart palpitations * Excess gas production Cause Sucrose intolerance can be caused by genetic mutations in which both parents must contain this gene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
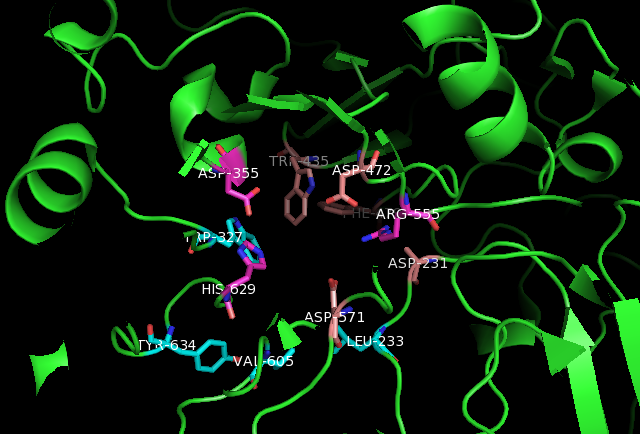
Sucrase-isomaltase
Sucrase-isomaltase is a bifunctional glucosidase (sugar-digesting enzyme) located on the brush border of the small intestine, encoded by the human gene ''SI''. It is a dual-function enzyme with two GH31 domains, one serving as the isomaltase, the other as a sucrose alpha-glucosidase. It has preferential expression in the apical membranes of enterocytes. The enzyme’s purpose is to digest dietary carbohydrates such as starch, sucrose and isomaltose. By further processing the broken-down products, energy in the form of ATP can be generated. Structure Sucrase-isomaltase consists of two enzymatic subunits: sucrase and isomaltase. The subunits originate from a polypeptide precursor, pro-SI. By heterodimerizing the two subunits, the sucrase-isomaltase complex is formed. The enzyme is anchored in the intestinal brush border membrane by a hydrophobic segment located near the N-terminus of the isomaltase subunit. Before the enzyme is anchored to the membrane, pro-SI is mannose-rich an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sucrose
Sucrose, a disaccharide, is a sugar composed of glucose and fructose subunits. It is produced naturally in plants and is the main constituent of white sugar. It has the molecular formula . For human consumption, sucrose is extracted and refined from either sugarcane or sugar beet. Sugar mills – typically located in tropical regions near where sugarcane is grown – crush the cane and produce raw sugar which is shipped to other factories for refining into pure sucrose. Sugar beet factories are located in temperate climates where the beet is grown, and process the beets directly into refined sugar. The Sugar refinery, sugar-refining process involves washing the raw sugar crystals before dissolving them into a sugar syrup which is filtered and then passed over carbon to remove any residual colour. The sugar syrup is then concentrated by boiling under a vacuum and crystallized as the final purification process to produce crystals of pure sucrose that are clear, odorless, and sweet. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Invertase
β-Fructofuranosidase is an enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis (breakdown) of the table sugar sucrose into fructose and glucose. Sucrose is a fructoside. Alternative names for β-fructofuranosidase include invertase, saccharase, glucosucrase, β-fructosidase, invertin, fructosylinvertase, alkaline invertase, and acid invertase. The resulting mixture of fructose and glucose is called inverted sugar syrup. Related to invertases are sucrases. Invertases and sucrases hydrolyze sucrose to give the same mixture of glucose and fructose. Invertase is a glycoprotein that hydrolyses (cleaves) the non-reducing terminal β-fructofuranoside residues. Invertases cleave the O-C(fructose) bond, whereas the sucrases cleave the O-C(glucose) bond. Invertase cleaves the α-1,2-glycosidic bond of sucrose. For industrial use, invertase is usually derived from yeast. It is also synthesized by bees, which use it to make honey from nectar. The temperature optimum is 60 °C and a pH optimum i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Celiac Sprue
Coeliac disease (British English) or celiac disease (American English) is a long-term autoimmune disorder, primarily affecting the small intestine. Patients develop hypersensitivity, intolerance to gluten, which is present in foods such as wheat, rye, spelt and barley. Classic symptoms include gastrointestinal problems such as chronic diarrhea, diarrhoea, abdominal distention, malabsorption, Anorexia (symptom), loss of appetite, and among children failure to thrive, failure to grow normally. Non-classic symptoms are more common, especially in people older than two years. There may be mild or absent gastrointestinal symptoms, a wide number of systemic disease, symptoms involving any part of the body, or no obvious symptoms. Due to the frequency of these symptoms, coeliac disease is often considered a systemic disease, rather than a gastrointestinal condition. Coeliac disease was first described as a disease which initially presents during childhood; however, it may develop at a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fructose
Fructose (), or fruit sugar, is a Ketose, ketonic monosaccharide, simple sugar found in many plants, where it is often bonded to glucose to form the disaccharide sucrose. It is one of the three dietary monosaccharides, along with glucose and galactose, that are absorbed by the gut directly into the blood of the portal vein during digestion. The liver then converts most fructose and galactose into glucose for distribution in the bloodstream or deposition into glycogen. Fructose was discovered by French chemist Augustin-Pierre Dubrunfaut in 1847. The name "fructose" was coined in 1857 by the English chemist William Allen Miller. Pure, dry fructose is a sweet, white, odorless, crystalline solid, and is the most water-soluble of all the sugars. Fructose is found in honey, tree and vine fruits, flowers, Berry, berries, and most List of root vegetables, root vegetables. Commercially, fructose is derived from sugar cane, sugar beets, and maize. High-fructose corn syrup is a mixture of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glucose
Glucose is a sugar with the Chemical formula#Molecular formula, molecular formula , which is often abbreviated as Glc. It is overall the most abundant monosaccharide, a subcategory of carbohydrates. It is mainly made by plants and most algae during photosynthesis from water and carbon dioxide, using energy from sunlight. It is used by plants to make cellulose, the most abundant carbohydrate in the world, for use in cell walls, and by all living Organism, organisms to make adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is used by the cell as energy. In energy metabolism, glucose is the most important source of energy in all organisms. Glucose for metabolism is stored as a polymer, in plants mainly as amylose and amylopectin, and in animals as glycogen. Glucose circulates in the blood of animals as blood sugar. The naturally occurring form is -glucose, while its Stereoisomerism, stereoisomer L-glucose, -glucose is produced synthetically in comparatively small amounts and is less biologicall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lactose Intolerance
Lactose intolerance is caused by a lessened ability or a complete inability to digest lactose, a sugar found in dairy products. Humans vary in the amount of lactose they can tolerate before symptoms develop. Symptoms may include abdominal pain, bloating, diarrhea, flatulence, and nausea. These symptoms typically start thirty minutes to two hours after eating or drinking something containing lactose, with the severity typically depending on the amount consumed. Lactose intolerance does not cause damage to the gastrointestinal tract. Lactose intolerance is due to the lack of the enzyme lactase in the small intestines to break lactose down into glucose and galactose. There are four types: primary, secondary, developmental, and congenital. Primary lactose intolerance occurs as the amount of lactase declines as people grow up. Secondary lactose intolerance is due to injury to the small intestine. Such injury could be the result of infection, celiac disease, inflammatory bowel disea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrolysis
Hydrolysis (; ) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chemical bonds. The term is used broadly for substitution reaction, substitution, elimination reaction, elimination, and solvation reactions in which water is the nucleophile. Biological hydrolysis is the cleavage of Biomolecule, biomolecules where a water molecule is consumed to effect the separation of a larger molecule into component parts. When a carbohydrate is broken into its component sugar molecules by hydrolysis (e.g., sucrose being broken down into glucose and fructose), this is recognized as saccharification. Hydrolysis reactions can be the reverse of a condensation reaction in which two molecules join into a larger one and eject a water molecule. Thus hydrolysis adds water to break down, whereas condensation builds up by removing water. Types Usually hydrolysis is a chemical process in which a molecule of water is added to a substance. Sometimes this addition causes both the su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Small Intestine
The small intestine or small bowel is an organ (anatomy), organ in the human gastrointestinal tract, gastrointestinal tract where most of the #Absorption, absorption of nutrients from food takes place. It lies between the stomach and large intestine, and receives bile and pancreatic juice through the pancreatic duct to aid in digestion. The small intestine is about long and folds many times to fit in the abdomen. Although it is longer than the large intestine, it is called the small intestine because it is narrower in diameter. The small intestine has three distinct regions – the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum. The duodenum, the shortest, is where preparation for absorption through small finger-like protrusions called intestinal villus, intestinal villi begins. The jejunum is specialized for the absorption through its lining by enterocytes: small nutrient particles which have been previously digested by enzymes in the duodenum. The main function of the ileum is to absorb vitami ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Robin
The American robin (''Turdus migratorius'') is a migratory bird of the true thrush genus and Turdidae, the wider thrush family. It is named after the European robin because of its reddish-orange breast, though the two species are not closely related, with the European robin belonging to the Old World flycatcher family. The American robin is widely distributed throughout North America, wintering from southern Canada to central Mexico and along the Pacific coast. According to the Partners in Flight database (2019), the American robin is the most abundant landbird in North America (with 370million individuals), ahead of red-winged blackbirds, introduced European starlings, mourning doves and house finches. It has seven subspecies. The species is active mostly during the day and assembles in large flocks at night. Its diet consists of invertebrates (such as beetle grubs, earthworms, and caterpillars), fruits, and berries. It is one of the earliest bird species to lay its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |