|
Hohhot
Hohhot,; abbreviated zh, c=呼市, p=Hūshì, labels=no formerly known as Kweisui, is the Capital (political), capital of Inner Mongolia in the North China, north of the China, People's Republic of China, serving as the region's administrative, economic and cultural center.''The New Encyclopædia Britannica'', 15th Edition (1977), Volume I, p. 275. Its population was 3,446,100 inhabitants as of the 2020 census, of whom 2,944,889 lived in the metropolitan area consisting of 4 urban districts (including Hohhot Economic and Development Zone) plus the Tumed Left Banner. The name of the city in Mongolian means "Blue City", although it is also wrongly referred to as the "Green City."Perkins (1999), p. 212. The color blue in Mongol culture is associated with the sky, eternity and purity. In Chinese, the name can be translated as ''Qīng Chéng'' ( zh, c=青城 , l=Distinguishing blue from green in language#Chinese, Blue/Green City) The name has also been variously romanized as Kokota ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inner Mongolia
Inner Mongolia, officially the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, is an Autonomous regions of China, autonomous region of China. Its border includes two-thirds of the length of China's China–Mongolia border, border with the country of Mongolia. Inner Mongolia also accounts for a small section of China's China–Russia border, border with Russia (Zabaykalsky Krai). Its capital is Hohhot; other major cities include Baotou, Chifeng, Tongliao, and Ordos City, Ordos. The autonomous region was established in 1947, incorporating the areas of the former Republic of China (1912–1949), Republic of China provinces of Suiyuan, Chahar Province, Chahar, Rehe Province, Rehe, Liaobei, and Xing'an Province, Xing'an, along with the northern parts of Gansu and Ningxia. Its area makes it the List of Chinese administrative divisions by area, third largest Chinese administrative subdivision, constituting approximately and 12% of China's total land area. Due to its long span from east to west, Inn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xincheng District, Hohhot
Xincheng District (Mongolian: ; zh, s=新城区) is one of four districts of the prefecture-level city of Hohhot, the capital of Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China. It is located in the northeast of central Hohhot, with Saihan District to its south, Huimin District to its west, Wuchuan County to its north, and Zhuozi County of Ulanqab to its east. The District spans 700 square kilometers and has 699,672 inhabitants as of the 2020 census. Subdivisions Huimin District is made up of 7 subdistricts and 1 town. Transport Railway stations Xincheng District houses Hohhot's two major railway stations, with the older Hohhot railway station of the Beijing–Baotou railway, first built in 1921, located in the west of the district, and the newer Hohhot East railway station of the Zhangjiakou–Hohhot high-speed railway, first built in 2010, located in the east. Metro Xincheng is currently served by two lines and 24 stations of the Hohhot Metro. * - Xinhua Square , Peop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dazhao Temple (Hohhot)
Dazhao Temple, also known as the Hongci or Wuliang Temple and as the Ih Juu (, sci , SASM/GNC , "Great Temple"), is a Tibetan Buddhist monastery of the Gelugpa order in the city of Hohhot in Inner Mongolia in North China. It is the oldest and largest temple in the city and is located West of Danan Street in the Yuquan District. In 1557, when the Tümed Mongol leader Altan Khan began its construction, it was the first building of Hohhot; the rest of the city subsequently growing around it. The temple is said to have been completed in 1579 during the Ming dynasty. The Dazhao Temple owes its fame to its astounding silver Sakyamuni Buddha statue. The 3rd Dalai Lama, Sonam Gyatso, visited the temple in 1586 and consecrated the silver Buddha statue. As a consequence, Hohhot became a religious center for people from all over Mongolia who came to receive its blessings. The temple also has a shrine that was dedicated to the Kangxi Emperor in the late 17th century and mural ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bao Gang
Bao Gang (; born May 1969) is a Chinese politician of Mongolian ethnicity, currently serving as vice chairman of Inner Mongolia and party secretary of the capital city Hohhot. Early life and education Bao was born into a Mongolian family, in Fuxin County, Liaoning, in May 1969. In 1987, he entered Inner Mongolia University, majoring in national economic management. He earned his MBA from Tsinghua University in July 2009. Career Bao worked in government after university in 1991. Beginning in July 1991, he assumed various posts in the General Office of Inner Mongolia Autonomous Regional People's Government, including section member, deputy director, and director. After a short period at the State-Owned Assets Supervision and Administration Commission of Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, in September 2006, he was appointed secretary of the Hohhot Municipal Commission for Discipline Inspection, and was promoted to member of the standing committee of the Hohhot Municipal Committee o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Five Pagoda Temple (Hohhot)
The Five Pagoda Temple (; Mongolian: Tabun suburγan-u süm-e), also known as the "Precious Pagoda of the Buddhist Relics of the Diamond Throne" (), is a Buddhist temple in the city of Hohhot in Inner Mongolia in north-west China. It is located in the older part of the city in the vicinity of Qingcheng Park. The construction of the pagoda by the Mongol monk Yangcarci began in 1727 and was completed in 1732. The stupa, which is situated at the northernmost part of the temple complex, is surmounted by five pagodas and has 1,563 images of Buddhas carved into its walls each one differing slightly from the other. Against the northern wall, outside the stupa, one can find three large stone carvings representing: * the wheel of life (left), * a representation of the universe according to Buddhist cosmology (middle), and * a rare Mongolian cosmological map, which illustrates the zodiac and positions of numerous stars. It is the only such map discovered yet in China from this era ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Altan Khan
Altan Khan of the Tümed (2 January 1508 – 13 January 1582; ; Chinese: 阿勒坦汗), whose given name was Anda ( Mongolian: Алтан (Аньда); Chinese: 俺答), was the leader of the Tümed Mongols de facto ruler of the Right Wing, or western tribes, of the Mongols, and the first Ming Shunyi King (順義王). He was the grandson of Dayan Khan (1464–1543), a descendant of Kublai Khan (1215–1294), who had managed to unite a tribal league between the Khalkha Mongols in the north and the Chahars (Tsakhars) to the south. His name means "Golden Khan" in the Mongolian language. Consolidation of power Borjigin Barsboladiin Altan was the second son of Bars Bolud Jinong, and a grandson of Batumongke Dayan Khan who had re-unified the Mongolian nobility in an attempt to regain the glory of the Yuan dynasty. Altan Khan ruled the Tümed and belonged to the Right Wing of the Mongols along with his elder brother Gün Bilig, who ruled the Ordos. After Gün Bilig's death ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhaojun Tomb
The Zhaojun Tomb (), located by the Da Hi River nine kilometers south of Hohhot, Inner Mongolia, is said to be the resting place of Wang Zhaojun, a commoner woman from the Han dynasty who married a Xiongnu ''Chanyu'', nomadic chieftain from the steppes. The tomb is also referred to by its Mongolian name, Temür Urkhu (), meaning "Iron Wall". Another nickname, "Green Mound" (), refers to a legend that in autumn, when grass and trees wither, those plants on the cemetery mound continue to prosper. The tomb, one of the major attractions in the city of Hohhot, occupies some 13,000 m2 of land, with a 33-metre mound containing Zhaojun's coffin. The tomb is honorary, Wang Zhaojun is not actually buried here. Her true grave and cause of death is unknown. Still the "tomb" is visited by thousands of Chinese tourists each year and is noted for its attractive scenery. The first Chinese mention of the cemetery in written record is in the Tang dynasty, by Du You () in ''A Comprehensive Guide' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern Mongolian
In the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region of China, the Mongolian language is the official provincial language (alongside Chinese). Mongols are the second largest ethnic group (after Han Chinese), comprising about 17 percent of the population. There are at least 4.1 million ethnic Mongols in Inner Mongolia, including subgroups like the Chahars, Ordos, Baarin, Khorchin, Kharchin, and Buryats. While there is a standardized dialect of the Mongolian language in Inner Mongolia (in contrast to the standard language in the state of Mongolia, where the Khalkha make up most of the population), different Mongolian dialects continue to be spoken by different subgroups of the Mongols. Some proposed the Peripheral Mongolian dialect group to cover the Mongolian dialects in Inner Mongolia. Overview The Mongolian language is the most widely spoken and best-known member of the Mongolic language family. Most speakers of the Mongolian language reside in the independent state of Mongolia and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
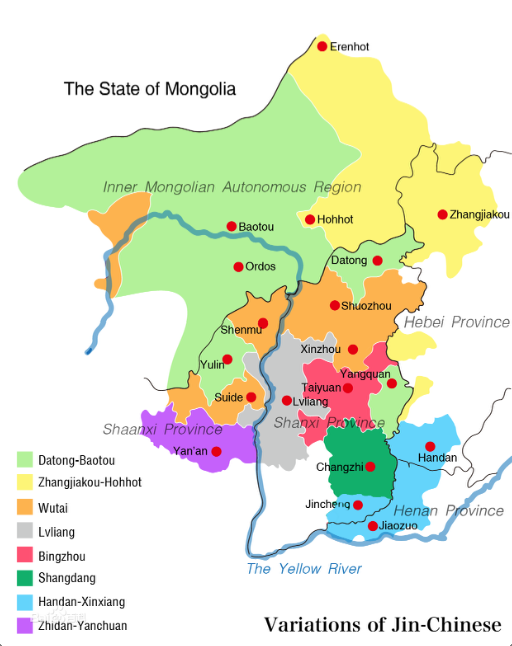
Jin Chinese
Jin () is a group of Chinese linguistic varieties spoken by roughly 48 million people in northern China, including most of Shanxi province, much of central Inner Mongolia, and adjoining areas in Hebei, Henan, and Shaanxi provinces. The status of Jin is disputed among linguists; some prefer to include it within Mandarin, but others set it apart as a closely related but separate sister group. Classification After the concept of Mandarin Chinese was proposed, the Jin dialects were universally included within it, mainly because Chinese linguists paid little attention to these dialects at the time. In order to promote Standard Mandarin in the early days of People's Republic of China, linguists started to research various dialects in Shanxi, comparing these dialects with Standard Mandarin for helping the locals to learn it more quickly. During this period, a few linguists discovered some unique features of Jin Chinese that do not exist in other northern Mandarin dialects, planting t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telephone Numbers In China
Telephone numbers in the People's Republic of China are administered according to the Telecommunications Network Numbering Plan of China. The structure of telephone numbers for landlines and mobile service is different. Landline telephone numbers have area codes, whereas mobile numbers do not. In major cities, landline numbers consist of a two-digit area code followed by an eight-digit local number. In other places, landline numbers consist of a three-digit area code followed by a seven- or eight-digit local number. Mobile phone numbers consist of eleven digits. Landline calls within the same area do not require the area code. Calls to other areas require dialing the trunk prefix ''0'' and the area code. The Special administrative regions of China, special administrative regions of Hong Kong and Macau are not part of this numbering plan, and use the calling codes +852, 852 and +853, 853 respectively. Mobile phones In mainland China, mobile phone numbers have eleven digits in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autonomous Regions Of China
The autonomous regions ( zh, s=自治区, p=Zìzhìqū) are one of four types of province-level divisions of China, province-level divisions of the People's Republic of China. Like provinces of China, Chinese provinces, an autonomous region has its own local government, but under the law of the People's Republic of China, an autonomous region has more legislative rights, such as the right to "formulate self-government regulations and other separate regulations." An autonomous region is the highest level of Autonomous administrative divisions of China, minority autonomous entity in China, which has a comparably higher population of a particular minority ethnic group. There are five autonomous regions in China: Guangxi, Inner Mongolia, Inner Mongolia (Nei Menggu), Ningxia, Tibet Autonomous Region, Tibet (Xizang), and Xinjiang. History Established in 1947, the Inner Mongolia, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region became the first autonomous region in the Communist-controlled China ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |