|
Ruki Sound Law
The ruki sound law, also known as the ruki rule or iurk rule, is a historical sound change that took place in the satem branches of the Indo-European language family, namely in Balto-Slavic, Armenian, and Indo-Iranian. According to this sound law, an original changed to (a sound similar to English ⟨sh⟩) after the consonants , , , and the semi-vowels (*u̯) and (*i̯), as well as the syllabic allophones , , and : : > / _ Specifically, the initial stage involves the retraction of the coronal sibilant after semi-vowels, , or a velar consonant , or . In the second stage, leveling of the sibilant system resulted in retroflexion (cf. Sanskrit ष and Proto-Slavic), and later retraction to velar in Slavic and some Middle Indic languages. This rule was first formulated by Holger Pedersen, and it is sometimes known as ''Pedersen's law'', although this term is also applied to another sound law concerning stress in the Balto-Slavic languages. The name "ruki" come ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sound Change
In historical linguistics, a sound change is a change in the pronunciation of a language. A sound change can involve the replacement of one speech sound (or, more generally, one phonetic feature value) by a different one (called phonetic change) or a more general change to the speech sounds that exist (''phonological change''), such as the merger of two sounds or the creation of a new sound. A sound change can eliminate the affected sound, or a new sound can be added. Sound changes can be environmentally conditioned if the change occurs in only some sound environments, and not others. The term "sound change" refers to diachronic changes, which occur in a language's sound system. On the other hand, " alternation" refers to changes that happen synchronically (within the language of an individual speaker, depending on the neighbouring sounds) and do not change the language's underlying system (for example, the ''-s'' in the English plural can be pronounced differently depend ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
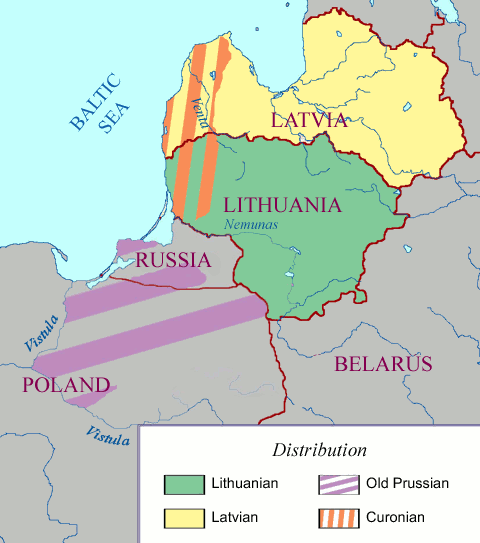
Baltic Languages
The Baltic languages are a branch of the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family spoken natively or as a second language by a population of about 6.5–7.0 million people''"Lietuviai Pasaulyje"'' (PDF) (in Lithuanian). Lietuvos statistikos departamentas. Retrieved 5 May 2015. mainly in areas extending east and southeast of the Baltic Sea in Europe. Together with the Slavic languages, they form the Balto-Slavic languages, Balto-Slavic branch of the Indo-European family. Scholars usually regard them as a single Subgrouping, subgroup divided into two branches: West Baltic languages, West Baltic (containing only extinct languages) and East Baltic languages, East Baltic (containing at least two Modern language, living languages, Lithuanian language, Lithuanian, Latvian l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southeastern Katë Dialect
Southeastern Katë is a dialect of the Katë language spoken by the Kom and Kata in parts of Afghanistan and Pakistan. It also includes the so-called ''Kamviri'' and ''Mumviri'' (spoken in Mangul, Sasku and Gabalgrom in the Bashgal Valley) dialects. Innovations According to Halfmann (2024), the primary innovations of the Southeastern dialect include secondary vowel length from monophthongization of vowel + ''v'', a progressive suffix ''-n-'', intervocalic consonant lenition (usually sibilants and velars), post-nasal voicing, and merger of Proto-Nuristani pre-tonic ''*a'' and ''*ā'' as ''a''. Phonology The inventory as described by Richard Strand. In addition, there is stress. The neutral articulatory posture, as in the reduced vowel , consists of the tip of the tongue behind the lower teeth and a raised tongue root is linked with a raised larynx, producing a characteristic pitch for unstressed vowels of about an octave above the pitch of a relaxed larynx. Conso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kalasha-ala
Nuristani Kalasha ('), also known as ''Waigali'', is a Nuristani language spoken by about 10,000 people in the Nuristan Province of Afghanistan. The native name is ''Kalaṣa-alâ'' 'Kalasha-language'. "Waigali" refers to the dialect of the Väi people of the upper part of the Waigal Valley, centered on the town of Waigal, which is distinct from the dialect of the Čima-Nišei people who inhabit the lower valley. The word 'Kalasha' is the native ethnonym for all the speakers of the southern Nuristani languages. Nuristani Kalasha belongs to the Indo-European language family, and is in the southern Nuristani group of the Indo-Iranian branch. It is closely related to Zemiaki and to Tregami, the lexical similarity with the latter being approximately 76% to 80%. It shares its name with the Indo-Aryan Kalasha language (''Kalaṣa-mun''), spoken in Pakistan's southern Chitral District, but the two languages belong to different branches of Indo-Iranian. Speakers of Nuristani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Katë Language
Katë, also known as Kati or Kamkata-vari, is a Nuristani languages, Nuristani language. It is a dialect continuum comprising three separate dialects spoken mostly in Afghanistan, with additional speakers in the Chitral District of Pakistan deriving from recent migrations a century ago. The ''Kata-vari'' (comprising Western and Northeastern) and ''Kamviri'' (comprising Southeastern) dialects are sometimes erroneously reckoned as two separate languages, but according to linguist Richard Strand they form one language. The Katë language is the largest Nuristani language, spoken by 40,000–60,000 people, from the Kata (people), Kata, Kom people (Afghanistan), Kom, Mumo, Kshto and some smaller Nuristani people, Black-Robed tribes in parts of Afghanistan and Pakistan. The most used alternative names for the language are ''Kati'' or ''Bashgali''. A descriptive grammar of Katë was written by Jakob Halfmann in 2024. Name The name, pronounced , is the ethnonym of the Kata people. Cog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Askunu Language
Ashkun (') is a Nuristani language spoken by the Ashkun people – also known as the Âṣkun, Âṣkuňu, Askina, Saňu, Sainu, Yeshkun, Wamas, or Grâmsaňâ – from the region of the central Pech Valley around Wama, Afghanistan, Wâmâ and in some eastern tributary valleys of the upper Alingar River in Afghanistan's Nuristan Province. Other major places where the language of Ashkun is spoken are Nuristan Province, Pech Valley in Wama District, eastern side of the Lower Alingar Valley in Nurgaram and Duab districts, Malil wa Mushfa, Titin, Kolatan and Bajagal valleys. It is classified as a member of the Nuristani languages, Nuristani sub-family of the Indo-Iranian languages. Name The name ''Ashkun'' comes from ''Âṣkuňu'' in the local language. The alternative name ''Saňu'' in Ashkun, denoting a group of people living in Wâmâ, has cognates in other Nuristani languages, such as Kamviri dialect, Kamviri ''Ćâňu'' , Kata-vari dialect, Katë ''Ćâvřu'' , and Wasi-wari, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laryngeal Theory
The laryngeal theory is a theory in historical linguistics positing that the Proto-Indo-European (PIE) language included a number of laryngeal consonants that are not linguistic reconstruction, reconstructable by direct application of the comparative method (linguistics), comparative method to the Indo-European family. The "missing" sounds remain consonants of an indeterminate place of articulation towards the back of the mouth, though further information is difficult to derive. Proponents aim to use the theory to: * Produce greater regularity in the reconstruction of PIE phonology than from the reconstruction that is produced by the comparative method. * Extend the general occurrence of the Indo-European ablaut to syllables with reconstructed vowel phonemes other than or . In its earlier form (#History, see below), the theory proposed two sounds in PIE. Combined with a reconstructed or , the sounds produce vowel phonemes that would not otherwise be predicted by the rules o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iranian Languages
The Iranian languages, also called the Iranic languages, are a branch of the Indo-Iranian languages in the Indo-European language family that are spoken natively by the Iranian peoples, predominantly in the Iranian Plateau. The Iranian languages are grouped in three stages: Old Iranian (until 400 BCE), Middle Iranian (400 BCE – 900 CE) and New Iranian (since 900 CE). The two directly attested Old Iranian languages are Old Persian (from the Achaemenid Empire) and Old Avestan (the language of the Avesta). Of the Middle Iranian languages, the better understood and recorded ones are Middle Persian (from the Sasanian Empire), Parthian (from the Parthian Empire), and Bactrian (from the Kushan and Hephthalite empires). Number of speakers , '' Ethnologue'' estimates that there are 86 languages in the group. Terminology and grouping Etymology The term ''Iran'' derives directly from Middle Persian , first attested in a third-century inscription at Naqsh-e Rostam, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palatal Approximant
The voiced palatal approximant is a type of consonant used in many spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is ; the equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is j, and in the Americanist phonetic notation it is . When this sound occurs in the form of a palatal glide it is frequently, but not exclusively, denoted as a superscript ''j'' in IPA. This sound is traditionally called a Yod (letter), ''yod'', after its name in Hebrew. This is reflected in the names of certain Sound change, phonological changes, such as Phonological history of English consonant clusters#Yod-dropping, ''yod-dropping'' and Phonological history of English consonant clusters#Yod-coalescence, ''yod-coalescence''. The palatal approximant can often be considered the semivowel, semivocalic equivalent of the close front unrounded vowel . They alternation (linguistics), alternate with each other in certain languages, such as French language, French, and in the diphthongs of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Front Vowel
A front vowel is a class of vowel sounds used in some spoken languages, its defining characteristic being that the highest point of the tongue is positioned approximately as far forward as possible in the mouth without creating a constriction that would otherwise make it a consonant. Front vowels are sometimes also called bright vowels because they are perceived as sounding brighter than the back vowels. Near-front vowels are essentially a type of front vowel; no language is known to contrast front and near-front vowels based on backness alone. Rounded front vowels are typically centralized, that is, near-front in their articulation. This is one reason they are written to the right of unrounded front vowels in the IPA vowel chart. Partial list The front vowels that have dedicated symbols in the International Phonetic Alphabet are: * close front unrounded vowel * close front compressed vowel * near-close front unrounded vowel * near-close front compressed vowel * clos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voiceless Velar Fricative
The voiceless velar fricative is a type of consonantal sound used in some spoken languages. It was part of the consonant inventory of Old English and can still be found in some dialects of English, most notably in Scottish English, e.g. in ''loch'', ''broch'' or ''saugh'' (willow). The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is , the Latin letter x. It is also used in broad transcription instead of the symbol , the Greek chi, for the voiceless uvular fricative. There is also a voiceless post-velar fricative (also called pre-uvular) in some languages, which can be transcribed as or . For voiceless pre-velar fricative (also called post-palatal), see voiceless palatal fricative. Some scholars also posit the voiceless velar approximant distinct from the fricative, used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is , but this symbol is not suitable in case of the voiceless velar appr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slavic Languages
The Slavic languages, also known as the Slavonic languages, are Indo-European languages spoken primarily by the Slavs, Slavic peoples and their descendants. They are thought to descend from a proto-language called Proto-Slavic language, Proto-Slavic, spoken during the Early Middle Ages, which in turn is thought to have descended from the earlier Proto-Balto-Slavic language, linking the Slavic languages to the Baltic languages in a Balto-Slavic languages, Balto-Slavic group within the Indo-European family. The current geographical distribution of natively spoken Slavic languages includes the Balkans, Central and Eastern Europe, and all the way from Western Siberia to the Russian Far East. Furthermore, the diasporas of many Slavic peoples have established isolated minorities of speakers of their languages all over the world. The number of speakers of all Slavic languages together was estimated to be 315 million at the turn of the twenty-first century. It is the largest and most d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |