|
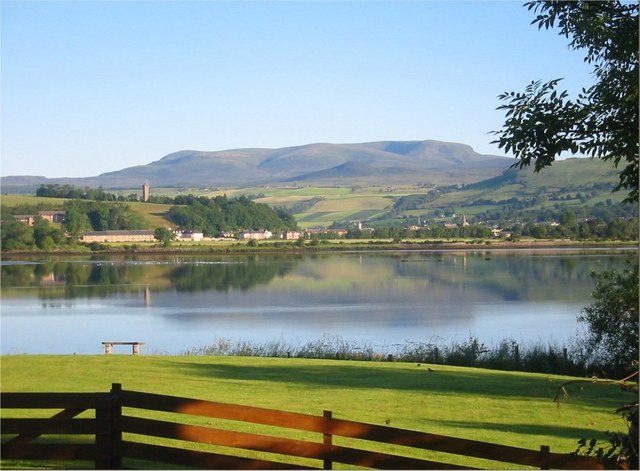
River Conon
The River Conon () is a river in the Scottish Highlands, Highlands of Scotland. It begins at Loch Luichart, and flows in a south-easterly direction to be joined by the River Meig at Scatwell before passing through Loch Achonachie. It is joined by the Black Water (Conon), Black Water at Moy Bridge, and the River Orrin at Urray, before flowing past Conon Bridge and into the Cromarty Firth (and thence the Moray Firth and North Sea). The river is part of the Conon hydro-electric power scheme, with dams at Loch Luichart, Loch Meig and Loch Achonachie, and power stations at Luichart and Torr Achilty. This major scheme was developed by the North of Scotland Hydro-Electric Board between 1946 and 1961. Prior to that, a small power station had been built at the Falls of Conon in the 1920s, and a private scheme for the Brahan Estate was commissioned in 2015 at Dunglass Island. The river system is fished for trout and salmon, but populations of these fish have not always been as healthy as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moray Firth
The Moray Firth (; , or ) is a roughly triangular inlet (or firth) of the North Sea, north and east of Inverness, which is in the Highland council area of the north of Scotland. It is the largest firth in Scotland, stretching from Duncansby Head (near John o' Groats) in the north, in the Highland council area, and Fraserburgh in the east, in the Aberdeenshire council area, to Inverness and the Beauly Firth in the west. Therefore, three council areas have Moray Firth coastline: Highland to the west and north of the Moray Firth and Highland, Moray and Aberdeenshire to the south. The firth has more than of coastline, much of which is cliff. Etymology The firth is named after the 10th-century Province of Moray, whose name in turn is believed to derive from the sea of the firth itself. The local names ''Murar'' or ''Morar'' are suggested to derive from , the Gaelic for sea, whilst ''Murav'' and ''Morav'' are believed to be rooted in Celtic words (sea) and (side), co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lochluichart Railway Station
Lochluichart railway station is a railway station on the Kyle of Lochalsh Line, serving the village of Lochluichart in the north of Scotland. The station is located at the north edge of Loch Luichart, from , between Garve and Achanalt. ScotRail, which manages the station, operates all services. History The station was opened as Lochluichart High by the Dingwall and Skye Railway on 1 August 1871 as a private station for Lady Ashburton on the Lochluichart Estate. It became a public station by 1887. Others suggest that it opened as a private station (under the name Lochluichart Lodge) in August 1870, becoming public (and renamed to Lochluichart High) in 1871. In 1949, Lochluichart was planned to be relocated to allow the flooding of the area by the Glascarnoch-Luichart-Torr Achilty hydroelectric scheme. On 3 May 1954, a new station was opened as Lochluichart as a result of a hydro electric Hydroelectricity, or hydroelectric power, is electricity generated from hydropower ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dornoch
Dornoch (; ; ) is a town, seaside resort, parish and former royal burgh in the county of Sutherland in the Highlands of Scotland. It lies on the north shore of the Dornoch Firth, near to where it opens into the Moray Firth to the east. The town is within the Highland local government council area. The town is near the A9 road, to which it is linked by the A949 and the B9168. The town also has a grass air strip suitable for small aircraft and helicopters. History The name 'Dornoch' is derived from the Gaelic for 'pebbly place', suggesting that the area contained pebbles the size of a fist (''dorn'') which could therefore be used as weapons. Archaeological excavations during the development of a new business park in 1997 revealed a building, evidence for ironworking and part of a whale, dating from the 8th to the 11th centuries AD. The archaeologists surmised that the findings were of an industrial area on the edge of a settlement and that a settlement existed at Dor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trade Facilities Act
The Trade Facilities Acts were a series of Acts of the Parliament of the United Kingdom that were designed to alleviate the problem of large scale unemployment in the aftermath of the First World War. Acts were passed in 1921, 1922, 1924, 1925 and 1926 by four successive governments. The acts enabled companies to borrow money, with the capital and interest guaranteed by the government, for projects which would create employment. By the end of the scheme in March 1927, almost £75 million (equivalent to £ billion in ) had been guaranteed to a range of industries. Whether the acts had a significant effect on unemployment has been debated, but one lasting legacy was the funding of the extension and refurbishment of what became the London Underground Northern line. Background Following the end of the First World War, Britain saw a short period of economic boom, which then turned into a major recession. The costs of materials and labour were significantly greater than in the pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strathpeffer
Strathpeffer () is a village and spa town in Ross and Cromarty, Highland, Scotland, with a population of 1,469. Geography It lies in a strath west of Dingwall, with the elevation ranging from above sea level. Sheltered on the west and north, it has a comparatively dry and warm climate. History The strategic location of the village has led to several battles being fought in the area : *Blar Nan Ceann (battle (field) of the heads), lies at the western end of the modern village (). Very little is known about the battle there, not even its date, other than the MacKenzies of Seaforth defeated the MacDonells of Glengarry and some incident took place at a well near the battlefield, subsequently called Tobar a' Chinn (well of the head). * Battle of Blar Na Pairce (battle (field) of the park), in approximately 1486 saw the local MacKenzies, under their chief Kenneth MacKenzie, defeat a large invading force of MacDonalds. The battlefield lies south-west of the modern village, on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A9 Road (Scotland)
The A9 is a major road in Scotland running from the Falkirk council area in central Scotland to Scrabster Harbour, Thurso in the far north, via Stirling, Bridge of Allan, Perth and Inverness. At , it is the longest road in Scotland and the fifth-longest A-road in the United Kingdom. Historically it was the main road between Edinburgh and John o' Groats, and has been called ''the spine of Scotland''. It is one of the three major north–south trunk routes linking the Central Belt to the Highlands – the others being the A82 and the A90. The road's origins lie in the military roads building programme of the 18th century, further supplemented by the building of several bridges in later years. The A9 route was formally designated in 1923, and originally ran from Edinburgh to Inverness. The route was soon extended north from Inverness up to John O'Groats. By the 1970s the route was hampered by severe traffic congestion, and an extensive upgrading programme was undertaken on t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dingwall
Dingwall (, ) is a town and a royal burgh in the Highland (council area), Highland council area of Scotland. It has a population of 5,491. It was an east-coast harbour that now lies inland. Dingwall Castle was once the biggest castle north of Stirling. On the town's present-day outskirts lies Tulloch Castle, parts of which may date back to the 12th century. In 1411 the Battle of Dingwall is said to have taken place between the Clan Mackay and the Clan Donald. History Early history Its name, derived from the Scandinavian (field or meeting-place of the ''thing (assembly), thing'', or local assembly; compare Tynwald, Tingwall (other), Tingwall, Thingwall in the British Isles alone, plus many others across northern Europe), preserves the Viking connections of the town; Gaels call it (), meaning "the mouth of the Peffery" or meaning "cabbage town". The site of the , and of the medieval Moothill, thought to have been established by the Vikings after they invaded in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Telford
Thomas Telford (9 August 1757 – 2 September 1834) was a Scottish civil engineer. After establishing himself as an engineer of road and canal projects in Shropshire, he designed numerous infrastructure projects in his native Scotland, as well as harbours and tunnels. Such was his reputation as a prolific designer of highways and related bridges, he was dubbed the 'Colossus of Roads' (a pun on the Colossus of Rhodes), and, reflecting his command of all types of civil engineering in the early 19th century, he was elected as the first president of the Institution of Civil Engineers, a post he held for 14 years until his death. The town of Telford in Shropshire was named after him. Early career Telford was born on 9 August 1757, at Glendinning, a hill farm east of Eskdalemuir Kirk, in the rural List of Church of Scotland parishes, parish of Westerkirk, in Eskdale, Dumfries and Galloway, Eskdale, Dumfriesshire. His father John Telford, a shepherd, died soon after Thomas was born. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Far North Line
The Far North Line is a rural railway line entirely within the Highland area of Scotland, extending from Inverness to Thurso and Wick. As the name suggests, it is the northernmost railway in the United Kingdom. The line is entirely single-track, with only passing loops at some intermediate stations allowing trains to pass each other. Like other railway lines in the Highlands and northern Lowlands, it is not electrified and all trains are diesel-powered. Route The line links the city of Inverness, the largest city in the Scottish Highlands, with the towns of Wick and Thurso at the northeastern tip of Britain. Like the A9 trunk road north of Inverness, the Far North Line broadly follows the east-facing coastline of the Moray Firth, with all three termini located on the coast. As such, the railway links many of the same places as the road. Many more places were served by both the railway and the road before three new road bridges were built: across the Beauly Firth (betw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conon Bridge Railway Station
Conon Bridge is a railway station on the Far North Line, Far North and Kyle of Lochalsh Lines, which serves the villages of Conon Bridge and Maryburgh in the Scotland, Scottish Highland (council area), Highlands. Initially known as Conon, it originally closed in 1960 and reopened on 8 February 2013. The station is from , between Muir of Ord railway station, Muir of Ord and Dingwall railway station, Dingwall. History Original station The original railway station (then named just Conon) was opened by Inverness and Ross-shire Railway on 11 June 1862 and closed on 13 June 1960. The original station had two platforms and was the junction with the partially constructed Cromarty and Dingwall Light Railway. 2013 reopening The rebuilt station was projected to open by 2012 as Conon Bridge. In March 2012, Network Rail revealed that agreement had been reached with the Highlands and Islands Transport Partnership for it to provide £100,000 towards the construction of a single four- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |