|
Shoulder Surfing (computer Security)
In computer security, shoulder surfing is a social engineering technique used to obtain information such as personal identification numbers (PINs), passwords, and other confidential data by looking over the victim's shoulder. Unauthorized users watch the keystrokes inputted on a device or listen to sensitive information being spoken, which is also known as eavesdropping. Methods and history Shoulder surfing can be performed at close range (by directly looking over the victim's shoulder) or at long range with, for example, a pair of binoculars or similar hardware. Attackers do not need technical skills to perform this method, and keen observation of the victims' surroundings and typing patterns is sufficient. In the early 1980s, shoulder surfing was practiced near public pay phones to steal calling card digits and make long-distance calls or to sell them for lower prices than the original purchaser paid. However, the advent of modern-day technologies like hidden cameras and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Security
Computer security (also cybersecurity, digital security, or information technology (IT) security) is a subdiscipline within the field of information security. It consists of the protection of computer software, systems and computer network, networks from Threat (security), threats that can lead to unauthorized information disclosure, theft or damage to computer hardware, hardware, software, or Data (computing), data, as well as from the disruption or misdirection of the Service (economics), services they provide. The significance of the field stems from the expanded reliance on computer systems, the Internet, and wireless network standards. Its importance is further amplified by the growth of smart devices, including smartphones, televisions, and the various devices that constitute the Internet of things (IoT). Cybersecurity has emerged as one of the most significant new challenges facing the contemporary world, due to both the complexity of information systems and the societi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
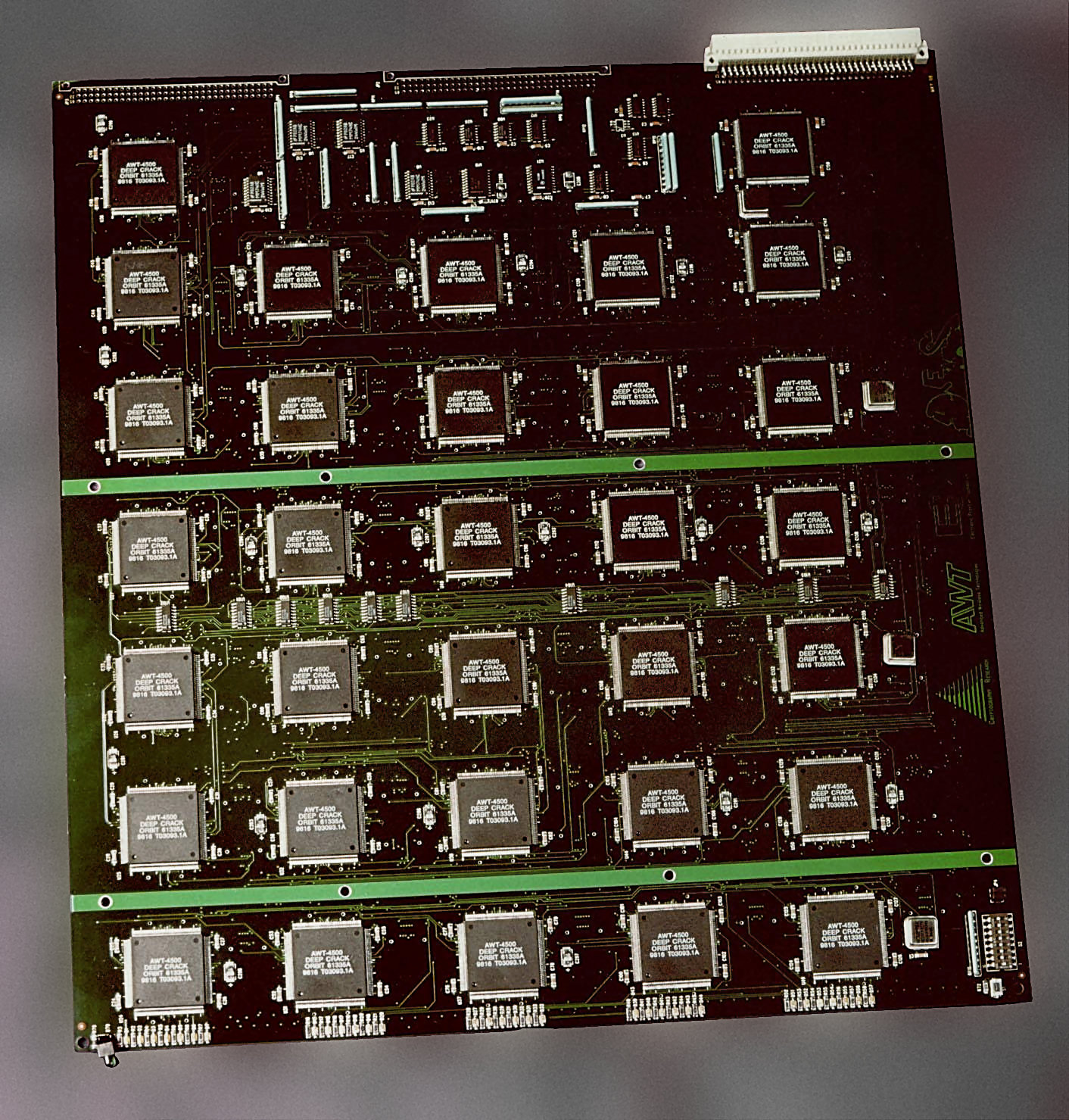
Brute-force Attack
In cryptography, a brute-force attack or exhaustive key search is a cryptanalytic attack that consists of an attacker submitting many possible keys or passwords with the hope of eventually guessing correctly. This strategy can theoretically be used to break any form of encryption that is not information-theoretically secure. However, in a properly designed cryptosystem the chance of successfully guessing the key is negligible. When cracking passwords, this method is very fast when used to check all short passwords, but for longer passwords other methods such as the dictionary attack are used because a brute-force search takes too long. Longer passwords, passphrases and keys have more possible values, making them exponentially more difficult to crack than shorter ones due to diversity of characters. Brute-force attacks can be made less effective by obfuscating the data to be encoded making it more difficult for an attacker to recognize when the code has been cracked or by ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hacking (computer Security)
Hacking may refer to: Places * Hacking, an area within Hietzing, Vienna, Austria People * David Hacking, 3rd Baron Hacking (born 1938), British barrister and peer * Douglas Hewitt Hacking, 1st Baron Hacking (1884–1950), British Conservative politician * Ian Hacking (1936–2023), Canadian philosopher of science * Philip Hacking (1931–2024), English Anglican priest, and itinerant evangelical speaker Sports * Hacking (falconry), the practice of raising falcons in captivity then later releasing into the wild * Hacking (rugby), tripping an opposing player * Pleasure riding, horseback riding for purely recreational purposes, also called hacking * Shin-kicking, an English martial art also called hacking Technology * Hacker, a computer expert with advanced technical knowledge ** Hacker culture, activity within the computer programmer subculture * Security hacker, someone who breaches defenses in a computer system ** Cybercrime, which involves security hacking * Phone hacki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phishing
Phishing is a form of social engineering and a scam where attackers deceive people into revealing sensitive information or installing malware such as viruses, worms, adware, or ransomware. Phishing attacks have become increasingly sophisticated and often transparently mirror the site being targeted, allowing the attacker to observe everything while the victim navigates the site, and transverses any additional security boundaries with the victim. As of 2020, it is the most common type of cybercrime, with the Federal Bureau of Investigation's Internet Crime Complaint Center reporting more incidents of phishing than any other type of cybercrime. The term "phishing" was first recorded in 1995 in the cracking toolkit AOHell, but may have been used earlier in the hacker magazine '' 2600''. It is a variation of ''fishing'' and refers to the use of lures to "fish" for sensitive information. Measures to prevent or reduce the impact of phishing attacks include legislation, user educa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Information Diving
Information diving is the practice of recovering technical data, sometimes confidential or secret, from discarded material. In recent times, this has chiefly been from data storage elements in discarded computers, most notably recoverable data remaining on hard drives. Those in charge of discarding computers usually neglect to erase the hard drive. It is often in such circumstances for an information diver to copy installed software (e.g., word processors, operating systems, computer games, etc.). Other data may also be available, such as credit card information that was stored on the machine. Companies claim to be especially careful with customer data, but the number of data breaches by any type of entity (e.g., education, health care, insurance, government, ...) suggest otherwise. In the UK, information diving has been referred to as "binology". Today, files, letters, memos, photographs, IDs, passwords, credit cards, and more can be found in dumpsters. Many people do not conside ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Credit Card Fraud
Credit card fraud is an inclusive term for fraud committed using a payment card, such as a credit card or debit card. The purpose may be to obtain goods or services or to make payment to another account, which is controlled by a criminal. The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) is the data security standard created to help financial institutions process card payments securely and reduce card fraud. Credit card fraud can be authorised, where the genuine customer themselves processes payment to another account which is controlled by a criminal, or unauthorised, where the account holder does not provide authorisation for the payment to proceed and the transaction is carried out by a third party. In 2018, unauthorised financial fraud losses across payment cards and remote banking totalled £844.8 million in the United Kingdom. Whereas banks and card companies prevented £1.66 billion in unauthorised fraud in 2018. That is the equivalent to £2 in every £3 of atte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virtual Reality Headset
A virtual reality headset (or VR headset) is a Head-mounted display, head-mounted device that uses 3D near-eye displays and positional tracking to provide a virtual reality environment for the user. VR headsets are widely used with Virtual reality game, VR video games, but they are also used in other applications, including simulators and trainers. VR headsets typically include a stereoscopic display (providing separate images for each eye), Stereophonic sound, stereo sound, and sensors like accelerometers and gyroscopes for tracking the pose tracking, pose of the user's head to match the orientation of the virtual camera with the user's eye positions in the real world. Augmented reality (AR) headsets are VR headsets that enable the user to see and interact with the outside world. Examples of AR headsets include the Apple Vision Pro and Meta Quest 3. VR headsets typically use at least one MEMS IMU for three degrees of freedom (3DOF) motion tracking, and optionally more tracking t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Authentication
Authentication (from ''authentikos'', "real, genuine", from αὐθέντης ''authentes'', "author") is the act of proving an Logical assertion, assertion, such as the Digital identity, identity of a computer system user. In contrast with identification, the act of indicating a person or thing's identity, authentication is the process of verifying that identity. Authentication is relevant to multiple fields. In art, antiques, and anthropology, a common problem is verifying that a given artifact was produced by a certain person, or in a certain place (i.e. to assert that it is not counterfeit), or in a given period of history (e.g. by determining the age via carbon dating). In computer science, verifying a user's identity is often required to allow access to confidential data or systems. It might involve validating personal identity documents. In art, antiques and anthropology Authentication can be considered to be of three types: The ''first'' type of authentication is accep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Login
In computer security, logging in (or logging on, signing in, or signing on) is the process by which an individual gains access to a computer system or program by identifying and authenticating themselves. Typically, user credentials consist of a username and a password. These credentials themselves are sometimes referred to as ''a'' login. Modern secure systems often require a second factor, such as email or SMS confirmation for extra security. Social login allows a user to use an existing cell phone number, or user credentials from another email or social networking service to sign in or create an account on a new website. When access is no longer needed, the user can log out, log off, sign out or sign off. Procedure Logging in is usually used to enter a specific page, website, platform or application, which trespassers cannot see. Once the user is logged in, the login token may be used to track what actions the user has taken while connected to the site. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multi-factor Authentication
Multi-factor authentication (MFA; two-factor authentication, or 2FA) is an electronic authentication method in which a user is granted access to a website or application only after successfully presenting two or more distinct types of evidence (or factors) to an authentication mechanism. MFA protects personal data—which may include personal identification or financial assets—from being accessed by an unauthorized third party that may have been able to discover, for example, a single password. Usage of MFA has increased in recent years. Security issues which can cause the bypass of MFA are fatigue attacks, phishing and SIM swapping. Accounts with MFA enabled are significantly less likely to be compromised. Authentication factors Authentication takes place when someone tries to log into a computer resource (such as a computer network, device, or application). The resource requires the user to supply the identity by which the user is known to the resource, along wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Personal Digital Assistant
A personal digital assistant (PDA) is a multi-purpose mobile device which functions as a personal information manager. Following a boom in the 1990s and 2000s, PDAs were mostly displaced by the widespread adoption of more highly capable smartphones, in particular those based on iOS and Android (operating system), Android in the late 2000s, and thus saw a rapid decline. A PDA has an electronic visual display. Most models also have audio capabilities, allowing usage as a portable media player, and also enabling many of them to be used as telephones. By the early 2000s, nearly all PDA models had the ability to access the Internet, intranets or extranets via Wi-Fi or wireless WANs, and since then generally included a web browser. Sometimes, instead of buttons, later PDAs employ touchscreen technology. History The first PDA, the Psion Organiser, Organiser, was released in 1984 by Psion (company), Psion, followed by Psion Series 3, Psion's Series 3, in 1991. The latter began to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
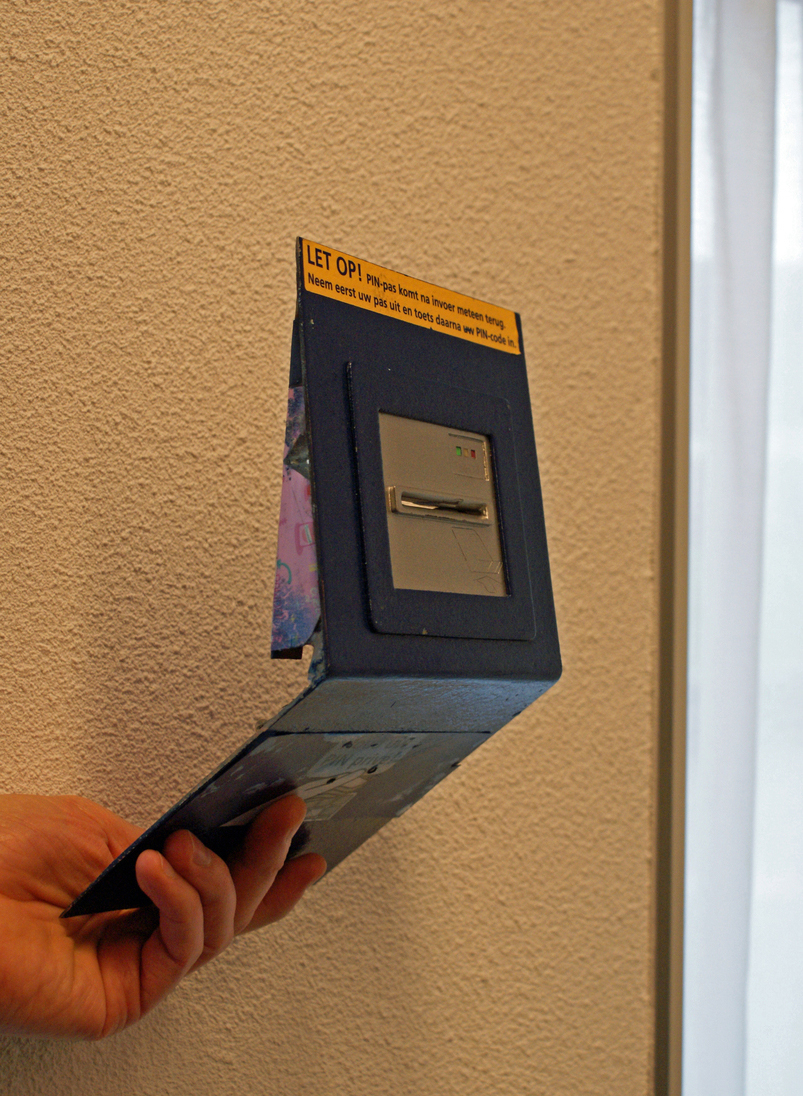
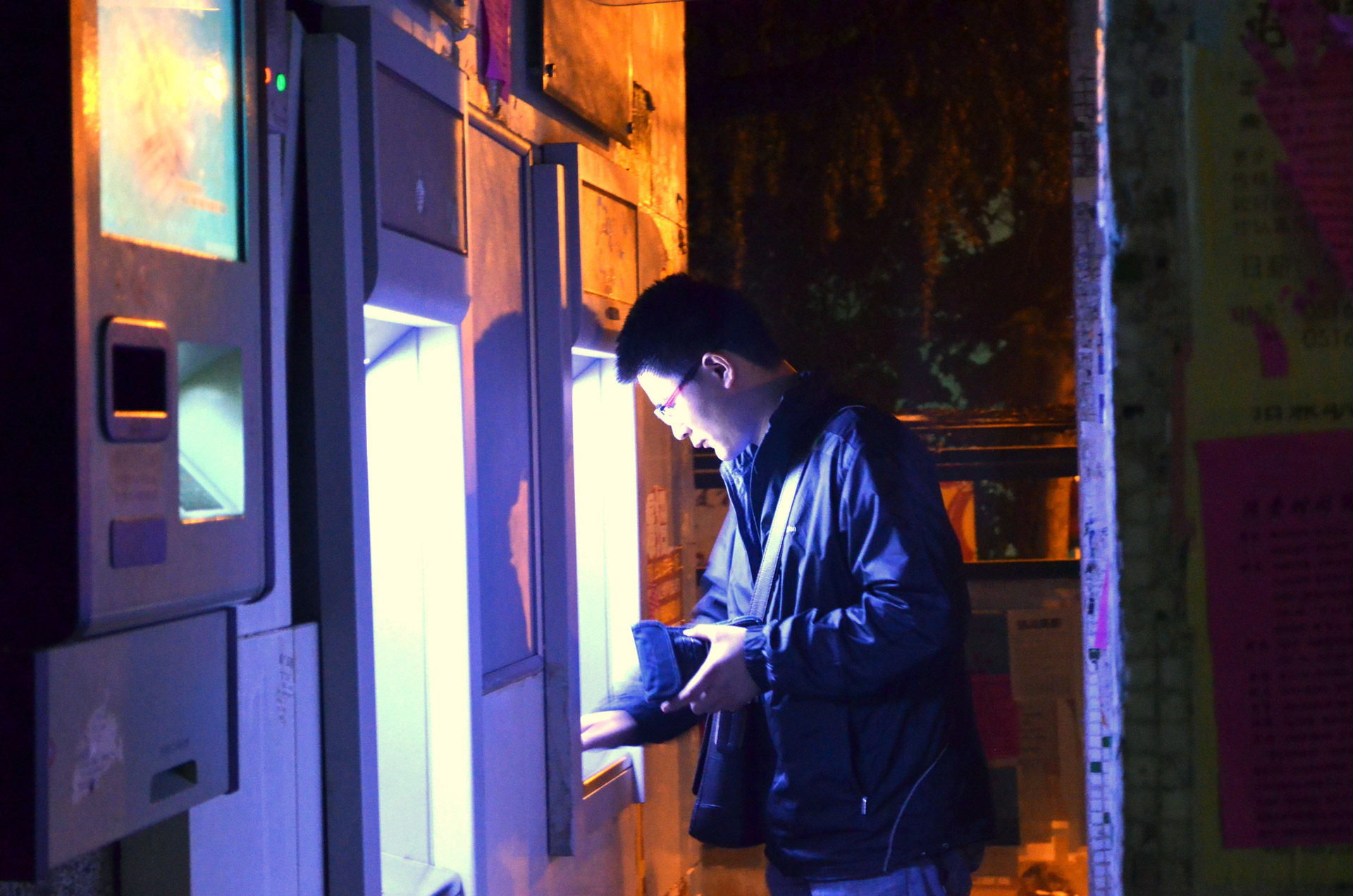
Automatic Teller Machine
An automated teller machine (ATM) is an electronic telecommunications device that enables customers of financial institutions to perform financial transactions, such as cash withdrawals, deposits, funds transfers, balance inquiries or account information inquiries, at any time and without the need for direct interaction with bank staff. ATMs are known by a variety of other names, including automatic teller machines (ATMs) in the United States (sometimes RAS syndrome, redundantly as "ATM machine"). In Canada, the term automated banking machine (ABM) is also used, although ATM is also very commonly used in Canada, with many Canadian organizations using ATM rather than ABM. In British English, the terms cashpoint, cash machine and hole in the wall are also used. ATMs that are Independent ATM deployer, not operated by a financial institution are known as "White-label ABMs, white-label" ATMs. Using an ATM, customers can access their bank deposit or credit accounts in order to make ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |