|
Photosensitive
Photosensitivity is the amount to which an object reacts upon receiving photons, especially visible light. In medicine, the term is principally used for abnormal reactions of the skin, and two types are distinguished, photoallergy and phototoxicity. The photosensitive ganglion cells in the mammalian eye are a separate class of light-detecting cells from the photoreceptor cells that function in vision. Skin reactions Human medicine Sensitivity of the skin to a light source can take various forms. People with particular skin types are more sensitive to sunburn. Particular medications make the skin more sensitive to sunlight; these include most of the tetracycline antibiotics, heart drugs amiodarone, and Sulfonamide (medicine), sulfonamides. Some dietary supplements, such as St. John's Wort, include photosensitivity as a possible side effect. Particular conditions lead to increased light sensitivity. Patients with systemic lupus erythematosus experience skin symptoms after sunligh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photoreceptor Cell
A photoreceptor cell is a specialized type of neuroepithelial cell found in the retina that is capable of visual phototransduction. The great biological importance of photoreceptors is that they convert light (visible electromagnetic radiation) into signals that can stimulate biological processes. To be more specific, photoreceptor proteins in the cell absorb photons, triggering a change in the cell's membrane potential. There are currently three known types of photoreceptor cells in mammalian eyes: rod cell, rods, cone cell, cones, and intrinsically photosensitive retinal ganglion cells. The two classic photoreceptor cells are rods and cones, each contributing information used by the visual system to form an image of the environment, Visual perception, sight. Rods primarily mediate scotopic vision (dim conditions) whereas cones primarily mediate photopic vision (bright conditions), but the processes in each that supports phototransduction is similar. The intrinsically photosen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
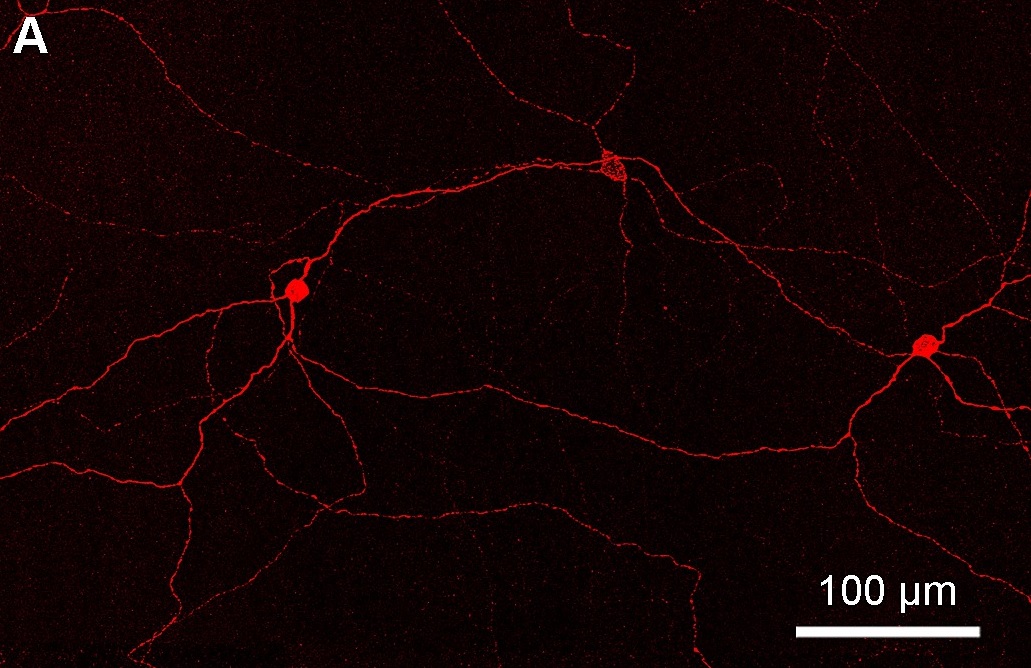
Photosensitive Ganglion Cell
Intrinsically photosensitive retinal ganglion cells (ipRGCs), also called photosensitive retinal ganglion cells (pRGC), or melanopsin-containing retinal ganglion cells (mRGCs), are a type of neuron in the retina of the mammalian eye. The presence of an additional photoreceptor was first suspected in 1927 when mice lacking rod and cone cells still responded to changing light levels through pupil constriction; this suggested that rods and cones are not the only light-sensitive tissue. However, it was unclear whether this light sensitivity arose from an additional retinal photoreceptor or elsewhere in the body. Recent research has shown that these retinal ganglion cells, unlike other retinal ganglion cells, are intrinsically photosensitive due to the presence of melanopsin, a light-sensitive protein. Therefore, they constitute a third class of photoreceptors, in addition to rod and cone cells. Overview Compared to the rods and cones, the ipRGCs respond more sluggishly and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypericin
Hypericin is a carbopolycyclic compound derived from bisanthene with antidepressant properties, found in various ''Hypericum'' species, and is being studied for treating cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Opinions differ on the extent to which hypericin exhibits antidepressant effects. According to some scholars, hypericin, along with other active compounds in ''Hypericum perforatum'' (St. John’s wort), contributes to the antidepressant effects of the total plant extract. According to others, hypericin does not significantly inhibit monoamine oxidase and thus is unlikely to account for the antidepressant effects of ''Hypericum'' extract. While another hypericin shows affinity mainly for NMDA receptors, suggesting that other plant constituents likely play a more significant role in its antidepressant effects. Hypericin is a structurally complex phenanthroperylene quinone with potential Evidence-based medicine, medical and photoreceptive applications. It is red-colored, photosensiti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Urticaria
Solar urticaria (SU) is a rare condition in which exposure to ultraviolet or UV radiation, or sometimes even visible light, induces a case of urticaria or hives that can appear in both covered and uncovered areas of the skin. It is classified as a type of physical urticaria. The classification of disease types is somewhat controversial. One classification system distinguished various types of SU based on the wavelength of the radiation that causes the breakout; another classification system is based on the type of allergen that initiates a breakout. The agent in the human body responsible for the reaction to radiation, known as the photoallergen, has not yet been identified. The disease itself can be difficult to diagnose properly because it is so similar to other dermatological disorders, such as polymorphous light eruption or PLE. The most helpful test is a diagnostic phototest, a specialized test which confirms the presence of an abnormal sunburn reaction. Once recognized, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypericum Perforatum
''Hypericum perforatum'', commonly known as St. John's wort (sometimes perforate St. John's wort or common St. John's wort), is a flowering plant in the family Hypericaceae. It is a hairless, Perennial, perennial herb with woody Root, roots, yellow Flower, flowers marked by black glands, and leaves that appear Perforation, perforated due to translucent glands, producing thousands of seeds per plant. ''H. perforatum'' is the type species of its genus, known for its historical use in folklore and traditional medicine. Probably a Hybrid (biology), hybrid between the closely related ''Hypericum attenuatum, H. attenuatum'' and ''Hypericum maculatum, H. maculatum'' (imperforate St. John's wort) that originated in Siberia, the species has Cosmopolitan distribution, spread worldwide. It can further hybridize with related species due to its Polyploidy, allopolyploid nature. It is native to much of Europe, West Asia, West and Central Asia, and parts of Africa and China and has been wide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photon
A photon () is an elementary particle that is a quantum of the electromagnetic field, including electromagnetic radiation such as light and radio waves, and the force carrier for the electromagnetic force. Photons are massless particles that can move no faster than the speed of light measured in vacuum. The photon belongs to the class of boson particles. As with other elementary particles, photons are best explained by quantum mechanics and exhibit wave–particle duality, their behavior featuring properties of both waves and particles. The modern photon concept originated during the first two decades of the 20th century with the work of Albert Einstein, who built upon the research of Max Planck. While Planck was trying to explain how matter and electromagnetic radiation could be in thermal equilibrium with one another, he proposed that the energy stored within a material object should be regarded as composed of an integer number of discrete, equal-sized parts. To explain the pho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photosensitizer
Photosensitizers are light absorbers that alter the course of a photochemical reaction. They usually are catalysts. They can function by many mechanisms; sometimes they abstract an electron from the substrate, and sometimes they abstract a hydrogen atom from the substrate. At the end of this process, the photosensitizer returns to its ground state, where it remains chemically intact, poised to absorb more light. One branch of chemistry which frequently utilizes photosensitizers is polymer chemistry, using photosensitizers in reactions such as photopolymerization, photocrosslinking, and photodegradation. Photosensitizers are also used to generate prolonged excited electronic states in organic molecules with uses in photocatalysis, photon upconversion and photodynamic therapy. Generally, photosensitizers absorb electromagnetic radiation consisting of Infrared, infrared radiation, Light, visible light radiation, and Ultraviolet, ultraviolet radiation and transfer absorbed energy into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Snow Blindness
Photokeratitis or ultraviolet keratitis is a painful eye condition caused by exposure of insufficiently protected Human eye, eyes to the ultraviolet (UV) rays from either natural (e.g. intense direct or reflected sunlight) or artificial (e.g. the electric arc during welding) sources. Photokeratitis is akin to a sunburn of the cornea and conjunctiva. The injury may be prevented by wearing eye protection that blocks most of the ultraviolet radiation, such as Welding helmet#Goggles, welding goggles with the proper filters, a welder's helmet, sunglasses rated for sufficient UV protection, or appropriate snow goggles. The condition is usually managed by removal from the source of ultraviolet radiation, covering the corneas, and administration of pain relief. Photokeratitis is known by a number of different terms, including snow blindness, arc eye, welder's flash, sand eyes, bake eyes, corneal flash burns, flash burns, niphablepsia, or keratoconjunctivitis photoelectrica. Signs and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photophobia
Photophobia is a medical symptom of abnormal intolerance to visual perception of light. As a medical symptom, photophobia is not a morbid fear or phobia, but an experience of discomfort or pain to the eyes due to light exposure or by presence of actual physical sensitivity of the eyes, though the term is sometimes additionally applied to abnormal or irrational fear of light, such as heliophobia. The term ''photophobia'' comes . Causes Patients may develop photophobia as a result of several different medical conditions, related to the human eye, eye, the nervous system, genetic, or other causes. Photophobia may manifest itself in an increased response to light starting at any step in the visual system, such as: * Too much light entering the eye. Too much light can enter the eye if it is damaged, such as with corneal abrasion and retinal damage, or if its pupil is unable to normally constrict (seen with damage to the oculomotor nerve). * Due to albinism, the lack of pigment in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heliotropism
Heliotropism, a form of tropism, is the diurnal or seasonal motion of plant parts (flowers or leaves) in response to the direction of the Sun. The habit of some plants to move in the direction of the Sun, a form of tropism, was already known by the Ancient Greeks. They named one of those plants after that property ''Heliotropium'', meaning "sun turn". The Greeks assumed it to be a passive effect, presumably the loss of fluid on the illuminated side, that did not need further study. Aristotle's logic that plants are passive and immobile organisms prevailed. In the 19th century, however, botanists discovered that growth processes in the plant were involved, and conducted increasingly in-depth experiments. A. P. de Candolle called this phenomenon in ''any'' plant ''heliotropism'' (1832). It was renamed phototropism in 1892 because it is a response to light rather than to the sun, and because the phototropism of algae in lab studies at that time strongly depended on the brightness (pos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bergaptene
Bergapten (5-methoxypsoralen) is a naturally-occurring organic chemical compound produced by numerous plant species, especially from the carrot family Apiaceae and the citrus family Rutaceae. For example, bergapten has been extracted from 24 species of the genus '' Heracleum'' in the family Apiaceae. Cited by Mitchell and Rook (1979). In the family Rutaceae, various ''Citrus'' species contain significant amounts of bergapten, especially the bergamot orange, the micrantha, and certain varieties of lime and bitter orange. Bergapten belongs to a class of chemical compounds known as the furanocoumarins. In 1834, Kalbrunner isolated 5-methoxypsoralen from bergamot essential oil, hence the common name "bergapten". It was the first furanocoumarin to be isolated and identified. Toxicity Bergapten is a derivative of psoralen, the parent compound of a family of naturally-occurring organic compounds known as the linear furanocoumarins (so called since they exhibit a linear chemical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digital Camera ISO
Film speed is the measure of a photographic film's sensitivity to light, determined by sensitometry and measured on various numerical scales, the most recent being the ISO system introduced in 1974. A closely related system, also known as ISO, is used to describe the relationship between exposure and output image lightness in digital cameras. Prior to ISO, the most common systems were ASA in the United States and DIN in Europe. The term ''speed'' comes from the early days of photography. Photographic emulsions that were more sensitive to light needed less time to generate an acceptable image and thus a complete exposure could be finished faster, with the subjects having to hold still for a shorter length of time. Emulsions that were less sensitive were deemed "slower" as the time to complete an exposure was much longer and often usable only for still life photography. Exposure times for photographic emulsions shortened from hours to fractions of a second by the late 19th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |