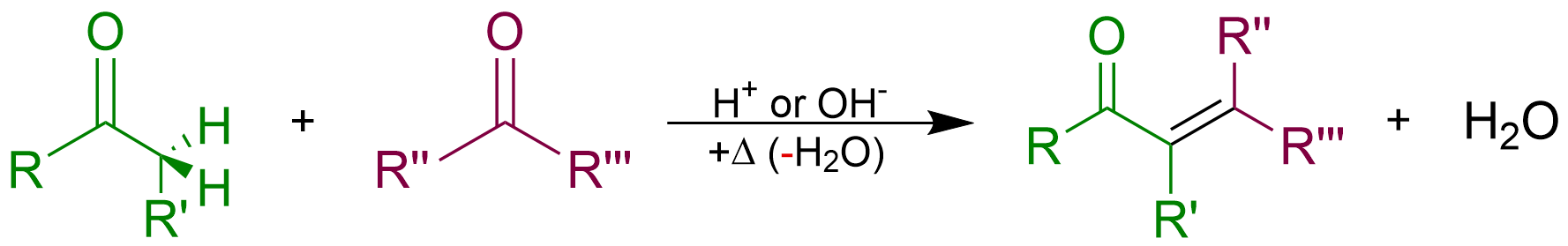|
Self-condensation
Self-condensation is an organic reaction in which a chemical compound containing a carbonyl group acts both as the electrophile and the nucleophile in an aldol condensation. It is also called a symmetrical aldol condensation as opposed to a mixed aldol condensation in which the electrophile and nucleophile are different species. For example, two molecules of acetone condense to a single compound mesityl oxide in the presence of an ion-exchange resin: :2 CH3COCH3 → (CH3)2C=CH(CO)CH3 + H2O For synthetic uses, this is generally an undesirable, but spontaneous and favored side-reaction of mixed aldol condensation, and special precautions are needed to prevent it. Preventing self-condensation In many cases, self-condensation is an unwanted side-reaction. Therefore, chemists have adopted many ways to prevent this from occurring when performing a crossed aldol reaction. The use of a more reactive electrophile, and a non-enolizable partner If acetophenone and benzaldehyde are put tog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aldol Condensation
An aldol condensation is a condensation reaction in organic chemistry in which two carbonyl moieties (of aldehydes or ketones) react to form a β-hydroxyaldehyde or β-hydroxyketone (an aldol reaction), and this is then followed by dehydration to give a conjugated enone. The overall reaction is as follows (where the Rs can be H): Aldol condensations are important in organic synthesis and biochemistry as ways to form carbon–carbon bonds. In its usual form, it involves the nucleophilic addition of a ketone enolate to an aldehyde to form a β-hydroxy ketone, or "aldol" (aldehyde + alcohol), a structural unit found in many naturally occurring molecules and pharmaceuticals. The term ''aldol condensation'' is also commonly used, especially in biochemistry, to refer to just the first (addition) stage of the process—the aldol reaction itself—as catalyzed by aldolases. However, this is formally an addition reaction rather than a condensation reaction because it does n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Reaction
Organic reactions are chemical reactions involving organic compounds. The basic organic chemistry reaction types are addition reactions, elimination reactions, substitution reactions, pericyclic reactions, rearrangement reactions, photochemical reactions and redox reactions. In organic synthesis, organic reactions are used in the construction of new organic molecules. The production of many man-made chemicals such as drugs, plastics, food additives, fabrics depend on organic reactions. The oldest organic reactions are combustion of organic fuels and saponification of fats to make soap. Modern organic chemistry starts with the Wöhler synthesis in 1828. In the history of the Nobel Prize in Chemistry awards have been given for the invention of specific organic reactions such as the Grignard reaction in 1912, the Diels-Alder reaction in 1950, the Wittig reaction in 1979 and olefin metathesis in 2005. Classifications Organic chemistry has a strong tradition of naming a specific reacti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitromethane
Nitromethane, sometimes shortened to simply "nitro", is an organic compound with the chemical formula . It is the simplest organic nitro compound. It is a polar liquid commonly used as a solvent in a variety of industrial applications such as in extractions, as a reaction medium, and as a cleaning solvent. As an intermediate in organic synthesis, it is used widely in the manufacture of pesticides, explosives, fibers, and coatings. Nitromethane is used as a fuel additive in various motorsports and hobbies, e.g. Top Fuel drag racing and miniature internal combustion engines in radio control, control line and free flight model aircraft. Preparation Nitromethane is produced industrially by combining propane and nitric acid in the gas phase at 350–450 °C (662–842 °F). This exothermic reaction produces the four industrially significant nitroalkanes: nitromethane, nitroethane, 1-nitropropane, and 2-nitropropane. The reaction involves free radicals, includin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TiCl4
Titanium tetrachloride is the inorganic compound with the formula . It is an important intermediate in the production of titanium metal and the pigment titanium dioxide. is a volatile liquid. Upon contact with humid air, it forms thick clouds of titanium dioxide () and hydrochloric acid, a reaction that was formerly exploited for use in smoke machines. It is sometimes referred to as "tickle" or "tickle 4" due to the phonetic resemblance of its molecular formula () to the word. Properties and structure is a dense, colourless distillable liquid, although crude samples may be yellow or even red-brown. It is one of the rare transition metal halides that is a liquid at room temperature, being another example. This property reflects the fact that molecules of weakly self-associate. Most metal chlorides are polymers, wherein the chloride atoms bridge between the metals. Its melting and boiling points are similar to those of . has a "closed" electronic shell, with the same num ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acetaldehyde
Acetaldehyde (IUPAC systematic name ethanal) is an organic chemical compound with the formula CH3 CHO, sometimes abbreviated by chemists as MeCHO (Me = methyl). It is a colorless liquid or gas, boiling near room temperature. It is one of the most important aldehydes, occurring widely in nature and being produced on a large scale in industry. Acetaldehyde occurs naturally in coffee, bread, and ripe fruit, and is produced by plants. It is also produced by the partial oxidation of ethanol by the liver enzyme alcohol dehydrogenase and is a contributing cause of hangover after alcohol consumption. Pathways of exposure include air, water, land, or groundwater, as well as drink and smoke. Consumption of disulfiram inhibits acetaldehyde dehydrogenase, the enzyme responsible for the metabolism of acetaldehyde, thereby causing it to build up in the body. The International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) has listed acetaldehyde as a Group 1 carcinogen. Acetaldehyde is "one of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triethylamine
Triethylamine is the chemical compound with the formula N(CH2CH3)3, commonly abbreviated Et3N. It is also abbreviated TEA, yet this abbreviation must be used carefully to avoid confusion with triethanolamine or tetraethylammonium, for which TEA is also a common abbreviation. It is a colourless volatile liquid with a strong fishy odor reminiscent of ammonia. Like diisopropylethylamine (Hünig's base), triethylamine is commonly employed in organic synthesis, usually as a base. Synthesis and properties Triethylamine is prepared by the alkylation of ammonia with ethanol: :NH3 + 3 C2H5OH → N(C2H5)3 + 3 H2O The pKa of protonated triethylamine is 10.75,David Evans Research Group and it can be used to prepare buffer solutions at that pH. The |
Trimethylsilyl Chloride
Trimethylsilyl chloride, also known as chlorotrimethylsilane is an organosilicon compound (silyl halide), with the formula (CH3)3SiCl, often abbreviated Me3SiCl or TMSCl. It is a colourless volatile liquid that is stable in the absence of water. It is widely used in organic chemistry. Preparation TMSCl is prepared on a large scale by the ''direct process'', the reaction of methyl chloride with a silicon-copper alloy. The principal target of this process is dimethyldichlorosilane, but substantial amounts of the trimethyl and monomethyl products are also obtained. The relevant reactions are (Me = CH3): : x MeCl + Si → Me3SiCl, Me2SiCl2, MeSiCl3, other products Typically about 2–4% of the product stream is the monochloride, which forms an azeotrope with MeSiCl3. Reactions and uses TMSCl is reactive toward nucleophiles, resulting in the replacement of the chloride. In a characteristic reaction of TMSCl, the nucleophile is water, resulting in hydrolysis to give the hexameth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclohexanone And Acetone
Cyclohexanone is the organic compound with the formula (CH2)5CO. The molecule consists of six-carbon cyclic molecule with a ketone functional group. This colorless oily liquid has an odor reminiscent of acetone. Over time, samples of cyclohexanone assume a pale yellow color. Cyclohexanone is slightly soluble in water and miscible with common organic solvents. Billions of kilograms are produced annually, mainly as a precursor to nylon. Production Cyclohexanone is produced by the oxidation of cyclohexane in air, typically using cobalt catalysts: :C6H12 + O2 → (CH2)5CO + H2O This process forms cyclohexanol as a by-product, and this mixture, called "KA Oil" for ketone-alcohol oil, is the main feedstock for the production of adipic acid. The oxidation involves radicals and the hydroperoxide C6H11O2H as an intermediate. In some cases, purified cyclohexanol, obtained by hydration of cyclohexene, is the precursor. Alternatively, cyclohexanone can be produced by the partial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclohexanone
Cyclohexanone is the organic compound with the formula (CH2)5CO. The molecule consists of six-carbon cyclic molecule with a ketone functional group. This colorless oily liquid has an odor reminiscent of acetone. Over time, samples of cyclohexanone assume a pale yellow color. Cyclohexanone is slightly soluble in water and miscible with common organic solvents. Billions of kilograms are produced annually, mainly as a precursor to nylon. Production Cyclohexanone is produced by the oxidation of cyclohexane in air, typically using cobalt catalysts: :C6H12 + O2 → (CH2)5CO + H2O This process forms cyclohexanol as a by-product, and this mixture, called "KA Oil" for ketone-alcohol oil, is the main feedstock for the production of adipic acid. The oxidation involves radicals and the hydroperoxide C6H11O2H as an intermediate. In some cases, purified cyclohexanol, obtained by hydration of cyclohexene, is the precursor. Alternatively, cyclohexanone can be produced by the par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lithium Diisopropyl Amide
Lithium diisopropylamide (commonly abbreviated LDA) is a chemical compound with the molecular formula . It is used as a strong base and has been widely utilized due to its good solubility in non-polar organic solvents and non-nucleophilic nature. It is a colorless solid, but is usually generated and observed only in solution. It was first prepared by Hamell and Levine in 1950 along with several other hindered lithium diorganylamides to effect the deprotonation of esters at the α position without attack of the carbonyl group. Preparation and structure LDA is commonly formed by treating a cooled (0 to −78 °C) mixture of tetrahydrofuran and diisopropylamine with ''n''-butyllithium. When dissociated, the diisopropylamide anion can become protonated to form diisopropylamine. Diisopropylamine has a p''K''a value of 36. Therefore, its conjugate base is suitable for the deprotonation of compounds with greater acidity, importantly, such weakly acidic compounds (carbon acids) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acetophenone Nitromethane Condensation
Acetophenone is the organic compound with the formula C6H5C(O)CH3. It is the simplest aromatic ketone. This colorless, viscous liquid is a precursor to useful resins and fragrances. Production Acetophenone is formed as a byproduct of the cumene process, the industrial route for the synthesis of phenol and acetone. In the Hock rearrangement of isopropylbenzene hydroperoxide, migration of a methyl group rather than the phenyl group gives acetophenone and methanol as a result of an alternate rearrangement of the intermediate: :C6H5C(CH3)2O2H -> C6H5C(O)CH3 + CH3OH The cumene process is conducted on such a large scale that even the small amount of acetophenone by-product can be recovered in commercially useful quantities. Acetophenone is also generated from ethylbenzene hydroperoxide. Ethylbenzene hydroperoxide is primarily converted to 1-phenylethanol (α-methylbenzyl alcohol) in the process with a small amount of by-product acetophenone. Acetophenone is recovered or hydroge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NaOH
Sodium hydroxide, also known as lye and caustic soda, is an inorganic compound with the formula NaOH. It is a white solid ionic compound consisting of sodium cations and hydroxide anions . Sodium hydroxide is a highly caustic base and alkali that decomposes proteins at ordinary ambient temperatures and may cause severe chemical burns. It is highly soluble in water, and readily absorbs moisture and carbon dioxide from the air. It forms a series of hydrates . The monohydrate crystallizes from water solutions between 12.3 and 61.8 °C. The commercially available "sodium hydroxide" is often this monohydrate, and published data may refer to it instead of the anhydrous compound. As one of the simplest hydroxides, sodium hydroxide is frequently used alongside neutral water and acidic hydrochloric acid to demonstrate the pH scale to chemistry students. Sodium hydroxide is used in many industries: in the manufacture of pulp and paper, textiles, drinking water, soaps and dete ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |