|
Slioch
Slioch () is a mountain in the Scottish Highlands situated in Wester Ross, eight kilometres north of the village of Kinlochewe. Slioch reaches an elevation of and towers above the southeastern end of Loch Maree to give one of the best known and most photographed sights (from the A832 road) in the Highlands. VisitScotland, the Scottish national tourist agency, has used video footage of Slioch in its television advertisements. The mountain is composed of Torridonian sandstone on a base of Lewisian Gneiss and has steep crags on three sides and allows easy access for the walker only from the south east where the large open corrie of Coire na Sleaghaich has two ridges on its flanks which the walker can use. The mountain's name comes from the Gaelic word "sleagh" and means "the spear" and this only becomes obvious when Slioch is viewed from Lochan Fada to the northeast, from here the subsidiary top of Sgùrr an Tuill Bhàin (The Peak of the White Hollow) (933 metres) dominates ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drumblade
Drumblade is a hamlet in north-western Aberdeenshire, Scotland, which lies 4¾ miles east of the town of Huntly. Schools Drumblade Primary School is a primary school with a nursery unit, and a total roll of 53 as of 2013. It is a feeder school for The Gordon Schools, Huntly. It made the national news in 2012 when its pet ducks disappeared, presumed stolen. History Drumblade Stone Circle, or Ston(e)yfield, is the remains of an ancient stone circle. It is about east of Huntly. Drumblade is the site of the Battle of Slioch in December 1307, involving Robert the Bruce. Notable residents * William Garden Blaikie minister, later Free Church A free church is any Christian denomination that is intrinsically separate from government (as opposed to a state church). A free church neither defines government policy, nor accept church theology or policy definitions from the government. A f ... moderator * George Ramsay Davidson minister of Drumblade from 1828 to 1842 References ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Torridonian
The Torridonian is the informal name given to a sequence of Mesoproterozoic to Neoproterozoic sedimentary rocks that outcrop in a strip along the northwestern coast of Scotland and some parts of the Inner Hebrides from the Isle of Mull in the southwest to Cape Wrath in the northeast. They lie unconformably on the Archaean to Paleoproterozoic basement rocks of the Lewisian complex and unconformably beneath the Cambrian to Lower Ordovician rocks of the Ardvreck Group. History of research The sequence was first mapped as a unit by John MacCulloch and was initially assumed to be part of the Old Red Sandstone. The first name used specifically for this sequence was "Torridon Sandstone" introduced in 1866 by James Nicol. By 1892 the term was shortened to "Torridonian" by the Geological Survey. In 1893 the survey had subdivided the Torridonian into four units, the Diabaig, Applecross, Aultbea and Cailleach Head groups (which are now the names of formations within the Torridon Grou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Munros
A Munro (; ) is defined as a mountain in Scotland with a height over , and which is on the Scottish Mountaineering Club (SMC) official list of Munros; there is no explicit topographical prominence requirement. The best known Munro is Ben Nevis (Beinn Nibheis), the highest mountain in the British Isles at 4,411 ft (1,345 m). Munros are named after Sir Hugh Munro, 4th Baronet (1856–1919), who produced the first list of such hills, known as ''Munro's Tables'', in 1891. Also included were what Munro considered lesser peaks, now known as Munro Tops, which are also over 3,000 feet but are lower than the nearby primary mountain. The publication of the original list is usually considered to be the Epoch (reference date), epoch event of modern peak bagging. The list has been the subject of subsequent variation and , the Scottish Mountaineering Club has listed 282 Munros and 226 Munro Tops. "Munro bagging" is the activity of climbing all the listed Munros. , 7,654 people had rep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ken Wilson (mountaineering Writer)
Kenneth John Wilson (7 February 1941 – 11 June 2016) was a British writer, publisher and editor of books and magazines about climbing and mountaineering. The British Mountaineering Council's ''Summit Magazine'' described him as "one of the most influential voices in British climbing". In 1974 he edited and contributed to the first editions of the book ''Hard Rock'' which ''The Guardian'' considered was "among the most influential climbing books of the 20th century." Early life Wilson was born in Solihull to Blanche (née Colman) and John Wilson, a salesman of stationery. He attended Birmingham College of Art where he studied architecture and photography before working for the architectural photographer Henk Snoek for four years in London. During this time he met his future wife Gloria – they married in 1971 and had two children. Based on his experience from the early 1950s with a holiday in the Lake District and with climbing and walking with the scouts, in 1968 he took up ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Torridon Hills
The Torridon Hills surround Torridon village in the Northwest Highlands of Scotland. The name is usually applied to the mountains to the north of Glen Torridon. They are among the most dramatic and spectacular peaks in the British Isles and made of some of the oldest rocks in the world. Many are over high, so are considered Munros. Rock types These are mainly made of a type of sandstone, known as Torridonian sandstone (see Geology of Great Britain), which over time has become eroded to produce the unique characteristics of the Torridon Hills. In geology, Torridonian describes a series of proterozoic arenaceous sedimentary rocks of Precambrian age. They are amongst the oldest rocks in Britain, and sit on yet older rocks, Lewisian gneiss. Some of the highest peaks, such as Beinn Eighe are crowned by white Cambrian quartzite, which gives those peaks a distinctive appearance. Some of the quartzite contains fossilized worm burrows and known as pipe rock. It is circa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dundonnell And Fisherfield Forest
file:Footpath to Coire Mhic Fhearchair - geograph.org.uk - 713058.jpg, Fisherfield Forest The Dundonnell and Fisherfield Forest covers a large mountainous area of Wester Ross in the Northwest Highlands of Scotland, lying between Loch Maree and Little Loch Broom. It is sometimes nicknamed ''The Great Wilderness'', as the area is entirely devoid of permanent settlements. Although termed a ''forest'' the area has very few trees. It is in fact a deer forest; an area maintained by the owners primarily for deer stalking. Three estates cover the principal area of the forest. Dundonnell Estate (134 km2) covers the northwest part of the forest, including the northwestern flanks of An Teallach, whilst Eilean Darach estate covers 262 km2 in the northeast, including the northeast flank of An Teallach. The plurality of the area, including all the southern and central sections, forms the 323 km2 Letterewe estate. Mountains Three of the most famous mountains in the area are An Te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trig Point
A triangulation station, also known as a trigonometrical point, and sometimes informally as a trig, is a fixed surveying station, used in geodetic surveying and other surveying projects in its vicinity. The station is usually set up by a mapping organisation with known coordinates and elevation published. Numerous stations are installed on summits for purposes of visibility and prominence. A graven metal plate on the top of a pillar may provide a mounting point for a theodolite or reflector, often using some form of kinematic coupling to ensure reproducible positioning. Use Trigonometrical stations form networks of triangulation. Positions of land boundaries, roads, railways, bridges and other infrastructure can be accurately located by the network, a task essential to the construction of modern infrastructure. Apart from the known stations set up by government, some temporary trigonometrical stations are set up near construction sites for monitoring the precision and progr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Feral Goat
The feral goat is the domestic goat (''Capra hircus'') when it has become established in the wild. Feral goats occur in many parts of the world. Species Feral goats consist of many breeds of domestic goats, all of which stem from the wild goat (''C. aegagrus''). Although breeds can look different, they all share similar characteristics. Physically, both domestic and feral goats can be identified by their prominent straight horns (more prominent on male goats), rectangular pupils, and coarse hair. In addition, most domestic goats/feral goats weigh around , with heavier goats tending to be wild goats. Behavior The feral goat is seen in Australia, New Zealand, Great Britain, Ireland, Hawaii, Brazil, Honduras, Lebanon, Panama, Madagascar, the Comoros, Mauritius, Réunion, New Guinea, the Galápagos Islands, Cuba, and in many other parts of the world. When feral goats reach large populations in habitats which are not adapted to them, they may become an invasive species with seri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cirque
A (; from the Latin word ) is an amphitheatre-like valley formed by Glacier#Erosion, glacial erosion. Alternative names for this landform are corrie (from , meaning a pot or cauldron) and ; ). A cirque may also be a similarly shaped landform arising from fluvial erosion. The concave shape of a glacial cirque is open on the downhill side, while the cupped section is generally steep. Cliff-like slopes, down which ice and glaciated debris combine and converge, form the three or more higher sides. The floor of the cirque ends up bowl-shaped, as it is the complex convergence zone of combining ice flows from multiple directions and their accompanying rock burdens. Hence, it experiences somewhat greater erosion forces and is most often overdeepening, overdeepened below the level of the cirque's low-side outlet (stage) and its down-slope (backstage) valley. If the cirque is subject to seasonal melting, the floor of the cirque most often forms a tarn (lake), tarn (small lake) behind a d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
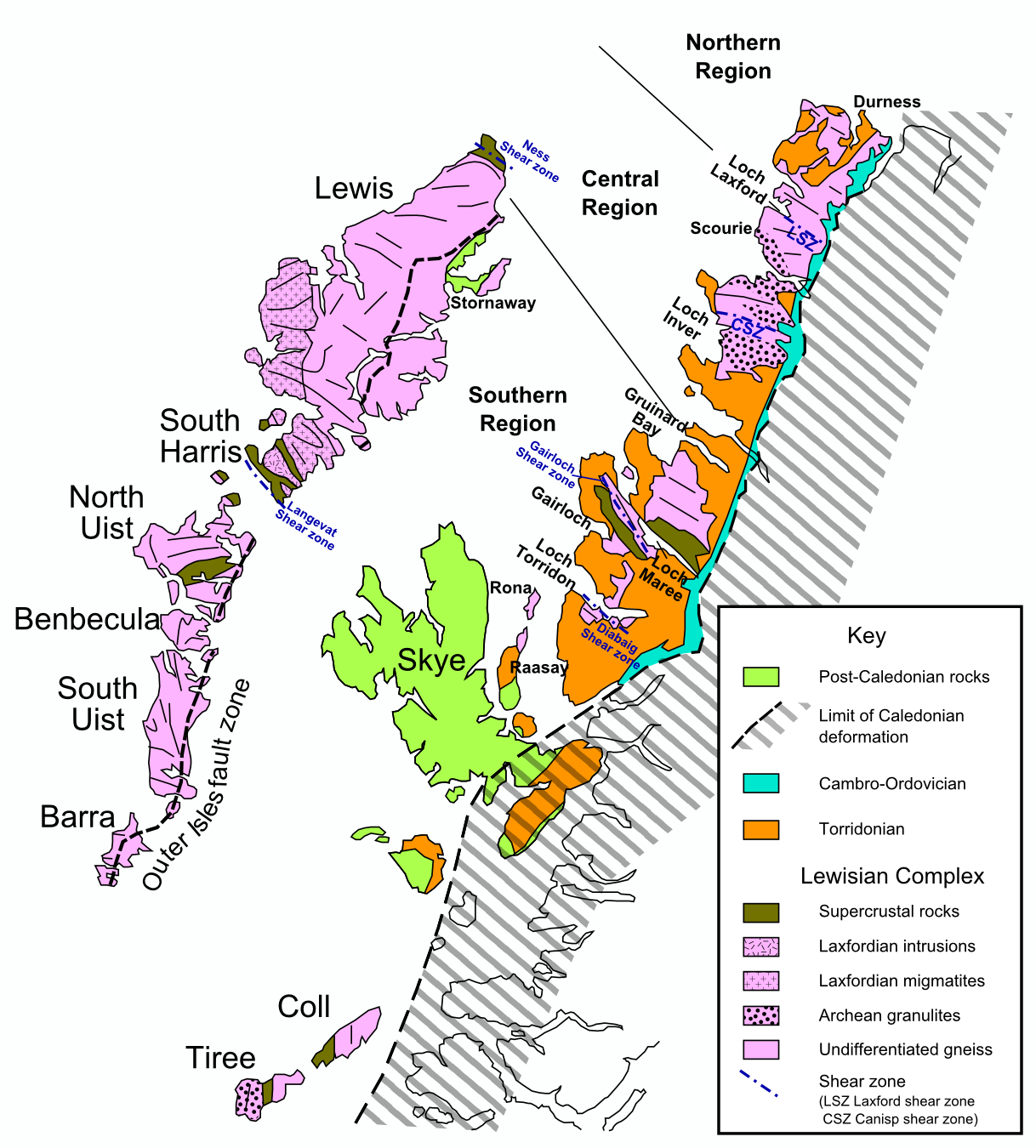
Lewisian Complex
The Lewisian complex or Lewisian gneiss is a suite of Precambrian metamorphic rocks that outcrop in the northwestern part of Scotland, forming part of the Hebridean terrane and the North Atlantic craton, North Atlantic Craton. These rocks are of Archean, Archaean and Paleoproterozoic age, ranging from 3.0–1.7 billion years (Year#SI prefix multipliers, Ga). They form the Basement (geology), basement on which the Stoer Group, Wester Ross Supergroup and probably the Loch Ness Supergroup sediments were deposited. The Lewisian consists mainly of Granite, granitic gneisses with a minor amount of supracrustal rocks. Rocks of the Lewisian complex were caught up in the Caledonian orogeny, appearing in the hanging walls of many of the thrust faults formed during the late stages of this tectonic event. Distribution The main outcrops of the Lewisian complex are on the islands of the Outer Hebrides, including Isle of Lewis, Lewis, from which the complex takes its name. It is also exp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sandstone
Sandstone is a Clastic rock#Sedimentary clastic rocks, clastic sedimentary rock composed mainly of grain size, sand-sized (0.0625 to 2 mm) silicate mineral, silicate grains, Cementation (geology), cemented together by another mineral. Sandstones comprise about 20–25% of all sedimentary rocks. Most sandstone is composed of quartz or feldspar, because they are the most resistant minerals to the weathering processes at the Earth's surface. Like uncemented sand, sandstone may be imparted any color by impurities within the minerals, but the most common colors are tan, brown, yellow, red, grey, pink, white, and black. Because sandstone beds can form highly visible cliffs and other topography, topographic features, certain colors of sandstone have become strongly identified with certain regions, such as the red rock deserts of Arches National Park and other areas of the Southwestern United States, American Southwest. Rock formations composed of sandstone usually allow the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |