|
Persistent Homology Group
In persistent homology, a persistent homology group is a multiscale analog of a homology group that captures information about the evolution of topological features across a filtration of spaces. While the ordinary homology group represents nontrivial homology classes of an individual topological space, the persistent homology group tracks only those classes that remain nontrivial across multiple parameters in the underlying filtration. Analogous to the ordinary Betti number, the ranks of the persistent homology groups are known as the persistent Betti numbers. Persistent homology groups were first introduced by Herbert Edelsbrunner, David Letscher, and Afra Zomorodian in a 2002 paper ''Topological Persistence and Simplification'', one of the foundational papers in the fields of persistent homology and topological data analysis, based largely on the persistence barcodes and the persistence algorithm, that were first described by Serguei Barannikov in the 1994 paper. Since then ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Persistent Homology
In topological data analysis, persistent homology is a method for computing topological features of a space at different spatial resolutions. More persistent features are detected over a wide range of spatial scales and are deemed more likely to represent true features of the underlying space rather than artifacts of sampling, noise, or particular choice of parameters. To find the persistent homology of a space, the space must first be represented as a simplicial complex. A distance function on the underlying space corresponds to a filtration of the simplicial complex, that is a nested sequence of increasing subsets. One common method of doing this is via taking the sublevel filtration of the distance to a point cloud, or equivalently, the offset filtration on the point cloud and taking its nerve in order to get the simplicial filtration known as Čech filtration. A similar construction uses a nested sequence of Vietoris–Rips complexes known as the Vietoris–Rips filtration. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monotonic Function
In mathematics, a monotonic function (or monotone function) is a function between ordered sets that preserves or reverses the given order. This concept first arose in calculus, and was later generalized to the more abstract setting of order theory. In calculus and analysis In calculus, a function f defined on a subset of the real numbers with real values is called ''monotonic'' if it is either entirely non-decreasing, or entirely non-increasing. That is, as per Fig. 1, a function that increases monotonically does not exclusively have to increase, it simply must not decrease. A function is termed ''monotonically increasing'' (also ''increasing'' or ''non-decreasing'') if for all x and y such that x \leq y one has f\!\left(x\right) \leq f\!\left(y\right), so f preserves the order (see Figure 1). Likewise, a function is called ''monotonically decreasing'' (also ''decreasing'' or ''non-increasing'') if, whenever x \leq y, then f\!\left(x\right) \geq f\!\left(y\right), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plane (mathematics)
In mathematics, a plane is a two-dimensional space or flat surface that extends indefinitely. A plane is the two-dimensional analogue of a point (zero dimensions), a line (one dimension) and three-dimensional space. When working exclusively in two-dimensional Euclidean space, the definite article is used, so ''the'' Euclidean plane refers to the whole space. Several notions of a plane may be defined. The Euclidean plane follows Euclidean geometry Euclidean geometry is a mathematical system attributed to ancient Greek mathematics, Greek mathematician Euclid, which he described in his textbook on geometry, ''Euclid's Elements, Elements''. Euclid's approach consists in assuming a small set ..., and in particular the parallel postulate. A projective plane may be constructed by adding "points at infinity" where two otherwise parallel lines would intersect, so that every pair of lines intersects in exactly one point. The elliptic plane may be further defined by adding a metr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
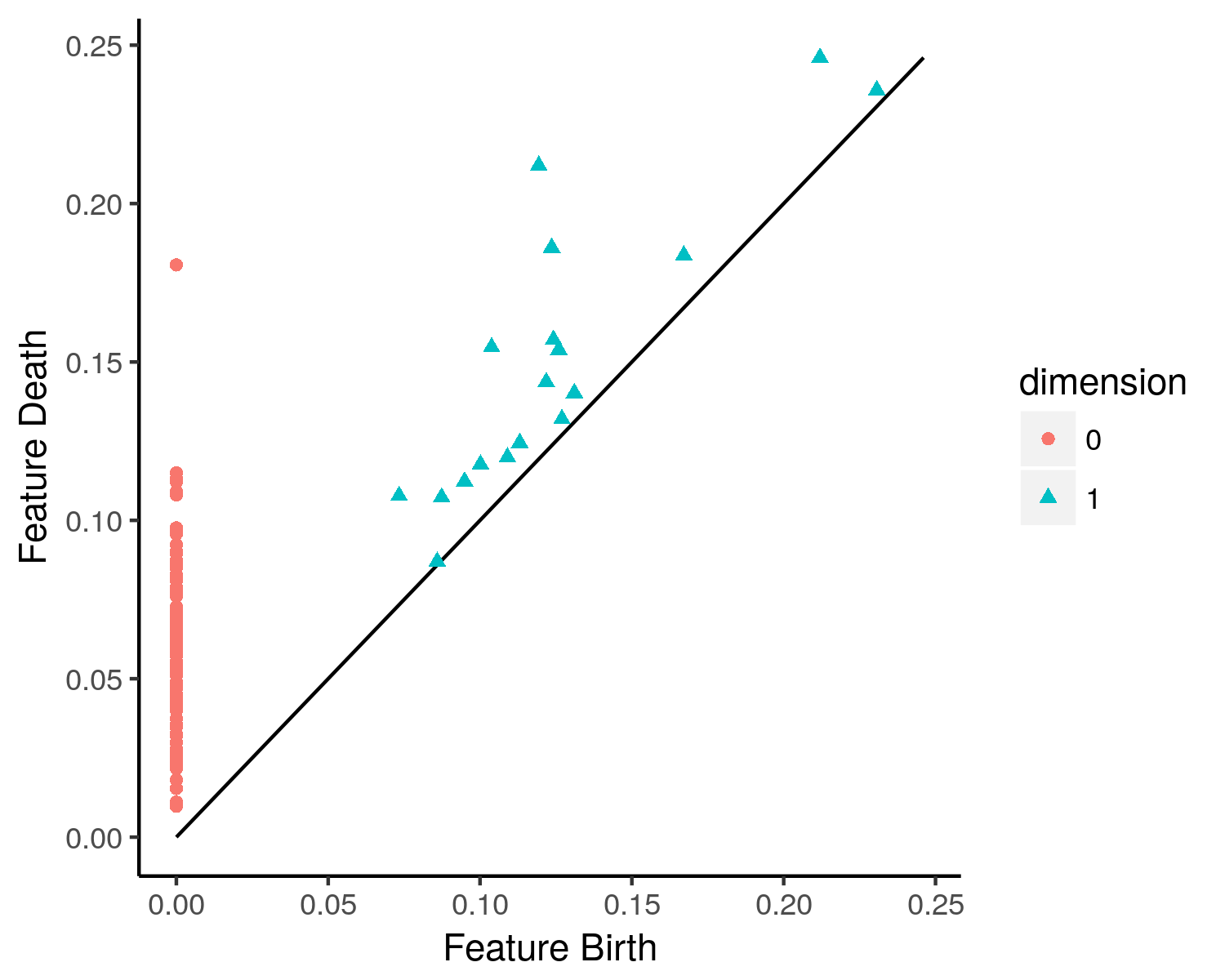
Persistence Diagram
Persistence or Persist may refer to: Math and computers * Image persistence, in LCD monitors * Persistence (computer science), the characteristic of data that outlives the execution of the program that created it * Persistence of a number, a mathematical quality of numbers * Persistent data structure, a data structure that always preserves the previous version of itself when it is modified * Persistent world, in virtual reality and computer games Science * Multidrug tolerance, a dormant, persistent state of a bacterial population * Persistence (botany), describing plant parts that remain attached to the plant after completing their function * Persistence (discontinuity), a concept in geotechnical engineering * Persistence (linguistics), a principle of grammaticalization * Persistence (psychology), a personality trait * Persistence of vision, a theory on how the illusion of motion in films is achieved * Persistence forecasting, predicting the future to be the same as the prese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multiset
In mathematics, a multiset (or bag, or mset) is a modification of the concept of a set that, unlike a set, allows for multiple instances for each of its elements. The number of instances given for each element is called the ''multiplicity'' of that element in the multiset. As a consequence, an infinite number of multisets exist that contain only elements and , but vary in the multiplicities of their elements: * The set contains only elements and , each having multiplicity 1 when is seen as a multiset. * In the multiset , the element has multiplicity 2, and has multiplicity 1. * In the multiset , and both have multiplicity 3. These objects are all different when viewed as multisets, although they are the same set, since they all consist of the same elements. As with sets, and in contrast to ''tuples'', the order in which elements are listed does not matter in discriminating multisets, so and denote the same multiset. To distinguish between sets and multisets, a notat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extended Real Number Line
In mathematics, the extended real number system is obtained from the real number system \R by adding two elements denoted +\infty and -\infty that are respectively greater and lower than every real number. This allows for treating the potential infinities of infinitely increasing sequences and infinitely decreasing series as actual infinities. For example, the infinite sequence (1,2,\ldots) of the natural numbers increases ''infinitively'' and has no upper bound in the real number system (a potential infinity); in the extended real number line, the sequence has +\infty as its least upper bound and as its limit (an actual infinity). In calculus and mathematical analysis, the use of +\infty and -\infty as actual limits extends significantly the possible computations. It is the Dedekind–MacNeille completion of the real numbers. The extended real number system is denoted \overline, \infty,+\infty/math>, or \R\cup\left\. When the meaning is clear from context, the symbol +\inf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interval (mathematics)
In mathematics, a real interval is the set of all real numbers lying between two fixed endpoints with no "gaps". Each endpoint is either a real number or positive or negative infinity, indicating the interval extends without a bound. A real interval can contain neither endpoint, either endpoint, or both endpoints, excluding any endpoint which is infinite. For example, the set of real numbers consisting of , , and all numbers in between is an interval, denoted and called the unit interval; the set of all positive real numbers is an interval, denoted ; the set of all real numbers is an interval, denoted ; and any single real number is an interval, denoted . Intervals are ubiquitous in mathematical analysis. For example, they occur implicitly in the epsilon-delta definition of continuity; the intermediate value theorem asserts that the image of an interval by a continuous function is an interval; integrals of real functions are defined over an interval; etc. Interval ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Image (mathematics)
In mathematics, for a function f: X \to Y, the image of an input value x is the single output value produced by f when passed x. The preimage of an output value y is the set of input values that produce y. More generally, evaluating f at each Element (mathematics), element of a given subset A of its Domain of a function, domain X produces a set, called the "image of A under (or through) f". Similarly, the inverse image (or preimage) of a given subset B of the codomain Y is the set of all elements of X that map to a member of B. The image of the function f is the set of all output values it may produce, that is, the image of X. The preimage of f is the preimage of the codomain Y. Because it always equals X (the domain of f), it is rarely used. Image and inverse image may also be defined for general Binary relation#Operations, binary relations, not just functions. Definition The word "image" is used in three related ways. In these definitions, f : X \to Y is a Function (mat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Persistence Module
A persistence module is a mathematical structure in persistent homology and topological data analysis that formally captures the persistence of topological features of an object across a range of scale parameters. A persistence module often consists of a collection of homology groups (or vector spaces if using field coefficients) corresponding to a filtration of topological spaces, and a collection of linear maps induced by the inclusions of the filtration. The concept of a persistence module was first introduced in 2005 as an application of graded modules over polynomial rings, thus importing well-developed algebraic ideas from classical commutative algebra theory to the setting of persistent homology. Since then, persistence modules have been one of the primary algebraic structures studied in the field of applied topology. Definition Single Parameter Persistence Modules Let T be a totally ordered set and let K be a field. The set T is sometimes called the ''indexing set''. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linear Map
In mathematics, and more specifically in linear algebra, a linear map (also called a linear mapping, linear transformation, vector space homomorphism, or in some contexts linear function) is a mapping V \to W between two vector spaces that preserves the operations of vector addition and scalar multiplication. The same names and the same definition are also used for the more general case of modules over a ring; see Module homomorphism. If a linear map is a bijection then it is called a . In the case where V = W, a linear map is called a linear endomorphism. Sometimes the term refers to this case, but the term "linear operator" can have different meanings for different conventions: for example, it can be used to emphasize that V and W are real vector spaces (not necessarily with V = W), or it can be used to emphasize that V is a function space, which is a common convention in functional analysis. Sometimes the term ''linear function'' has the same meaning as ''linear m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |