|
Quinuclidines
Quinuclidine is an organic compound with the formula . It is a bicyclic amine that can be viewed as a tied back version of triethylamine. It is a colorless solid. It is used as a reagent (base) and catalyst. It can be prepared by reduction of quinuclidone. Structure and chemical properties Regarding its structure, quinuclidine is unusual in that the methylene hydrogen atoms are eclipsed within each of the three ethylene linkages. Furthermore, the cyclohexane rings, of which there are three, adopt the boat conformations, not the usual chair conformations. Quinuclidine is a relatively strong organic base with p''K''a of the conjugate acid of 11.3. The basicity of other quinuclidines have been evaluated: 3-hydroxy- quinuclidine (9.9), 3-acetoxyquinuclidine (9.3), 3-chloroquinuclidine (8.9), DABCO (8.7), and 3-quinuclidone (7.2). It forms adducts with a variety of Lewis acids. Because of its compact structure, quinuclidine binds to trimethylborane more tightly than does t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quinuclidone
Quinuclidones are a class of bicyclic organic compounds with chemical formula C7H11NO with two structural isomers for the base skeleton 3-quinuclidone and 2-quinuclidone. 3-Quinuclidone (1-azabicyclo .2.2ctan-3-one) is an uneventful molecule that can be synthesized as the hydrochloric acid salt by a Dieckman condensation: The other isomer, 2-quinuclidone, appears equally uneventful, but in fact it has defied synthesis until 2006. The reason is that this molecule is very unstable because its amide group has the amine lone pair and the carbonyl group not properly aligned, as may be expected for an amide, as a result of steric strain. This behaviour is predicted by Bredt's Rule, and formal amide group resembles in fact an amine, as evidenced by the ease of salt formation. The organic synthesis of the tetrafluoroborate salt of 2-quinuclidone is a six-step affair starting from norcamphor the final step being an azide - ketone Schmidt reaction (38% yield): This compound rapi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
3-Quinuclidone
3-Quinuclidinone is a bicyclic organic compounds with chemical formula . Its basicity is indicated by the pKa of the conjugate acid, which is 7.2. In contrast quinuclidine is about 100x more basic. Synthesis and reactions Its hydrochloride salt can be synthesized by a Dieckman condensation: It is a precursor to quinuclidine. Organic reduction of 3-quinuclidone gives the compound quinuclidine, structurally related to DABCO, which has one additional bridgehead nitrogen atom. References {{DEFAULTSORT:Quinuclidone, 3- Quinuclidines Cyclic ketones ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aclidinium Bromide
Aclidinium bromide (INN) is a long-acting, inhaled muscarinic antagonist (LAMA) approved in the United States in July 2012 as a maintenance treatment for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Evidence shows that it can improve quality of life and prevent hospitalization in those with COPD. However, it does not appear to affect the risk of death or the frequency steroids are needed. It is unclear if it differs from the similar medication tiotropium or other commonly used medications from the class of LAMAs. Aclidinium is delivered via a multidose dry powder inhaler, the Genuair inhaler. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. Adverse effects The substance is generally well tolerated. Common side effects (in more than 1% of patients) are sinusitis, nasopharyngitis, headache, cough, diarrhoea and nausea. The latter is less common under the drug than under placebo. Skin reactions such as rash, as well as side effects that are typical of musc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lewis Acid
A Lewis acid (named for the American physical chemist Gilbert N. Lewis) is a chemical species that contains an empty orbital which is capable of accepting an electron pair from a Lewis base to form a Lewis adduct. A Lewis base, then, is any species that has a filled orbital containing an electron pair which is not involved in bonding but may form a dative bond with a Lewis acid to form a Lewis adduct. For example, NH3 is a Lewis base, because it can donate its lone pair of electrons. Trimethylborane CH3)3Bis a Lewis acid as it is capable of accepting a lone pair. In a Lewis adduct, the Lewis acid and base share an electron pair furnished by the Lewis base, forming a dative bond. In the context of a specific chemical reaction between NH3 and Me3B, a lone pair from NH3 will form a dative bond with the empty orbital of Me3B to form an adduct NH3•BMe3. The terminology refers to the contributions of Gilbert N. Lewis. From p. 142: "We are inclined to think of substances as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
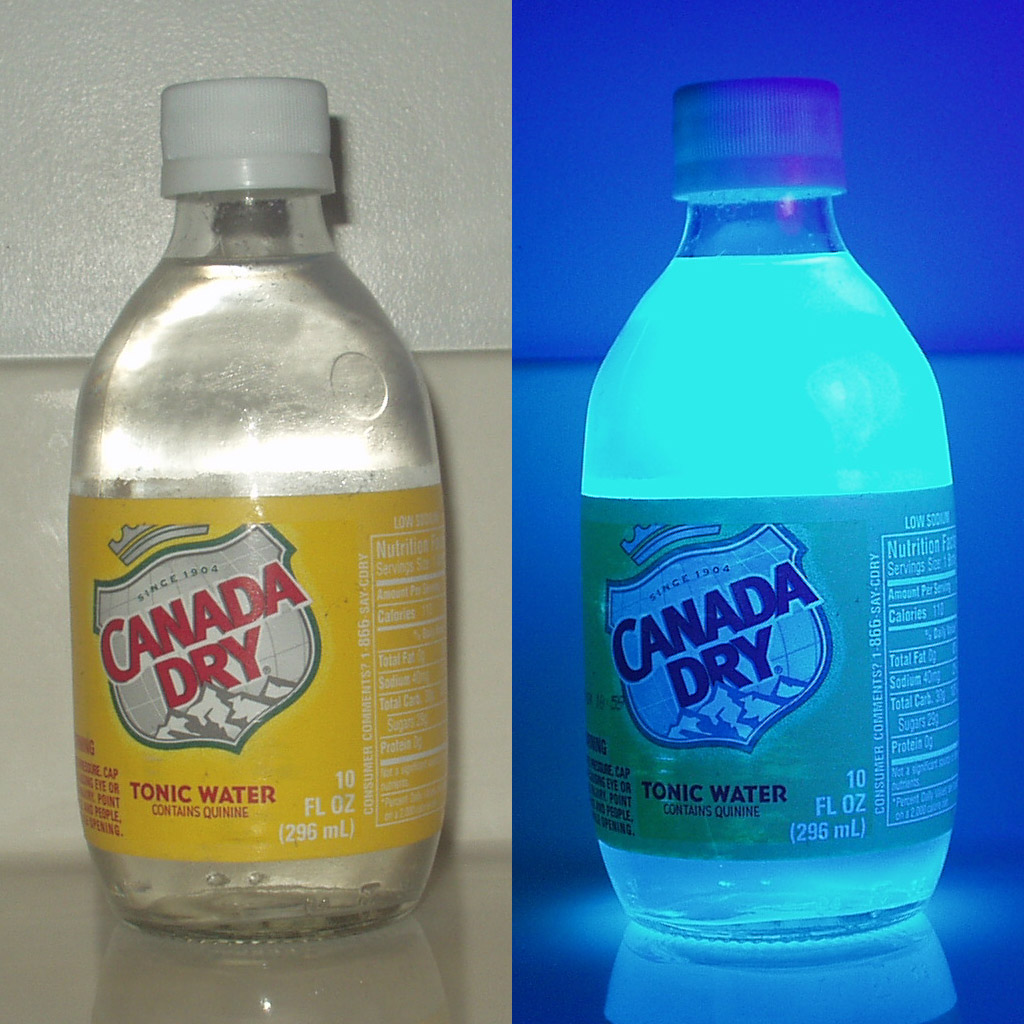
Quinine
Quinine is a medication used to treat malaria and babesiosis. This includes the treatment of malaria due to ''Plasmodium falciparum'' that is resistant to chloroquine when artesunate is not available. While sometimes used for nocturnal leg cramps, quinine is not recommended for this purpose due to the risk of serious side effects. It can be taken by mouth or intravenously. Malaria resistance to quinine occurs in certain areas of the world. Quinine is also used as an ingredient in tonic water and other beverages to impart a bitter taste. Common side effects include headache, tinnitus, ringing in the ears, vision issues, and sweating. More severe side effects include deafness, thrombocytopenia, low blood platelets, and an irregular heartbeat. Use can make one more prone to sunburn. While it is unclear if use during pregnancy carries potential for fetal harm, treating malaria during pregnancy with quinine when appropriate is still recommended. Quinine is an alkaloid, a natural ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cinchona
''Cinchona'' (pronounced or ) is a genus of flowering plants in the family Rubiaceae containing at least 23 species of trees and shrubs. All are native to the Tropical Andes, tropical Andean forests of western South America. A few species are reportedly naturalization (biology), naturalized in Central America, Jamaica, French Polynesia, Sulawesi, Saint Helena in the South Atlantic, and São Tomé and Príncipe off the coast of tropical Africa, and others have been cultivated in India and Java, where they have formed hybrids. ''Cinchona'' has been historically sought after for its medicinal value, as the bark of several species yields quinine and other alkaloids. These were the only effective treatments against malaria during the height of European colonialism, which made them of great economic and political importance. Trees in the genus are also known as fever trees because of their antimalarial properties. The artificial Quinine total synthesis, synthesis of quinine in 1944, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antimuscarinic
A muscarinic acetylcholine receptor antagonist, also simply known as a muscarinic antagonist or as an antimuscarinic agent, is a type of anticholinergic drug that blocks the activity of the muscarinic acetylcholine receptors (mAChRs). The muscarinic receptors are proteins involved in the transmission of signals through certain parts of the nervous system, and muscarinic receptor antagonists work to prevent this transmission from occurring. Notably, muscarinic antagonists reduce the activation of the parasympathetic nervous system. The normal function of the parasympathetic system is often summarised as "rest-and-digest", and includes slowing of the heart, an increased rate of digestion, Bronchoconstriction, narrowing of the airways, promotion of urination, and sexual arousal. Muscarinic antagonists counter this parasympathetic "rest-and-digest" response, and also work elsewhere in both the Central nervous system, central and peripheral nervous systems. Drugs with muscarinic antagon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solifenacin
Solifenacin, sold as the brand name Vesicare among others, is a medicine used to treat overactive bladder and neurogenic detrusor overactivity (NDO). It may help with incontinence, urinary frequency, and urinary urgency. Benefits appear similar to other medications in the class. It is taken by mouth. Common side effects include dry mouth, constipation, and urinary tract infection. Severe side effects may include urinary retention, QT prolongation, hallucinations, glaucoma, and anaphylaxis. It is unclear if use is safe during pregnancy. It is of the antimuscarinic class and works by decreasing bladder contractions. Solifenacin was approved for medical use in the United States in 2004. In 2022, it was the 210th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 1million prescriptions. Medical use It is used to treat overactive bladder. It may help with incontinence, urinary frequency, and urinary urgency. Benefits appear similar to other antimuscarini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropane
Tropane is a nitrogenous bicyclic organic compound. It is mainly known for the other alkaloids derived from it, which include atropine and cocaine, among others. Tropane alkaloids occur in plants of the families Erythroxylaceae (including coca) and Solanaceae (including mandrake, henbane, deadly nightshade, datura, potato, tomato). Structurally, tropane is cycloheptane with a nitrogen bridge between carbons 1 and 5 and an additional methyl group attached to the nitrogen. While carbons 1 and 5 are asymmetric carbons, tropane itself is optically inactive due to mirror symmetry. 8-Azabicyclo .2.1ctane (tropane without the ''N''-methyl group In organic chemistry, a methyl group is an alkyl derived from methane, containing one carbon atom bonded to three hydrogen atoms, having chemical formula (whereas normal methane has the formula ). In formulas, the group is often abbreviated a ...) is known as nortropane or nor-tropane. See also * Phenyltropane * Tropane alkaloid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quinine
Quinine is a medication used to treat malaria and babesiosis. This includes the treatment of malaria due to ''Plasmodium falciparum'' that is resistant to chloroquine when artesunate is not available. While sometimes used for nocturnal leg cramps, quinine is not recommended for this purpose due to the risk of serious side effects. It can be taken by mouth or intravenously. Malaria resistance to quinine occurs in certain areas of the world. Quinine is also used as an ingredient in tonic water and other beverages to impart a bitter taste. Common side effects include headache, tinnitus, ringing in the ears, vision issues, and sweating. More severe side effects include deafness, thrombocytopenia, low blood platelets, and an irregular heartbeat. Use can make one more prone to sunburn. While it is unclear if use during pregnancy carries potential for fetal harm, treating malaria during pregnancy with quinine when appropriate is still recommended. Quinine is an alkaloid, a natural ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trimethylborane
Trimethylborane (TMB) is a toxic, pyrophoric gas with the formula B(CH3)3 (which can also be written as Me3B, with Me representing methyl). Properties As a liquid it is colourless. The strongest line in the infrared spectrum is at 1330 cm−1 followed by lines at 3010 cm−1 and 1185 cm−1. Its melting point is −161.5 °C, and its boiling point is −20.2 °C. Vapour pressure is given by , where ''T'' is temperature in kelvins. Molecular weight is 55.914. The heat of vapourisation is 25.6 kJ/mol. Preparation Trimethylborane was first described in 1862 by Edward Frankland, who also mentioned its adduct with ammonia. Due to its dangerous nature the compound was no longer studied until 1921, when Alfred Stock and Friedrich Zeidler took advantage of the reaction between boron trichloride gas and dimethylzinc. Although the substance can be prepared using Grignard reagents the output is contaminated by unwanted products from the solvent. Trimet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |