|
Protactinium Compounds
Protactinium compounds are compounds containing the element protactinium (symbol: Pa). These compounds usually have protactinium in the +5 oxidation state, although these compounds can also exist in the +2, +3 and +4 oxidation states. Properties of protactinium compounds Here ''a'', ''b'' and ''c'' are lattice constants in picometers, No is space group number and ''Z'' is the number of formula units per unit cell; ''fcc'' stands for the face-centered cubic symmetry. Density was not measured directly but calculated from the lattice parameters. Oxides and oxygen-containing salts Protactinium oxides are known for the metal oxidation states +2, +4 and +5. The most stable is white pentoxide Pa2O5, which can be produced by igniting protactinium(V) hydroxide in air at a temperature of 500 °C.Greenwood, p. 1268 Its crystal structure is cubic, and the chemical composition is often non-stoichiometric, described as PaO2.25. Another phase of this oxide with orthorhombic symmetr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protactinium
Protactinium (formerly protoactinium) is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Pa and atomic number 91. It is a dense, silvery-gray actinide metal which readily reacts with oxygen, water vapor and inorganic acids. It forms various chemical compounds in which protactinium is usually present in the oxidation state +5, but it can also assume +4 and even +3 or +2 states. Concentrations of protactinium in the Earth's crust are typically a few parts per trillion, but may reach up to a few parts per million in some uraninite ore deposits. Because of its scarcity, high radioactivity and high toxicity, there are currently no uses for protactinium outside scientific research, and for this purpose, protactinium is mostly extracted from spent nuclear fuel. The element was first identified in 1913 by Kazimierz Fajans and Oswald Helmuth Göhring and named ''brevium'' because of the short half-life of the specific isotope studied, i.e. protactinium-234. A more stable isotope of p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
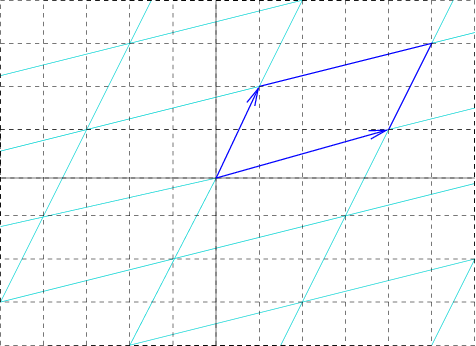
Unit Cell
In geometry, biology, mineralogy and solid state physics, a unit cell is a repeating unit formed by the vectors spanning the points of a lattice. Despite its suggestive name, the unit cell (unlike a unit vector, for example) does not necessarily have unit size, or even a particular size at all. Rather, the primitive cell is the closest analogy to a unit vector, since it has a determined size for a given lattice and is the basic building block from which larger cells are constructed. The concept is used particularly in describing crystal structure in two and three dimensions, though it makes sense in all dimensions. A lattice can be characterized by the geometry of its unit cell, which is a section of the tiling (a parallelogram or parallelepiped) that generates the whole tiling using only translations. There are two special cases of the unit cell: the primitive cell and the conventional cell. The primitive cell is a unit cell corresponding to a single lattice point, it is th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Instruments And Methods In Physics Research A
''Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research'' (Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res.) is a peer-reviewed scientific journal published by Elsevier Elsevier () is a Dutch academic publishing company specializing in scientific, technical, and medical content. Its products include journals such as '' The Lancet'', '' Cell'', the ScienceDirect collection of electronic journals, '' Trends'', .... It was established in 1957 as ''Nuclear Instruments''. It focuses on detectors descriptions and data analysis methods. History *''Nuclear Instruments'' (1957–1958) *''Nuclear Instruments and Methods'' (1959–1981) *''Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research'' (1981–present) :*''Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment'' (1984–present) :*''Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section B: Beam Interactions with Materials and Atoms'' (1984–present) External links'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiolysis
Radiolysis is the dissociation of molecules by ionizing radiation. It is the cleavage of one or several chemical bonds resulting from exposure to high-energy flux. The radiation in this context is associated with ionizing radiation; radiolysis is therefore distinguished from, for example, photolysis of the Cl2 molecule into two Cl-radicals, where (ultraviolet or visible spectrum) light is used. For example, water dissociates under alpha radiation into a hydrogen radical and a hydroxyl radical, unlike ionization of water which produces a hydrogen ion and a hydroxide ion. The chemistry of concentrated solutions under ionizing radiation is extremely complex. Radiolysis can locally modify redox conditions, and therefore the speciation and the solubility of the compounds. Water decomposition Of all the radiation-based chemical reactions that have been studied, the most important is the decomposition of water. When exposed to radiation, water undergoes a breakdown sequence into h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitrate
Nitrate is a polyatomic ion with the chemical formula . Salts containing this ion are called nitrates. Nitrates are common components of fertilizers and explosives. Almost all inorganic nitrates are soluble in water. An example of an insoluble nitrate is bismuth oxynitrate. Structure The ion is the conjugate base of nitric acid, consisting of one central nitrogen atom surrounded by three identically bonded oxygen atoms in a trigonal planar arrangement. The nitrate ion carries a formal charge of −1. This charge results from a combination formal charge in which each of the three oxygens carries a − charge, whereas the nitrogen carries a +1 charge, all these adding up to formal charge of the polyatomic nitrate ion. This arrangement is commonly used as an example of resonance. Like the isoelectronic carbonate ion, the nitrate ion can be represented by resonance structures: Dietary nitrate A rich source of inorganic nitrate in the human diets come from leafy green foods, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphate
In chemistry, a phosphate is an anion, salt, functional group or ester derived from a phosphoric acid. It most commonly means orthophosphate, a derivative of orthophosphoric acid . The phosphate or orthophosphate ion is derived from phosphoric acid by the removal of three protons . Removal of one or two protons gives the dihydrogen phosphate ion and the hydrogen phosphate ion ion, respectively. These names are also used for salts of those anions, such as ammonium dihydrogen phosphate and trisodium phosphate. File:3-phosphoric-acid-3D-balls.png, Phosphoricacid File:2-dihydrogenphosphate-3D-balls.png, Dihydrogenphosphate File:1-hydrogenphosphate-3D-balls.png, Hydrogenphosphate File:0-phosphate-3D-balls.png, Phosphate In organic chemistry, phosphate or orthophosphate is an organophosphate, an ester of orthophosphoric acid of the form where one or more hydrogen atoms are replaced by organic groups. An example is trimethyl phosphate, . The term also refers to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfate
The sulfate or sulphate ion is a polyatomic ion, polyatomic anion with the empirical formula . Salts, acid derivatives, and peroxides of sulfate are widely used in industry. Sulfates occur widely in everyday life. Sulfates are salt (chemistry), salts of sulfuric acid and many are prepared from that acid. Spelling "Sulfate" is the spelling recommended by International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry, IUPAC, but "sulphate" was traditionally used in British English. Structure The sulfate anion consists of a central sulfur atom surrounded by four equivalent oxygen atoms in a tetrahedron, tetrahedral arrangement. The symmetry is the same as that of methane. The sulfur atom is in the +6 oxidation state while the four oxygen atoms are each in the −2 state. The sulfate ion carries an overall charge (physics), charge of −2 and it is the conjugate acid, conjugate base of the bisulfate (or hydrogensulfate) ion, , which is in turn the conjugate base of , sulfuric acid. Organic sulf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basic Oxide
Basic oxides are oxides that show basic properties in opposition to acidic oxides and that either *react with water to form a base; or *react with an acid to form a salt and water which are called neutralization reactions. Etymology "Basic oxides" is a compound of the words "Basic" and "oxides". The word oxides referred to the chemical compounds that one or more oxygen atoms combined with another element such as H2O or CO2. Based on their acid-base characteristics oxides can be classified into four categories: acidic oxides, basic oxides, and amphoteric oxides and neutral oxides. Basic oxides, can also called base anhydrides which means "a base without water", are usually formed by reacting of oxygen with metals, especially alkali (+1 oxidation state) and alkaline earth metals (+2 oxidation state). Both of them are ionic oxide and can dissolve in water to form basic solutions of the metal hydroxide, whereas non-metals usually form acidic oxides. Basic oxide Li2O becomes ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perovskite Structure
A perovskite is any material with a crystal structure following the formula ABX3, which was first discovered as the mineral called perovskite, which consists of calcium titanium oxide (CaTiO3). The mineral was first discovered in the Ural mountains of Russia by Gustav Rose in 1839 and named after Russian mineralogist L. A. Perovski (1792–1856). 'A' and 'B' are two positively charged ions (i.e. cations), often of very different sizes, and X is a negatively charged ion (an anion, frequently oxide) that bonds to both cations. The 'A' atoms are generally larger than the 'B' atoms. The ideal cubic structure has the B cation in 6-fold coordination, surrounded by an octahedron of anions, and the A cation in 12-fold cuboctahedral coordination. Additional perovskite forms may exist where either/both the A and B sites have a configuration of A1x-1A2x and/or B1y-1B2y and the X may deviate from the ideal coordination configuration as ions within the A and B sites undergo changes i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrofluoric Acid
Hydrofluoric acid is a solution of hydrogen fluoride (HF) in water. Solutions of HF are colourless, acidic and highly corrosive. It is used to make most fluorine-containing compounds; examples include the commonly used pharmaceutical antidepressant medication fluoxetine (Prozac) and the material PTFE (Teflon). Elemental fluorine is produced from it. It is commonly used to etch glass and silicon wafers. Uses Production of organofluorine compounds The principal use of hydrofluoric acid is in organofluorine chemistry. Many organofluorine compounds are prepared using HF as the fluorine source, including Teflon, fluoropolymers, fluorocarbons, and refrigerants such as freon. Many pharmaceuticals contain fluorine. Production of inorganic fluorides Most high-volume inorganic fluoride compounds are prepared from hydrofluoric acid. Foremost are Na3AlF6, cryolite, and AlF3, aluminium trifluoride. A molten mixture of these solids serves as a high-temperature solvent for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfuric Acid
Sulfuric acid ( American spelling and the preferred IUPAC name) or sulphuric acid ( Commonwealth spelling), known in antiquity as oil of vitriol, is a mineral acid composed of the elements sulfur, oxygen and hydrogen, with the molecular formula . It is a colorless, odorless and viscous liquid that is miscible with water. Pure sulfuric acid does not exist naturally on Earth due to its strong affinity to water vapor; it is hygroscopic and readily absorbs water vapor from the air. Concentrated sulfuric acid is highly corrosive towards other materials, from rocks to metals, since it is an oxidant with powerful dehydrating properties. Phosphorus pentoxide is a notable exception in that it is not dehydrated by sulfuric acid, but to the contrary dehydrates sulfuric acid to sulfur trioxide. Upon addition of sulfuric acid to water, a considerable amount of heat is released; thus the reverse procedure of adding water to the acid should not be performed since the heat released ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrochloric Acid
Hydrochloric acid, also known as muriatic acid, is an aqueous solution of hydrogen chloride. It is a colorless solution with a distinctive pungent smell. It is classified as a strong acid. It is a component of the gastric acid in the digestive systems of most animal species, including humans. Hydrochloric acid is an important laboratory reagent and industrial chemical. History In the early tenth century, the Persian physician and alchemist Abu Bakr al-Razi ( 865–925, Latin: Rhazes) conducted experiments with sal ammoniac ( ammonium chloride) and vitriol (hydrated sulfates of various metals), which he distilled together, thus producing the gas hydrogen chloride. In doing so, al-Razi may have stumbled upon a primitive method for producing hydrochloric acid, as perhaps manifested in the following recipe from his ("The Book of Secrets"): However, it appears that in most of his experiments al-Razi disregarded the gaseous products, concentrating instead on the color c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



_0468.jpg)
