Aldol Condensation on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
An aldol condensation is a 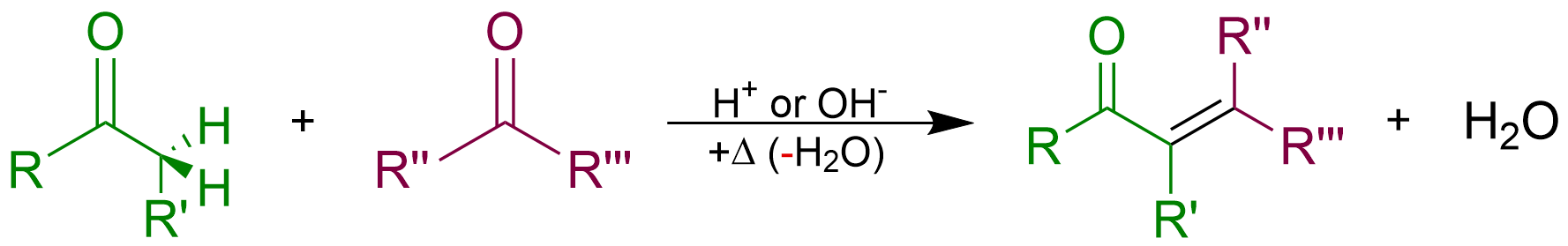 Aldol condensations are important in
Aldol condensations are important in  The term ''aldol condensation'' is also commonly used, especially in
The term ''aldol condensation'' is also commonly used, especially in
 The process begins when a free hydroxide (strong base) strips the highly acidic proton at the alpha carbon of the aldehyde. This deprotonation causes the electrons from the C–H bond to shift and create a new C–C pi bond. The new pi bond then acts as a nucleophile and attacks the remaining aldehyde in the solution, resulting in the formation of a new C–C bond and regeneration of the base catalyst. In the second part of the reaction, the presence of base leads to elimination of water and formation of a new C–C pi bond. The product is referred to as the aldol condensation product.
The process begins when a free hydroxide (strong base) strips the highly acidic proton at the alpha carbon of the aldehyde. This deprotonation causes the electrons from the C–H bond to shift and create a new C–C pi bond. The new pi bond then acts as a nucleophile and attacks the remaining aldehyde in the solution, resulting in the formation of a new C–C bond and regeneration of the base catalyst. In the second part of the reaction, the presence of base leads to elimination of water and formation of a new C–C pi bond. The product is referred to as the aldol condensation product.

 Pentaerythritol is produced on a large scale beginning with crossed aldol condensation of
Pentaerythritol is produced on a large scale beginning with crossed aldol condensation of 
 Ethyl glyoxylate 2 and glutaconate (diethyl-2-methylpent-2-enedioate) 1 react to ''isoprenetricarboxylic acid'' 3 (
Ethyl glyoxylate 2 and glutaconate (diethyl-2-methylpent-2-enedioate) 1 react to ''isoprenetricarboxylic acid'' 3 ( Occasionally, an aldol condensation is buried in a multistep reaction or in catalytic cycle as in the following example:
Occasionally, an aldol condensation is buried in a multistep reaction or in catalytic cycle as in the following example:
 In this reaction an ''alkynal'' 1 is converted into a
In this reaction an ''alkynal'' 1 is converted into a 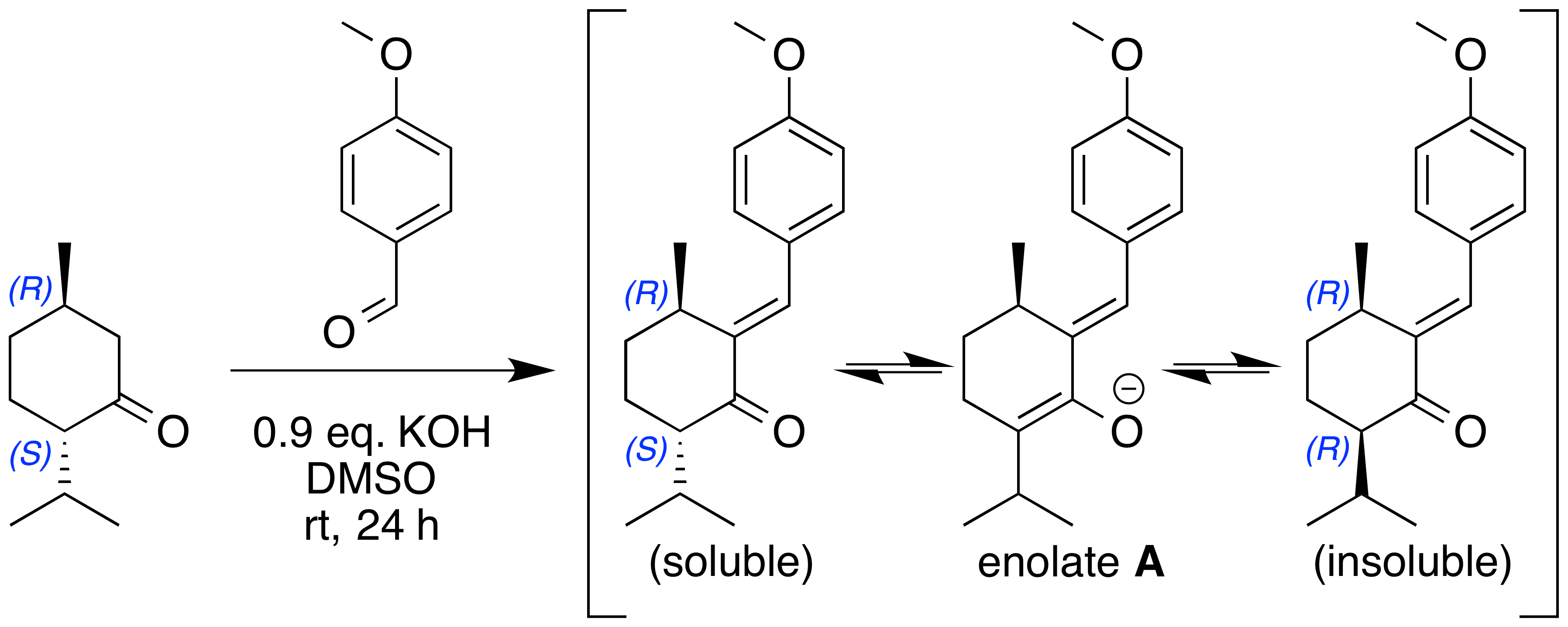 The product can epimerize by way of a common intermediate— enolate A—to convert between the original (''S'',''R'') and the (''R'',''R'') epimers. The (''R'',''R'') product is insoluble in the reaction solvent whereas the (''S'',''R'') is soluble. The precipitation of the (''R'',''R'') product drives the epimerization equilibrium reaction to form this as the major product.
The product can epimerize by way of a common intermediate— enolate A—to convert between the original (''S'',''R'') and the (''R'',''R'') epimers. The (''R'',''R'') product is insoluble in the reaction solvent whereas the (''S'',''R'') is soluble. The precipitation of the (''R'',''R'') product drives the epimerization equilibrium reaction to form this as the major product.
Organic Chemistry Portal
{{Organic reactions Condensation reactions Carbon-carbon bond forming reactions
condensation reaction
In organic chemistry, a condensation reaction is a type of chemical reaction in which two molecules are combined to form a single molecule, usually with the loss of a small molecule such as water. If water is lost, the reaction is also known as a ...
in organic chemistry
Organic chemistry is a subdiscipline within chemistry involving the science, scientific study of the structure, properties, and reactions of organic compounds and organic matter, organic materials, i.e., matter in its various forms that contain ...
in which two carbonyl
In organic chemistry, a carbonyl group is a functional group with the formula , composed of a carbon atom double bond, double-bonded to an oxygen atom, and it is divalent at the C atom. It is common to several classes of organic compounds (such a ...
moieties (of aldehyde
In organic chemistry, an aldehyde () (lat. ''al''cohol ''dehyd''rogenatum, dehydrogenated alcohol) is an organic compound containing a functional group with the structure . The functional group itself (without the "R" side chain) can be referred ...
s or ketone
In organic chemistry, a ketone is an organic compound with the structure , where R and R' can be a variety of carbon-containing substituents. Ketones contain a carbonyl group (a carbon-oxygen double bond C=O). The simplest ketone is acetone ( ...
s) react to form a β-hydroxyaldehyde or β-hydroxyketone (an aldol reaction
The aldol reaction (aldol addition) is a Chemical reaction, reaction in organic chemistry that combines two Carbonyl group, carbonyl compounds (e.g. aldehydes or ketones) to form a new β-hydroxy carbonyl compound. Its simplest form might invol ...
), and this is then followed by dehydration
In physiology, dehydration is a lack of total body water that disrupts metabolic processes. It occurs when free water loss exceeds intake, often resulting from excessive sweating, health conditions, or inadequate consumption of water. Mild deh ...
to give a conjugated enone.
The overall reaction equation is as follows (where the Rs can be H)
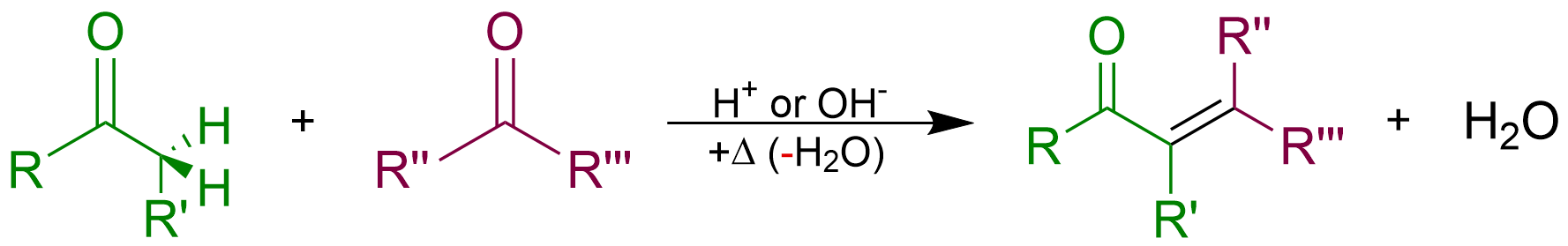 Aldol condensations are important in
Aldol condensations are important in organic synthesis
Organic synthesis is a branch of chemical synthesis concerned with the construction of organic compounds. Organic compounds are molecules consisting of combinations of covalently-linked hydrogen, carbon, oxygen, and nitrogen atoms. Within the gen ...
and biochemistry
Biochemistry, or biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. A sub-discipline of both chemistry and biology, biochemistry may be divided into three fields: structural biology, enzymology, a ...
as ways to form carbon–carbon bond
A carbon–carbon bond is a covalent bond between two carbon atoms. The most common form is the single bond: a bond composed of two electrons, one from each of the two atoms. The carbon–carbon single bond is a sigma bond and is formed between on ...
s.
In its usual form, it involves the nucleophilic addition of a ketone
In organic chemistry, a ketone is an organic compound with the structure , where R and R' can be a variety of carbon-containing substituents. Ketones contain a carbonyl group (a carbon-oxygen double bond C=O). The simplest ketone is acetone ( ...
enolate to an aldehyde
In organic chemistry, an aldehyde () (lat. ''al''cohol ''dehyd''rogenatum, dehydrogenated alcohol) is an organic compound containing a functional group with the structure . The functional group itself (without the "R" side chain) can be referred ...
to form a β-hydroxy ketone, or aldol (aldehyde + alcohol), a structural
A structure is an arrangement and organization of interrelated elements in a material object or system, or the object or system so organized. Material structures include man-made objects such as buildings and machines and natural objects such as ...
unit found in many naturally occurring molecules
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms that are held together by attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions that satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemistry ...
and pharmaceuticals
Medication (also called medicament, medicine, pharmaceutical drug, medicinal product, medicinal drug or simply drug) is a drug used to diagnose, cure, treat, or prevent disease. Drug therapy ( pharmacotherapy) is an important part of the ...
.
biochemistry
Biochemistry, or biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. A sub-discipline of both chemistry and biology, biochemistry may be divided into three fields: structural biology, enzymology, a ...
, to refer to just the first (addition) stage of the process—the aldol reaction
The aldol reaction (aldol addition) is a Chemical reaction, reaction in organic chemistry that combines two Carbonyl group, carbonyl compounds (e.g. aldehydes or ketones) to form a new β-hydroxy carbonyl compound. Its simplest form might invol ...
itself—as catalyzed by aldolases. However, the first step is formally an addition reaction
In organic chemistry, an addition reaction is an organic reaction in which two or more molecule
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms that are held together by Force, attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, ...
rather than a condensation reaction because it does not involve the loss of a small molecule.
Mechanism
The first part of this reaction is anAldol reaction
The aldol reaction (aldol addition) is a Chemical reaction, reaction in organic chemistry that combines two Carbonyl group, carbonyl compounds (e.g. aldehydes or ketones) to form a new β-hydroxy carbonyl compound. Its simplest form might invol ...
, the second part a dehydration—an elimination reaction
An elimination reaction is a type of organic reaction in which two substituents are removed from a molecule in either a one- or two-step mechanism. The one-step mechanism is known as the E2 reaction, and the two-step mechanism is known as the E1 r ...
(Involves removal of a water
Water is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is a transparent, tasteless, odorless, and Color of water, nearly colorless chemical substance. It is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known liv ...
molecule or an alcohol
Alcohol may refer to:
Common uses
* Alcohol (chemistry), a class of compounds
* Ethanol, one of several alcohols, commonly known as alcohol in everyday life
** Alcohol (drug), intoxicant found in alcoholic beverages
** Alcoholic beverage, an alco ...
molecule). Dehydration may be accompanied by decarboxylation
Decarboxylation is a chemical reaction that removes a carboxyl group and releases carbon dioxide (CO2). Usually, decarboxylation refers to a reaction of carboxylic acids, removing a carbon atom from a carbon chain. The reverse process, which is ...
when an activated carboxyl group
In organic chemistry, a carboxylic acid is an organic acid that contains a carboxyl group () attached to an R-group. The general formula of a carboxylic acid is often written as or , sometimes as with R referring to an organyl group (e.g. ...
is present. The aldol addition product can be dehydrated via two mechanisms; a strong base like potassium ''t''-butoxide, potassium hydroxide
Potassium hydroxide is an inorganic compound with the formula K OH, and is commonly called caustic potash.
Along with sodium hydroxide (NaOH), KOH is a prototypical strong base. It has many industrial and niche applications, most of which utili ...
or sodium hydride deprotonates the product to an enolate, which eliminates via the E1cB mechanism, while dehydration in acid proceeds via an E1 reaction mechanism. Depending on the nature of the desired product, the aldol condensation may be carried out under two broad types of conditions: kinetic control or thermodynamic control
Thermodynamic reaction control or kinetic reaction control in a chemical reaction can decide the composition in a reaction product mixture when competing pathways lead to different products and the reaction conditions influence the conversion (ch ...
. Both ketones and aldehydes are suitable for aldol condensation reactions. In the examples below, aldehydes are used.
Base-catalyzed aldol condensation
The mechanism for base-catalyzed aldol condensation can be seen in the image below.Acid-catalyzed aldol condensation
The mechanism for acid-catalyzed aldol condensation can be seen in the image below.Crossed aldol condensation
A crossed aldol condensation is a result of two dissimilar carbonyl compounds containing α-hydrogen(s) undergoing aldol condensation. Ordinarily, this leads to four possible products as either carbonyl compound can act as the nucleophile and self-condensation is possible, which makes a synthetically useless mixture. However, this problem can be avoided if one of the compounds does not contain an α-hydrogen, rendering it non-enolizable. In an aldol condensation between an aldehyde and a ketone, the ketone acts as the nucleophile, as its carbonyl carbon does not possess high electrophilic character due to the +I effect andsteric hindrance
Steric effects arise from the spatial arrangement of atoms. When atoms come close together there is generally a rise in the energy of the molecule. Steric effects are nonbonding interactions that influence the shape ( conformation) and reactivi ...
. Usually, the crossed product is the major one. Any traces of the self-aldol product from the aldehyde may be disallowed by first preparing a mixture of a suitable base and the ketone and then adding the aldehyde slowly to the said reaction mixture. Using too concentrated base could lead to a competing Cannizzaro reaction
The Cannizzaro reaction, named after its discoverer Stanislao Cannizzaro, is a chemical reaction which involves the base-induced disproportionation of two molecules of a non-enolizable aldehyde to give a primary alcohol and a carboxylic acid.
...
.
Examples
The Aldox process, developed byRoyal Dutch Shell
Shell plc is a British multinational oil and gas company, headquartered in London, England. Shell is a public limited company with a primary listing on the London Stock Exchange (LSE) and secondary listings on Euronext Amsterdam and the New ...
and Exxon
Exxon Mobil Corporation ( ) is an American multinational oil and gas corporation headquartered in Spring, Texas, a suburb of Houston. Founded as the largest direct successor of John D. Rockefeller's Standard Oil, the modern company was form ...
, converts propene
Propylene, also known as propene, is an unsaturated organic compound with the chemical formula . It has one double bond, and is the second simplest member of the alkene class of hydrocarbons. It is a colorless gas with a faint petroleum-like od ...
and syngas
Syngas, or synthesis gas, is a mixture of hydrogen and carbon monoxide in various ratios. The gas often contains some carbon dioxide and methane. It is principally used for producing ammonia or methanol. Syngas is combustible and can be used as ...
to 2-ethylhexanol
2-Ethylhexanol (abbreviated 2-EH) is an organic compound with the chemical formula . It is a branched, eight-carbon chiral alcohol. It is a colorless liquid that is poorly soluble in water but soluble in most organic solvents. It is produced on a l ...
via hydroformylation
In organic chemistry, hydroformylation, also known as oxo synthesis or oxo process, is an industrial process for the production of aldehydes () from alkenes (). This chemical reaction entails the net addition of a formyl group () and a hydrogen ...
to butyraldehyde, aldol condensation to 2-ethylhexanal and finally hydrogenation
Hydrogenation is a chemical reaction between molecular hydrogen (H2) and another compound or element, usually in the presence of a catalyst such as nickel, palladium or platinum. The process is commonly employed to redox, reduce or Saturated ...
.
acetaldehyde
Acetaldehyde (IUPAC systematic name ethanal) is an organic compound, organic chemical compound with the chemical formula, formula , sometimes abbreviated as . It is a colorless liquid or gas, boiling near room temperature. It is one of the most ...
and three equivalents of formaldehyde
Formaldehyde ( , ) (systematic name methanal) is an organic compound with the chemical formula and structure , more precisely . The compound is a pungent, colourless gas that polymerises spontaneously into paraformaldehyde. It is stored as ...
to give pentaerythrose, which is further reduced in a Cannizzaro reaction
The Cannizzaro reaction, named after its discoverer Stanislao Cannizzaro, is a chemical reaction which involves the base-induced disproportionation of two molecules of a non-enolizable aldehyde to give a primary alcohol and a carboxylic acid.
...
.
Scope
Ethyl 2-methylacetoacetate and campholenic aldehyde react in an Aldol condensation. The synthetic procedure is typical for this type of reaction. In the process, in addition to water, an equivalent of ethanol and carbon dioxide are lost indecarboxylation
Decarboxylation is a chemical reaction that removes a carboxyl group and releases carbon dioxide (CO2). Usually, decarboxylation refers to a reaction of carboxylic acids, removing a carbon atom from a carbon chain. The reverse process, which is ...
.
 Ethyl glyoxylate 2 and glutaconate (diethyl-2-methylpent-2-enedioate) 1 react to ''isoprenetricarboxylic acid'' 3 (
Ethyl glyoxylate 2 and glutaconate (diethyl-2-methylpent-2-enedioate) 1 react to ''isoprenetricarboxylic acid'' 3 (isoprene
Isoprene, or 2-methyl-1,3-butadiene, is a common volatile organic compound with the formula CH2=C(CH3)−CH=CH2. In its pure form it is a colorless volatile liquid. It is produced by many plants and animals (including humans) and its polymers ar ...
(2-methylbuta-1,3-diene) skeleton) with sodium ethoxide
Sodium ethoxide, also referred to as sodium ethanolate, is the Ionic compound, ionic, organic compound with the formula , , or NaOEt (Et = ethyl group, ethyl). It is a white solid, although impure samples appear yellow or brown. It dissolves in p ...
. This reaction product is very unstable with initial loss of carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalent bond, covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in a gas state at room temperature and at norma ...
and followed by many secondary reactions. This is believed to be due to steric strain resulting from the methyl
In organic chemistry, a methyl group is an alkyl derived from methane, containing one carbon atom bonded to three hydrogen atoms, having chemical formula (whereas normal methane has the formula ). In formulas, the group is often abbreviated as ...
group and the carboxylic
In organic chemistry, a carboxylic acid is an organic acid that contains a carboxyl group () attached to an R-group. The general formula of a carboxylic acid is often written as or , sometimes as with R referring to an organyl group (e. ...
group in the ''cis''-dienoid structure.
 Occasionally, an aldol condensation is buried in a multistep reaction or in catalytic cycle as in the following example:
Occasionally, an aldol condensation is buried in a multistep reaction or in catalytic cycle as in the following example:
 In this reaction an ''alkynal'' 1 is converted into a
In this reaction an ''alkynal'' 1 is converted into a cycloalkene
In organic chemistry, a cycloalkene or cycloolefin is a type of alkene hydrocarbon which contains a closed Ring (chemistry), ring of carbon atoms and either one or more double bonds, but has no Aromaticity, aromatic character. Some cycloalkenes, ...
7 with a ruthenium
Ruthenium is a chemical element; it has symbol Ru and atomic number 44. It is a rare transition metal belonging to the platinum group of the periodic table. Like the other metals of the platinum group, ruthenium is unreactive to most chem ...
catalyst and the actual condensation takes place with intermediate 3 through 5. Support for the reaction mechanism
In chemistry, a reaction mechanism is the step by step sequence of elementary reactions by which overall chemical reaction occurs.
A chemical mechanism is a theoretical conjecture that tries to describe in detail what takes place at each stage ...
is based on isotope labeling.
The reaction between menthone ((2''S'',5''R'')-2-isopropyl-5-methylcyclohexanone) and anisaldehyde (4-methoxybenzaldehyde) is complicated due to steric shielding of the ketone group. This obstacle is overcome by using a strong base such as potassium hydroxide
Potassium hydroxide is an inorganic compound with the formula K OH, and is commonly called caustic potash.
Along with sodium hydroxide (NaOH), KOH is a prototypical strong base. It has many industrial and niche applications, most of which utili ...
and a very polar solvent such as DMSO
Dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) is an organosulfur compound with the formula . This colorless liquid is the sulfoxide most widely used commercially. It is an important polar aprotic solvent that dissolves both polar and nonpolar compounds and is ...
in the reaction below:
 The product can epimerize by way of a common intermediate— enolate A—to convert between the original (''S'',''R'') and the (''R'',''R'') epimers. The (''R'',''R'') product is insoluble in the reaction solvent whereas the (''S'',''R'') is soluble. The precipitation of the (''R'',''R'') product drives the epimerization equilibrium reaction to form this as the major product.
The product can epimerize by way of a common intermediate— enolate A—to convert between the original (''S'',''R'') and the (''R'',''R'') epimers. The (''R'',''R'') product is insoluble in the reaction solvent whereas the (''S'',''R'') is soluble. The precipitation of the (''R'',''R'') product drives the epimerization equilibrium reaction to form this as the major product.
Other condensation reactions
There are other reactions of carbonyl compounds similar to aldol condensation: * When the base is an amine and the active hydrogen compound is sufficiently activated the reaction is called a Knoevenagel condensation. * In a Perkin reaction the aldehyde isaromatic
In organic chemistry, aromaticity is a chemical property describing the way in which a conjugated system, conjugated ring of unsaturated bonds, lone pairs, or empty orbitals exhibits a stabilization stronger than would be expected from conjugati ...
and the enolate generated from an anhydride
An acid anhydride is a type of chemical compound derived by the removal of water molecules from an acid (chemistry), acid.
In organic chemistry, organic acid anhydrides contain the functional group . Organic acid anhydrides often form when one ...
.
* Claisen-Schmidt condensation between an aldehyde or ketone having an α-hydrogen with an aromatic carbonyl compound lacking an α-hydrogen.
* A Claisen condensation involves two ester
In chemistry, an ester is a compound derived from an acid (either organic or inorganic) in which the hydrogen atom (H) of at least one acidic hydroxyl group () of that acid is replaced by an organyl group (R). These compounds contain a distin ...
compounds.
* A Dieckmann condensation involves two ester groups in the ''same molecule'' and yields a cyclic molecule
* In the Japp–Maitland condensation water is removed not by an elimination reaction but by a nucleophilic displacement
* A Robinson annulation
The Robinson annulation is a chemical reaction used in organic chemistry for ring formation. It was discovered by Robert Robinson (organic chemist), Robert Robinson in 1935 as a method to create a six membered ring by forming three new carbon–c ...
involves an α,β- unsaturated ketone
In organic chemistry, a ketone is an organic compound with the structure , where R and R' can be a variety of carbon-containing substituents. Ketones contain a carbonyl group (a carbon-oxygen double bond C=O). The simplest ketone is acetone ( ...
and a carbonyl
In organic chemistry, a carbonyl group is a functional group with the formula , composed of a carbon atom double bond, double-bonded to an oxygen atom, and it is divalent at the C atom. It is common to several classes of organic compounds (such a ...
group, which first engage in a Michael reaction prior to the aldol condensation.
* In the Guerbet reaction, an aldehyde, formed ''in situ
is a Latin phrase meaning 'in place' or 'on site', derived from ' ('in') and ' ( ablative of ''situs'', ). The term typically refers to the examination or occurrence of a process within its original context, without relocation. The term is use ...
'' from an alcohol, self-condenses to the dimerized alcohol.
See also
* Auwers synthesis * Aldol additionReferences
Notes
External links
Organic Chemistry Portal
{{Organic reactions Condensation reactions Carbon-carbon bond forming reactions