|
Six Frontier Towns
The Six Frontier Towns (), also known as the Six Garrisons and the Northern Frontier Towns (), were six military towns located in the Hetao region of the Northern Wei dynasty of China. The government established the towns during the Huangshi and Yanhe eras to prevent the southward invasion by the Rouran Khaganate. These towns were, from west to east, Woye, Huaishuo, Wuchuan, Fumin, Rouxuan and Huaihuang. The town of Woye was initially located in the old city of Woye of the Han dynasty, southwest of today's Linhe in Inner Mongolia. It was later relocated to Shuofang, north of today's Hanggin Banner. The town of Huaishuo was located in southwest of today's Guyang, Inner Mongolia. Later its name was changed to Shuozhou. The town of Wuchuan was located in the west of today's Wuchuan, Inner Mongolia. In 528, it became a district (郡). The town of Fumin was located in the southeast of today's Siziwang Banner. The town of Rouxuan was located in the northwest of today's Xinghe, Inner ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
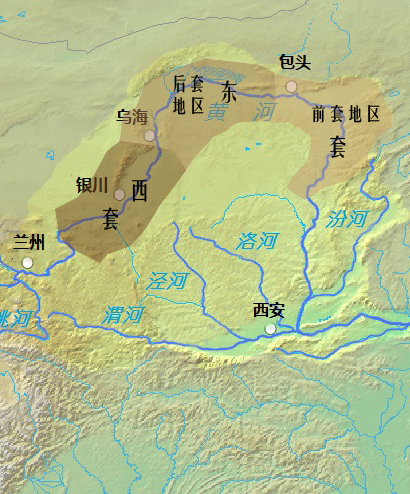
Hetao
Hetao () is a C-shaped region in northwestern China consisting of a collection of flood plains stretching from the banks of the northern half of the Ordos Loop, a large northerly rectangular bend of the Yellow River, that forms the river's entire middle section. The region makes up the northern margin of the Ordos Basin, bounded in the west by the Helan Mountains, the north by the Yin Mountains, the east by the northern portion of Lüliang Mountains, and the south by the Ordos Desert and the Loess Plateau (separated by the course of the Ming Great Wall). The Hetao region is divided into two main sections — the "West Loop" () in Ningxia, and the "East Loop" () in Inner Mongolia. The west section includes the alluvial Yinchuan Plain (, a.k.a. Ningxia Plain) around Shizuishan, Yinchuan, and Wuzhong, and the Weining Plain () around Zhongwei. The east section is further divided into two parts — the western "Back Loop" (), which includes the Bayannur Plain () around B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pinyin
Hanyu Pinyin, or simply pinyin, officially the Chinese Phonetic Alphabet, is the most common romanization system for Standard Chinese. ''Hanyu'' () literally means 'Han Chinese, Han language'—that is, the Chinese language—while ''pinyin'' literally means 'spelled sounds'. Pinyin is the official romanization system used in China, Singapore, Taiwan, and by the United Nations. Its use has become common when transliterating Standard Chinese mostly regardless of region, though it is less ubiquitous in Taiwan. It is used to teach Standard Chinese, normally written with Chinese characters, to students in mainland China and Singapore. Pinyin is also used by various Chinese input method, input methods on computers and to lexicographic ordering, categorize entries in some Chinese dictionaries. In pinyin, each Chinese syllable is spelled in terms of an optional initial (linguistics), initial and a final (linguistics), final, each of which is represented by one or more letters. Initi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tiele People
The Tiele ( zh, c=鐵勒, p=Tiělè),, Mongolian ''*Tegreg'' " eople of theCarts" also transliterated as Chile ( zh, c=敕勒, links=no), Dili ( zh, c=狄歷, links=no), Zhile ( zh, c=直勒, links=no) and Tele ( zh, c=特勒, links=no), who were also known by the Chinese exonym Gaoche ( zh, c=高車, links=no) or Gaoju,, "High Carts" were a tribal confederation of Turkic ethnic origins living to the north of China proper and in Central Asia, emerging after the disintegration of the confederacy of the Xiongnu. Chinese sources associate them with the earlier Dingling. Chile and Gaoche The names "Chile" (敕勒) and "Gaoche" ( 高車) first appear in Chinese records during the campaigns of Former Yan and Dai in 357 and 363 respectively. However, the protagonists were also addressed as " Dingling" in the records of the Southern Dynasties. The name ''Gaoche'' ("high cart") was a nickname given by the Chinese.Pulleyblank, "Central Asia and Non-Chinese Peoples of Ancient China", ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Han Chinese
The Han Chinese, alternatively the Han people, are an East Asian people, East Asian ethnic group native to Greater China. With a global population of over 1.4 billion, the Han Chinese are the list of contemporary ethnic groups, world's largest ethnic group, making up about 17.5% of the world population. The Han Chinese represent 91.11% of the population in China and 97% of the population in Taiwan. Han Chinese are also a significant Overseas Chinese, diasporic group in Southeast Asian countries such as Thailand, Malaysia, and Indonesia. In Singapore, people of Han Chinese or Chinese descent make up around 75% of the country's population. The Han Chinese have exerted a primary formative influence in the development and growth of Chinese civilization. Originating from Zhongyuan, the Han Chinese trace their ancestry to the Huaxia people, a confederation of agricultural tribes that lived along the middle and lower reaches of the Yellow River in the north central plains of Chin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xianbei
The Xianbei (; ) were an ancient nomadic people that once resided in the eastern Eurasian steppes in what is today Mongolia, Inner Mongolia, and Northeastern China. The Xianbei were likely not of a single ethnicity, but rather a multilingual, multi-ethnic confederation consisting of mainly Proto-Mongols (who spoke either pre-Proto-Mongolic,, quote: "The Xianbei confederation appears to have contained speakers of Pre-Proto-Mongolic, perhaps the largest constituent linguistic group, as well as former Xiongnu subjects, who spoke other languages, Turkic almost certainly being one of them."Pulleyblank, Edwin G. (1983). "The Chinese and Their Neighbors in Prehistoric and Early Historic China," in The Origins of Chinese Civilization, University of California Pressp. 452of pp. 411–466. or Para-Mongolic languages), and, to a minor degree, Tungusic and Turkic peoples. They originated from the Donghu people who splintered into the Wuhuan and Xianbei when they were defeated by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emperor Xiaowen Of Northern Wei
Emperor Xiaowen of Northern Wei ((北)魏孝文帝) (October 13, 467 – April 26, 499), personal name Tuoba Hong (拓拔宏), later Yuan Hong (元宏), was an emperor of China's Northern Wei dynasty, reigning from September 20, 471 to April 26, 499. Under the regent of Empress Dowager Feng, Emperor Xiaowen enacted a new land-tenure system named the equal-field system in 485, which was aimed at boosting agricultural production and tax receipts. The implementation of the equal-field system was largely due to the court's desire to break the economic power of local magnates who sheltered residents under their control living in fortified villages. Under this system, all land was owned by the state, and then equally distributed to taxpaying farmers. This system successfully created a stable fiscal infrastructure and a basis for universal military conscription for the Northern Wei, and continued well into the Tang dynasty. The equal-field program was coupled with another initiative, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uprisings Of Northern Wei
Rebellion is an uprising that resists and is organized against one's government. A rebel is a person who engages in a rebellion. A rebel group is a consciously coordinated group that seeks to gain political control over an entire state or a portion of a state. A rebellion is often caused by political, religious, or social grievances that originate from a perceived inequality or marginalization. ''Rebellion'' comes from Latin ''re'' and ''bellum'', and in Lockian philosophy refers to the responsibility of the people to overthrow unjust government. Classification Uprisings which revolt, resisting and taking direct action against an authority, law or policy, as well as organize, are rebellions. An insurrection is an uprising to change the government. If a government does not recognize rebels as belligerents, then they are insurgents and the revolt is an insurgency. In a larger conflict, the rebels may be recognized as belligerents without their government being recognized ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhangjiakou
Zhangjiakou (), also known as Kalgan and by several other names, is a prefecture-level city in northwestern Hebei province in Northern China, bordering Beijing to the southeast, Inner Mongolia to the north and west, and Shanxi to the southwest. In 2020, its population was 4,118,908 inhabitants, with an area of , divided into 17 counties and districts. The built-up (''or metro'') area, made of Qiaoxi, Qiaodong, Chongli, Xuanhua, Xiahuayuan Districts, is largely conurbated, with 1,413,861 inhabitants in 2020 in an area of . Since ancient times, Zhangjiakou has been a stronghold of military significance and vied for by multiple sides, hence it is nicknamed the Northern Gate of Beijing. Due to its strategic position on several important transport arteries, it is a critical node for travel between Hebei and Inner Mongolia and connecting northwest China, Mongolia, and Beijing. Dajingmen, an important gate and junction of the Great Wall of China, is located here. In the south, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhangbei County
Zhangbei County (), in northwestern Hebei province, China, is a county formerly in the Chahar (province), Chahar province. Its name, which literally means "North of Zhang[jiakou]", derives from the fact that it is north-northeast of Zhangjiakou. Zhangbei Town is the seat of the county government. Administrative divisions There are 4 towns and 14 townships under the county's administration. Towns: *Zhangbei Town (), Gonghui, Zhangbei County, Gonghui (), Ertai (town), Ertai (), Dahulun () Townships: *Tailugou Township (), Youlougou Township (), Mantouying Township (), Erquanjing Township (), Danjinghe Township (), Dahe Township, Zhangbei County, Dahe Township (), Hailiutu Township (), Liangmianjing Township (), Haojiaying Township (), Baimiaotan Township (), Xiao'ertai Township (), Zhanhai Township (), Sanhao Township (), Huangshiya Township () Climate Transportation *China National Highway 207 References External linksInformation of Zhangbei County County-level div ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ulanqab
Ulanqab or Ulan Chab ( zh, s=乌兰察布, p=Wūlánchábù; ''Ulaɣančab qota-means in Mongolian Ulaan-red, Tsab/tsav is-hills''; Mongolian Cyrillic: Улаанцав хот) is a region administered as a prefecture-level city in south-central Inner Mongolia, China. Its administrative centre is in Jining District, which was formerly a county-level city. It was established as a prefecture-level city on 1 December 2003, formed from the former Ulanqab League. The Ulanqab Stadium is located in the city. Ulaan Chab city has an area of . It borders Hohhot to the west, Mongolia to the north, Xilin Gol League to the northeast, Hebei to the east and Shanxi to the south. As of the 2020 census, its total population was, 1,706,328 inhabitants (2,143,590 in 2010) whom 550,231 inhabitants lived in the built-up (or metro) area made of Jining District and Qahar Right Front Banner largely conurbated in its northern part. The western part of Ulaan Chab used to be part of the now-defunct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siziwang Banner
Dorbod Banner or Siziwang Banner (; zh, c=四子王旗) is a Banner (Inner Mongolia), banner (County (People's Republic of China), county equivalent) in Ulanqab, Inner Mongolia, China, bordering Mongolia's Dornogovi Province to the northwest. It is located about north of Hohhot, the capital of Inner Mongolia. The banner spans , and has a population of 129,372 as of 2020. Its seat of government is located in Wulanhua. Toponymy The Chinese name for the banner ''siziwang'', literally "four princes", derives from the area's historic rule by four brothers. The Mongolian name for the banner ''dorbed'' means "of four". History The area of Dorbod Banner was ruled by four Mongol brothers, Sengge (Сэнгэ, ), Suonuobu (), Bonpo (Бумба, ) and Yi'erzhamu (), who were descendants of Hasar, a brother of Genghis Khan. They led their tribe in participating in the Manchu Qing Dynasty's conquest of Ming Dynasty, Ming China in the early 17th century. In recognition of their service, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hohhot
Hohhot,; abbreviated zh, c=呼市, p=Hūshì, labels=no formerly known as Kweisui, is the Capital (political), capital of Inner Mongolia in the North China, north of the China, People's Republic of China, serving as the region's administrative, economic and cultural center.''The New Encyclopædia Britannica'', 15th Edition (1977), Volume I, p. 275. Its population was 3,446,100 inhabitants as of the 2020 census, of whom 2,944,889 lived in the metropolitan area consisting of 4 urban districts (including Hohhot Economic and Development Zone) plus the Tumed Left Banner. The name of the city in Mongolian means "Blue City", although it is also wrongly referred to as the "Green City."Perkins (1999), p. 212. The color blue in Mongol culture is associated with the sky, eternity and purity. In Chinese, the name can be translated as ''Qīng Chéng'' ( zh, c=青城 , l=Distinguishing blue from green in language#Chinese, Blue/Green City) The name has also been variously romanized as Kokota ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |