|
Rhenium Dioxide
Rhenium(IV) oxide or rhenium dioxide is the inorganic compound with the formula ReO2. This gray to black crystalline solid is a laboratory reagent that can be used as a catalyst. It adopts the rutile structure. Synthesis and reactions It forms via comproportionation: :2 Re2O7 + 3 Re → 7 ReO2 Single crystals are obtained by chemical transport, using iodine as the transporting agent.: : ReO2 + I2 ReO2I2 At high temperatures it undergoes disproportionation: :7ReO2 → 2Re2O7 + 3Re It forms rhenates with alkaline hydrogen peroxide and oxidizing acid An oxidizing acid is a Brønsted acid that is a strong oxidizing agent. Most Brønsted acids can act as oxidizing agents, because the acidic proton can be reduced to hydrogen gas. Some acids contain other structures that act as stronger oxidizing ...s. In molten sodium hydroxide it forms sodium rhenate:G. Glemser "Sodium Rhenate (IV)" Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry, 2nd Ed. Edited by G. Brauer, Academi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhenium
Rhenium is a chemical element; it has symbol Re and atomic number 75. It is a silvery-gray, heavy, third-row transition metal in group 7 of the periodic table. With an estimated average concentration of 1 part per billion (ppb), rhenium is one of the rarest elements in the Earth's crust. It has one of the highest melting and boiling points of any element. It resembles manganese and technetium chemically and is mainly obtained as a by-product of the extraction and refinement of molybdenum and copper ores. It shows in its compounds a wide variety of oxidation states ranging from −1 to +7. Rhenium was originally discovered in 1908 by Masataka Ogawa, but he mistakenly assigned it as element 43 (now known as technetium) rather than element 75 and named it ''nipponium''. It was rediscovered in 1925 by Walter Noddack, Ida Tacke and Otto Berg, who gave it its present name. It was named after the river Rhine in Europe, from which the earliest samples had been obtained and worked co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catalyst
Catalysis () is the increase in rate of a chemical reaction due to an added substance known as a catalyst (). Catalysts are not consumed by the reaction and remain unchanged after it. If the reaction is rapid and the catalyst recycles quickly, very small amounts of catalyst often suffice; mixing, surface area, and temperature are important factors in reaction rate. Catalysts generally react with one or more reactants to form intermediates that subsequently give the final reaction product, in the process of regenerating the catalyst. The rate increase occurs because the catalyst allows the reaction to occur by an alternative mechanism which may be much faster than the noncatalyzed mechanism. However the noncatalyzed mechanism does remain possible, so that the total rate (catalyzed plus noncatalyzed) can only increase in the presence of the catalyst and never decrease. Catalysis may be classified as either homogeneous, whose components are dispersed in the same phase (usual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxidizing Acid
An oxidizing acid is a Brønsted acid that is a strong oxidizing agent. Most Brønsted acids can act as oxidizing agents, because the acidic proton can be reduced to hydrogen gas. Some acids contain other structures that act as stronger oxidizing agents than hydrogen ions. Generally, they contain oxygen in their anionic structure. These include nitric acid, perchloric acid, chloric acid, chromic acid, and concentrated sulfuric acid, among others. General properties Oxidizing acids, being strong oxidizing agents, can often oxidize certain less reactive metals, in which the active oxidizing agent is not H+ ions. For example, copper is a rather unreactive metal, and has no reaction with concentrated hydrochloric acid. However, even dilute nitric acid can oxidize copper to Cu2+ ions, with the nitrate ions acting as the effective oxidant: : 3 Cu + 8 HNO3 → 3 Cu2+ + 2 NO + 4 H2O + 6 Sometimes the concentration of the acid is a factor for it to be strongly oxidizing. Again, copper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen Peroxide
Hydrogen peroxide is a chemical compound with the formula . In its pure form, it is a very pale blue liquid that is slightly more viscosity, viscous than Properties of water, water. It is used as an oxidizer, bleaching agent, and antiseptic, usually as a dilute solution (3%–6% by weight) in water for consumer use and in higher concentrations for industrial use. Concentrated hydrogen peroxide, or "high-test peroxide", decomposes explosively when heated and has been used as both a monopropellant and an oxidizer in rocketry. Hydrogen peroxide is a reactive oxygen species and the simplest peroxide, a compound having an oxygen–oxygen single bond. It decomposes slowly into water and elemental oxygen when exposed to light, and rapidly in the presence of organic or reactive compounds. It is typically stored with a Stabilizer (chemistry), stabilizer in a weakly acidic solution in an opaque bottle. Hydrogen peroxide is found in biological systems including the human body. Enzymes that u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disproportionation
In chemistry, disproportionation, sometimes called dismutation, is a redox reaction in which one compound of intermediate oxidation state converts to two compounds, one of higher and one of lower oxidation state. The reverse of disproportionation, such as when a compound in an intermediate oxidation state is formed from precursors of lower and higher oxidation states, is called ''comproportionation'', also known as ''symproportionation''. More generally, the term can be applied to any desymmetrizing reaction where two molecules of one type react to give one each of two different types: : This expanded definition is not limited to redox reactions, but also includes some molecular autoionization reactions, such as the self-ionization of water. In contrast, some authors use the term ''redistribution'' to refer to reactions of this type (in either direction) when only ligand exchange but no redox is involved and distinguish such processes from disproportionation and comproportionati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iodine
Iodine is a chemical element; it has symbol I and atomic number 53. The heaviest of the stable halogens, it exists at standard conditions as a semi-lustrous, non-metallic solid that melts to form a deep violet liquid at , and boils to a violet gas at . The element was discovered by the French chemist Bernard Courtois in 1811 and was named two years later by Joseph Louis Gay-Lussac, after the Ancient Greek , meaning 'violet'. Iodine occurs in many oxidation states, including iodide (I−), iodate (), and the various periodate anions. As the heaviest essential mineral nutrient, iodine is required for the synthesis of thyroid hormones. Iodine deficiency affects about two billion people and is the leading preventable cause of intellectual disabilities. The dominant producers of iodine today are Chile and Japan. Due to its high atomic number and ease of attachment to organic compounds, it has also found favour as a non-toxic radiocontrast material. Because of the spec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Transport Reaction
In chemistry, a chemical transport reaction describes a process for purification and crystallization of non- volatile solids. The process is also responsible for certain aspects of mineral growth from the effluent of volcanoes. The technique is distinct from chemical vapor deposition, which usually entails decomposition of molecular precursors and which gives conformal coatings. The technique, which was popularized by Harald Schäfer, entails the reversible conversion of nonvolatile elements and chemical compounds into volatile derivatives. The volatile derivative migrates throughout a sealed reactor, typically a sealed and evacuated glass tube heated in a tube furnace. Because the tube is under a temperature gradient, the volatile derivative reverts to the parent solid and the transport agent is released at the end opposite to which it originated (see next section). The transport agent is thus catalytic. The technique requires that the two ends of the tube (which contai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
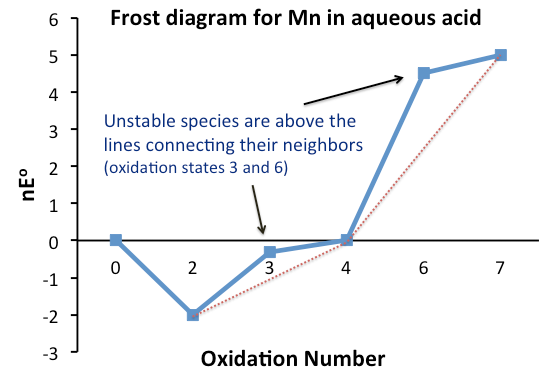
Comproportionation
Comproportionation or symproportionation is a chemical reaction where two reactants containing the same element but with different oxidation numbers, form a compound having an intermediate oxidation number. It is the opposite of disproportionation.Shriver, D. F.; Atkins, P. W.; Overton, T. L.; Rourke, J. P.; Weller, M. T.; Armstrong, F. A. (2006). “Inorganic Chemistry” W. H. Freeman, New York. . Frost diagrams In electrochemistry, the tendency of two redox species to disproportionate, or comproportionate, can be determined by examining their Frost diagram. It is a graphical plot of as a function of the oxidation number for the different redox species of a given element. The Gibbs free energy Δ''G''° is related to the reduction potential ''E''° by the formula: or , where ''n'' is the number of transferred electrons, and ''F'' is the Faraday constant ). If the value of for a species is lower than the line joining two adjacent, or more generally, neighboring speci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rutile
Rutile is an oxide mineral composed of titanium dioxide (TiO2), the most common natural form of TiO2. Rarer polymorphs of TiO2 are known, including anatase, akaogiite, and brookite. Rutile has one of the highest refractive indices at visible wavelengths of any known crystal and also exhibits a particularly large birefringence and high dispersion. Owing to these properties, it is useful for the manufacture of certain optical elements, especially polarization optics, for longer visible and infrared wavelengths up to about 4.5 micrometres. Natural rutile may contain up to 10% iron and significant amounts of niobium and tantalum. Rutile derives its name from the Latin ('red'), in reference to the deep red color observed in some specimens when viewed by transmitted light. Rutile was first described in 1803 by Abraham Gottlob Werner using specimens obtained in Horcajuelo de la Sierra, Madrid (Spain), which is consequently the type locality. Occurrence Rutile is a comm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solid
Solid is a state of matter where molecules are closely packed and can not slide past each other. Solids resist compression, expansion, or external forces that would alter its shape, with the degree to which they are resisted dependent upon the specific material under consideration. Solids also always possess the least amount of kinetic energy per atom/molecule relative to other phases or, equivalently stated, solids are formed when matter in the liquid / gas phase is cooled below a certain temperature. This temperature is called the melting point of that substance and is an intrinsic property, i.e. independent of how much of the matter there is. All matter in solids can be arranged on a microscopic scale under certain conditions. Solids are characterized by structural rigidity and resistance to applied external forces and pressure. Unlike liquids, solids do not flow to take on the shape of their container, nor do they expand to fill the entire available volume like a gas. Much ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxygen
Oxygen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group (periodic table), group in the periodic table, a highly reactivity (chemistry), reactive nonmetal (chemistry), nonmetal, and a potent oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as well as with other chemical compound, compounds. Oxygen is abundance of elements in Earth's crust, the most abundant element in Earth's crust, making up almost half of the Earth's crust in the form of various oxides such as water, carbon dioxide, iron oxides and silicates.Atkins, P.; Jones, L.; Laverman, L. (2016).''Chemical Principles'', 7th edition. Freeman. It is abundance of chemical elements, the third-most abundant element in the universe after hydrogen and helium. At standard temperature and pressure, two oxygen atoms will chemical bond, bind covalent bond, covalently to form dioxygen, a colorless and odorless diatomic gas with the chemical formula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |