|
Pseudo-Nennius
''The History of the Britons'' () is a purported history of early Britain written around 828 that survives in numerous recensions from after the 11th century. The ''Historia Brittonum'' is commonly attributed to Nennius, as some recensions have a preface written in that name. Some experts have dismissed the Nennian preface as a late forgery and argued that the work was actually an anonymous compilation. Overview The ''Historia Brittonum'' describes the supposed settlement of Britain by Trojan settlers and says that Britain was named for Brutus, a descendant of Aeneas. The "single most important source used by Geoffrey of Monmouth in his pseudohistorical ''Historia Regum Britanniae''" and through the enormous popularity of the latter work, this version of the early history of Britain, including the Trojan origin tradition, was incorporated into subsequent chronicles of the long-running history of the land, such as the Middle English '' Brut of England'', also known as ''The Chr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Recension
Recension is the practice of editing or revising a text based on critical analysis. When referring to manuscripts, this may be a revision by another author. The term is derived from the Latin ("review, analysis"). In textual criticism (as is the case with Biblical scholarship), the count noun ''recension'' is a family of manuscripts sharing similar traits; for example, the Alexandrian text-type may be referred to as the "Alexandrian recension". The term ''recension'' may also refer to the process of collecting and analyzing source texts in order to establish a tree structure leading backward to a hypothetical original text. "An adequate method of recension has only been rendered possible by the growth of Palaeography, i.e. the scientific study of ancient documents – the hands in which they are written, the age to which they belong and generally speaking the purposes, methods and circumstances of the men who produced them." F. W. Hall (1913A Companion to Classical Texts chap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annales Cambriae
The (Latin for ''Annals of Wales'') is the title given to a complex of Latin chronicles compiled or derived from diverse sources at St David's in Dyfed, Wales. The earliest is a 12th-century presumed copy of a mid-10th-century original; later editions were compiled in the 13th century. Despite the name, the record not only events in Wales, but also events in Ireland, Cornwall, England, Scotland and sometimes further afield, though the focus of the events recorded especially in the later two-thirds of the text is Wales. Sources The five principal versions of appear in four manuscripts: * A: London, British Library, Harley MS 3859, folios 190r–193r. * B: London (Kew), National Archives, MS. E.164/1 (K.R. Misc. Books, Series I) pp. 2–26 * C: London, British Library, MS. Cotton Domitian A.i, folios 138r–155r * D: Exeter, Cathedral Library, MS. 3514, pp. 523–28, the . * E: ''ibid.'', pp. 507–19, the . A is written in a hand of about 1100–1130 AD, and i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stemmatics
Textual criticism is a branch of textual scholarship, philology, and literary criticism that is concerned with the identification of textual variants, or different versions, of either manuscripts (mss) or of printed books. Such texts may range in dates from the earliest writing in cuneiform, impressed on clay, for example, to multiple unpublished versions of a 21st-century author's work. Historically, scribes who were paid to copy documents may have been literate, but many were simply copyists, mimicking the shapes of letters without necessarily understanding what they meant. This means that unintentional alterations were common when copying manuscripts by hand. Intentional alterations may have been made as well, for example, the censoring of printed work for political, religious or cultural reasons. The objective of the textual critic's work is to provide a better understanding of the creation and historical transmission of the text and its variants. This understanding may lead ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Felix Liebermann
Felix Liebermann (20 July 1851 – 7 October 1925) was a German historian, who is celebrated for his scholarly contributions to the study of medieval English history, particularly that of Anglo-Saxon and Anglo-Norman law. Life Felix Liebermann was born in 1851 in Berlin, then the capital of Prussia. He came from a Jewish-German family; his older brother was the painter Max Liebermann. Felix first pursued a career in banking and the textile industry, living for a time in Manchester, England. In 1873, he moved to Göttingen, Germany, to study early English history. Georg Waitz and Reinhold Pauli became his mentors. After his promotion in 1875 on the " Dialogue of the Exchequer" (), he rapidly earned a name for himself as a medievalist with a special focus on England. He served as an editor with the from 18771885. In 1896, he received honorary degrees from the universities of Oxford and Cambridge Cambridge ( ) is a List of cities in the United Kingdom, city and non-metropol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ferdinand Lot
Ferdinand Victor Henri Lot ( Le Plessis Piquet, 20 September 1866 – Fontenay-aux-Roses, 20 July 1952) was a French historian and medievalist. His masterpiece, ''The End of the Ancient World and the Beginnings of the Middle Ages'' (1927), presents an alternative account of the fall of the Roman Empire than does Edward Gibbon's ''Decline and Fall of the Roman Empire'', which had set the tone for Enlightenment scholarship in blaming the fall of classical civilization on Christianity. Lot was a member of the Académie des Inscriptions et Belles-Lettres, part of the Institut de France The ; ) is a French learned society, grouping five , including the . It was established in 1795 at the direction of the National Convention. Located on the Quai de Conti in the 6th arrondissement of Paris, the institute manages approximately ..., and an honorary professor at the Sorbonne. Lot married the Russian-French medieval scholar Myrrha Lot-Borodine in 1909. Select bibliography ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heinrich Zimmer (Celticist)
Heinrich Friedrich Zimmer (11 December 1851 – 29 July 1910) was a German Celtic studies, Celticist and Indologist. Born to a farming family in Kastellaun in the Rhineland-Palatinate in western Germany, he studied ancient languages at University of Strasbourg, Kaiser Wilhelm University in Strasbourg, Strassburg, going on to study Indology and Sanskrit under Rudolf von Roth at the University of Tübingen. In 1878 he became a lecturer at Humboldt University of Berlin, Friedrich Wilhelm University in Berlin, where the young Ferdinand de Saussure studied with him; in 1881 he became Professor of Sanskrit and Comparative Linguistics at the University of Greifswald. In 1901 he became the founding Professor of Celtic languages, Celtic at Friedrich Wilhelm University, the first position of its kind in Germany; his most celebrated student there was Rudolf Thurneysen. (He was followed in the post after his death by Kuno Meyer.) In 1902 he became a member of the Prussian Academy of Sciences a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Legend
A legend is a genre of folklore that consists of a narrative featuring human actions, believed or perceived to have taken place in human history. Narratives in this genre may demonstrate human values, and possess certain qualities that give the tale verisimilitude (literature), verisimilitude. Legend, for its active and passive participants, may include miracles. Legends may be transformed over time to keep them fresh and vital. Many legends operate within the realm of uncertainty, never being entirely believed by the participants, but also never being resolutely doubted. Legends are sometimes distinguished from myths in that they concern human beings as the main characters and do not necessarily have supernatural origins, and sometimes in that they have some sort of historical basis whereas myths generally do not. The Brothers Grimm defined ''legend'' as "Folklore, folktale historically grounded". A by-product of the "concern with human beings" is the long list of legendary crea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
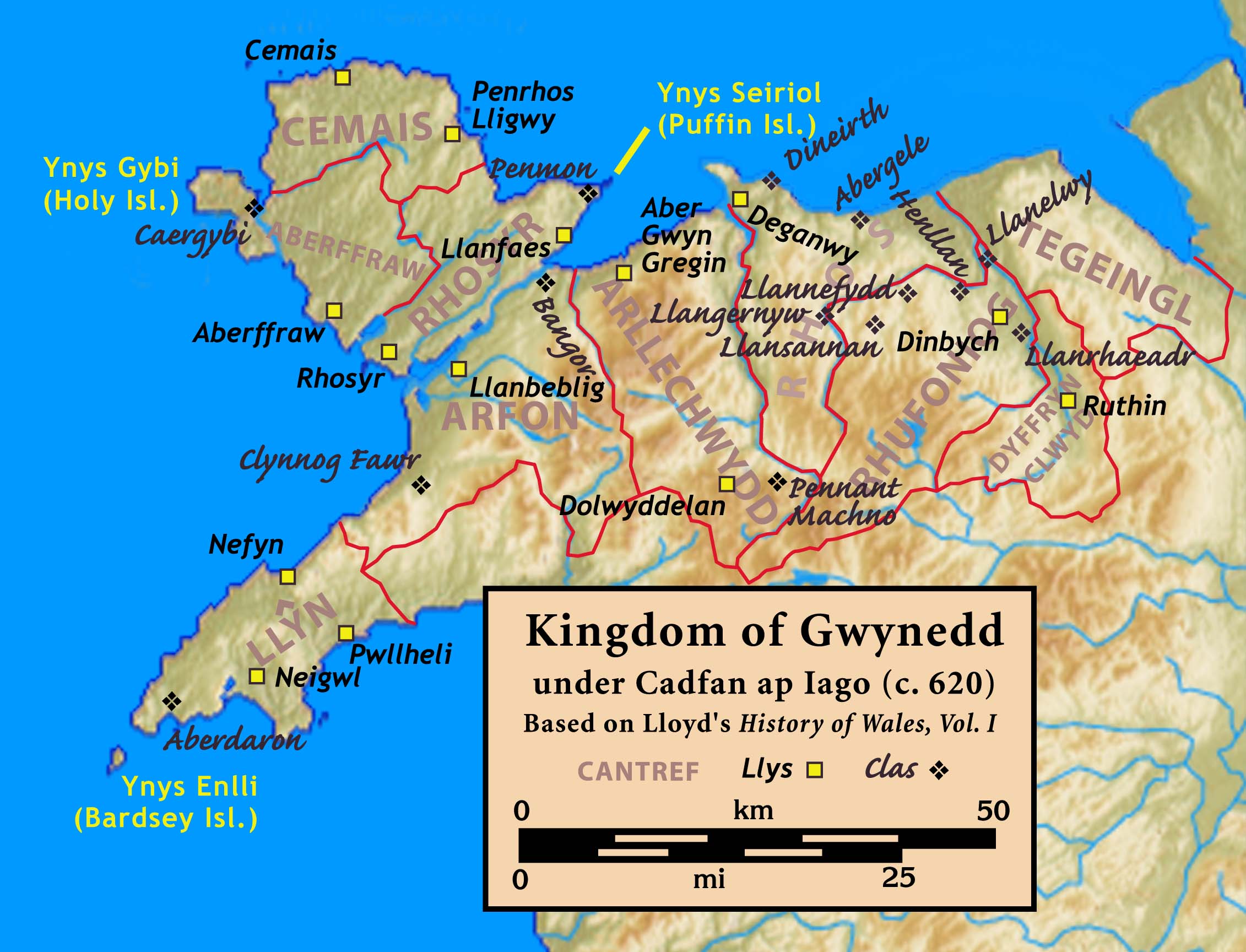
Kingdom Of Gwynedd
The Kingdom of Gwynedd (Medieval Latin: ; Middle Welsh: ) was a Wales in the Early Middle Ages, Welsh kingdom and a Roman Empire Succession of states, successor state that emerged in sub-Roman Britain in the 5th century during the Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain. Based in northwest Wales, the list of rulers of Gwynedd, rulers of Gwynedd repeatedly rose to dominance and were acclaimed as "King of the Britons" before losing their power in civil wars or invasions. The kingdom of Gruffydd ap Llywelynthe King of Wales from 1055 to 1063was shattered by a Timeline of conflict in Anglo-Saxon Britain, Saxon invasion in 1063 just prior to the Norman invasion of Wales, but the House of Aberffraw restored by Gruffudd ap Cynan slowly recovered and Llywelyn the Great of Gwynedd was able to proclaim the Principality of Wales at the Aberdyfi gathering of Welsh princes in 1216. In 1277, the Treaty of Aberconwy between Edward I of England and Llywelyn's grandson Llywelyn ap Gruffudd granted pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Merfyn Frych Ap Gwriad
Merfyn Frych ("Merfyn the Freckled"; Old Welsh ''Mermin''), also known as Merfyn ap Gwriad ("Merfyn son of Gwriad") and Merfyn Camwri ("Merfyn the Oppressor"), was King of Gwynedd from around 825 to 844, the first of its kings known not to have descended from the male line of King Cunedda.The Houses of Cunedda and Rhodri Mawr Welsh Medieval Law: The Laws of Howell the Good (1909) by Hywel ap Cadell, translated by Arthur Wade Wade-Evans Little is known of his reign and his primary notability is as the father of (Rhodri the Great) and founder of his dynasty, which was sometimes called the Merfynion after him. Merfyn came to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint Patrick
Saint Patrick (; or ; ) was a fifth-century Romano-British culture, Romano-British Christian missionary and Archbishop of Armagh, bishop in Gaelic Ireland, Ireland. Known as the "Apostle of Ireland", he is the primary patron saint of Ireland, the other patron saints being Brigid of Kildare and Columba. He is also the patron saint of Nigeria. Patrick was never formally Canonization, canonised by the Catholic Church, having lived before the current laws were established for such matters. He is venerated as a saint in the Catholic Church, the Lutheran Church, the Church of Ireland (part of the Anglican Communion), and in the Eastern Orthodox Church, where he is regarded as equal-to-apostles, equal-to-the-apostles and Enlightener of Ireland. The dates of Patrick's life cannot be fixed with certainty, but there is general agreement that he was active as a missionary in Ireland during the fifth century. A recent biography on Patrick shows a late fourth-century date for the saint i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Six Ages Of The World
The Six Ages of the World (Latin: ''sex aetates mundi''), also rarely Seven Ages of the World (Latin: ''septem aetates mundi''), is a Christian historical periodization first written about by Augustine of Hippo . It is based upon Christian religious events, from the creation of Adam to the events of Revelation. The six ages of history, with each age (Latin: ''aetas'') lasting approximately 1,000 years, were widely believed and in use throughout the Middle Ages, and until the Enlightenment, the writing of history was mostly the filling out of all or some part of this outline. The outline accounts for Seven Ages, just as there are seven days of the week, with the Seventh Age being eternal rest after the Final Judgement and End Times, just as the seventh day of the week is reserved for rest. It was normally called the Six Ages of the World because in Augustine's schema they were the ages of the world, of history, while the Seventh Age was not of this world but, as Bede later el ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theodor Mommsen
Christian Matthias Theodor Mommsen (; ; 30 November 1817 – 1 November 1903) was a German classical scholar, historian, jurist, journalist, politician and archaeologist. He is widely regarded as one of the greatest classicists of the 19th century. He received the 1902 Nobel Prize in Literature for his historical writings, including '' The History of Rome'', after having been nominated by 18 members of the Prussian Academy of Sciences. He was also a prominent German politician, as a member of the Prussian and German parliaments. His works on Roman law and on the law of obligations had a significant impact on the German civil code. Life Mommsen was born to German parents in Garding in the Duchy of Schleswig in 1817, then ruled by the king of Denmark, and grew up in Bad Oldesloe in Holstein, where his father was a Lutheran minister. He studied mostly at home, though he attended the Gymnasium Christianeum in Altona for four years. He studied Greek and Latin and receive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |