Isomaltase on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Isomaltase () is an
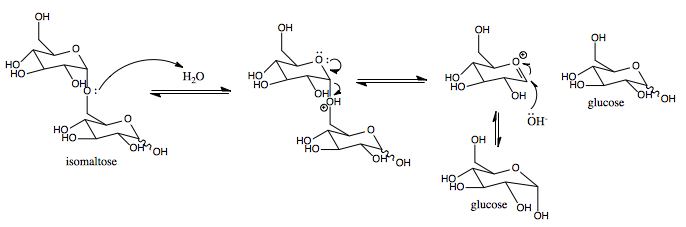 This enzyme catalyses the following
This enzyme catalyses the following
enzyme
An enzyme () is a protein that acts as a biological catalyst by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different mol ...
that breaks the bonds linking saccharide
A carbohydrate () is a biomolecule composed of carbon (C), hydrogen (H), and oxygen (O) atoms. The typical hydrogen-to-oxygen atomic ratio is 2:1, analogous to that of water, and is represented by the empirical formula (where ''m'' and ''n'' m ...
s, which cannot be broken by amylase
An amylase () is an enzyme that catalysis, catalyses the hydrolysis of starch (Latin ') into sugars. Amylase is present in the saliva of humans and some other mammals, where it begins the chemical process of digestion. Foods that contain large ...
or maltase
Maltase is an informal name for a family of enzymes that catalyze the hydrolysis of disaccharide maltose into two simple sugars of glucose. Maltases are found in plants, bacteria, yeast, humans, and other vertebrates.
Digestion of starch requi ...
. It digests polysaccharides at the alpha 1-6 linkages. Its substrate, alpha-limit dextrin, is a product of amylopectin digestion that retains its 1-6 linkage (its alpha 1-4 linkages having already been broken down by amylase). The product of the enzymatic digestion of alpha-limit dextrin
Dextrins are a group of low-molecular-weight carbohydrates produced by the hydrolysis of starch and glycogen. Dextrins are mixtures of polymers of D-glucose units linked by α-(1→4) or α-(1→6) glycosidic bonds.
Dextrins can be produced fro ...
by isomaltase is maltose
}
Maltose ( or ), also known as maltobiose or malt sugar, is a disaccharide formed from two units of glucose joined with an α(1→4) bond. In the isomer isomaltose, the two glucose molecules are joined with an α(1→6) bond. Maltose is the tw ...
.
Isomaltase helps amylase to digest alpha-limit dextrin to produce maltose. The human sucrase-isomaltase
Sucrase-isomaltase is a bifunctional glucosidase (sugar-digesting enzyme) located on the brush border of the small intestine, encoded by the human gene ''SI''. It is a dual-function enzyme with two GH31 domains, one serving as the isomaltase, the ...
is a dual-function enzyme with two GH31 domains, one serving as the isomaltase, the other as a sucrose alpha-glucosidase.
Nomenclature
Thesystematic name
A systematic name is a name given in a systematic way to one unique group, organism, object or chemical substance, out of a specific population or collection. Systematic names are usually part of a nomenclature.
A semisystematic name or semitrivi ...
of sucrase-isomaltase is oligosaccharide 6-alpha-glucohydrolase. This enzyme is also known as:
* Sucrase-alpha-dextrinase
* oligo-1,6-glucosidase,
* limit dextrin,
* so maltase,
* exo-oligo-1,6-glucosidase,
* dextrin 6alpha-glucanohydrolase,
* alpha-limit dextrin,
* dextrin 6-glucanohydrolase, and
* oligosaccharide alpha-1,6-glucohydrolase.
Mechanism
 This enzyme catalyses the following
This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the chemistry, chemical transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. When chemical reactions occur, the atoms are rearranged and the reaction is accompanied by an Gibbs free energy, ...
: Hydrolysis
Hydrolysis (; ) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chemical bonds. The term is used broadly for substitution reaction, substitution, elimination reaction, elimination, and solvation reactions in which water ...
of (1->6)-alpha-D-glucosidic linkages in some oligosaccharide
An oligosaccharide (; ) is a carbohydrate, saccharide polymer containing a small number (typically three to ten) of monosaccharides (simple sugars). Oligosaccharides can have many functions including Cell–cell recognition, cell recognition and ce ...
s produced from starch
Starch or amylum is a polymeric carbohydrate consisting of numerous glucose units joined by glycosidic bonds. This polysaccharide is produced by most green plants for energy storage. Worldwide, it is the most common carbohydrate in human diet ...
and glycogen
Glycogen is a multibranched polysaccharide of glucose that serves as a form of energy storage in animals, fungi, and bacteria. It is the main storage form of glucose in the human body.
Glycogen functions as one of three regularly used forms ...
by enzyme EC 3.2.1.1.
Hydrolysis
Hydrolysis (; ) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chemical bonds. The term is used broadly for substitution reaction, substitution, elimination reaction, elimination, and solvation reactions in which water ...
uses water to cleave chemical bonds. Sucrase-isomaltase’s mechanism results in a net retention of configuration at the anomeric center.
External links
*References
Hydrolases {{enzyme-stub