|
Pendraig
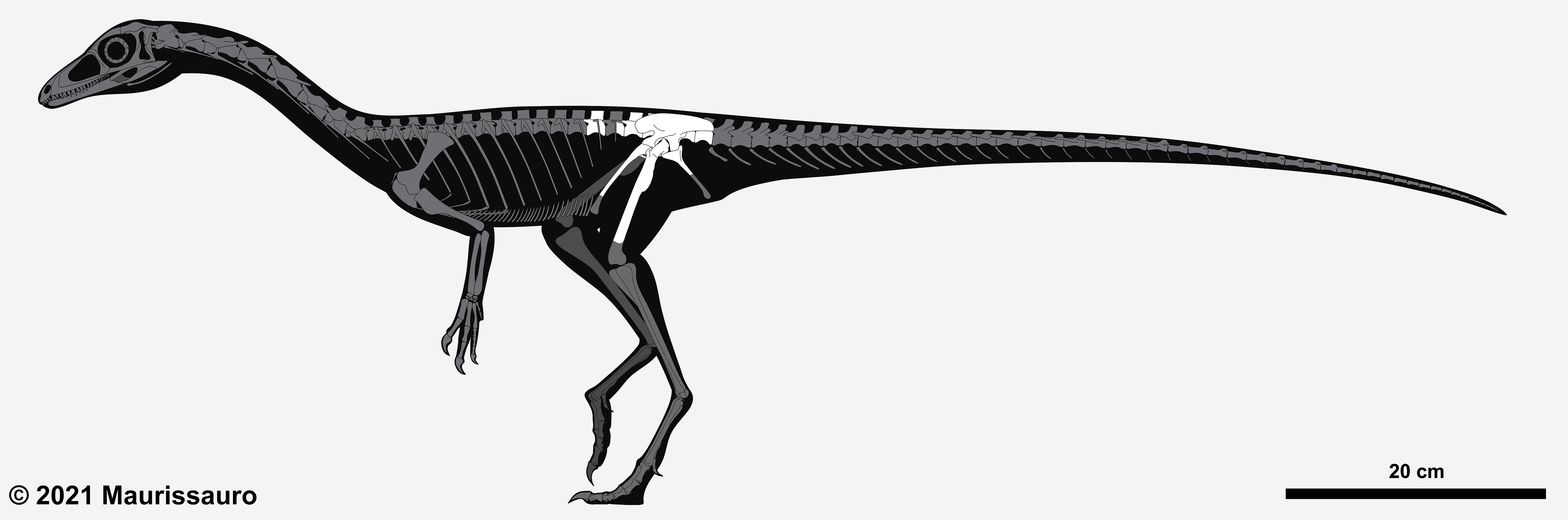
''Pendraig'' (meaning "chief dragon" in Middle Welsh) is a genus of coelophysoid theropod dinosaur from South Wales. It contains one species, ''Pendraig milnerae'', named after Angela Milner. The specimen was discovered in the Pant-y-Ffynnon quarry. In life it would have measured in length. History The holotype of ''Pendraig'' were found in the Pant-y-ffynnon Quarry in Wales in 1952 by Kermack and Robinson along with the holotypes of '' Pantydraco'' and '' Terrestrisuchus'', and were subsequently lost in the collections of the Natural History Museum, London. The fossils were originally thought to belong to a " coelurosaur" (in the outdated sense of the word) and even subsequently classified as a species of "''Syntarsus''" (now ''Megapnosaurus'' or ''Coelophysis''). Recently Angela Milner and Susannah Maidment rediscovered the fossils stored with some crocodile bones (likely '' Terrestrisuchus''). The fossils were named as representing a new genus of theropod in 2021. Descri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pendraig Milnerae Skeleton
''Pendraig'' (meaning "chief dragon" in Middle Welsh) is a genus of coelophysoid theropod dinosaur from South Wales. It contains one species, ''Pendraig milnerae'', named after Angela Milner. The specimen was discovered in the Pant-y-Ffynnon quarry. In life it would have measured in length. History The holotype of ''Pendraig'' were found in the Pant-y-ffynnon Quarry in Wales in 1952 by Kermack and Robinson along with the holotypes of ''Pantydraco'' and ''Terrestrisuchus'', and were subsequently lost in the collections of the Natural History Museum, London. The fossils were originally thought to belong to a "coelurosaur" (in the outdated sense of the word) and even subsequently classified as a species of "''Syntarsus''" (now ''Megapnosaurus'' or ''Coelophysis''). Recently Angela Milner and Susannah Maidment rediscovered the fossils stored with some crocodile bones (likely ''Terrestrisuchus''). The fossils were named as representing a new genus of theropod in 2021. Description ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pant-y-Ffynnon Quarry
Pant-y-Ffynnon Quarry is a stone quarry in the Vale of Glamorgan, Wales, around 3 kilometers east of Cowbridge. It contains fissure fill deposits dating to the Late Triassic (Rhaetian), hosted within karsts of Carboniferous aged limestone, primarily the Friars Point Limestone Formation. Remains of numerous small vertebrates, notably archosaurs, are known from the fissure fills in the quarry, similar to other Late Triassic-Early Jurassic fissure fill deposits known from Southwest England and southern Wales. History The quarry was likely in use since at least the 1910s, and the first fossil specimens discovered at the quarry were collected by palaeontologists Kenneth Kermack and Pamela Robinson of University College London , mottoeng = Let all come who by merit deserve the most reward , established = , type = Public research university , endowment = £143 million (2020) , budget = � ... bet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Megapnosaurus
''Megapnosaurus'' (meaning "big dead lizard", from Greek μεγα = "big", 'απνοος = "not breathing", "dead", σαυρος = "lizard") is an extinct genus of coelophysid theropod dinosaur that lived approximately 188 million years ago during the early part of the Jurassic Period in what is now Africa. The species was a small to medium-sized, lightly built, ground-dwelling, bipedal carnivore, that could grow up to long and weigh up to . It was originally given the genus name ''Syntarsus'', but that name was later determined to be preoccupied by a beetle. The species was subsequently given a new genus name, ''Megapnosaurus,'' by Ivie, Ślipiński & Węgrzynowicz in 2001. Some studies have classified it as a species within the genus ''Coelophysis,'' but this interpretation has been challenged by more subsequent studies and the genus is now considered valid. Discovery and history The first fossils of ''Megapnosaurus'' were found in 1963 by a group of students from Northle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angela Milner
Angela Cheryl Milner (3 October 1947 – 13 August 2021) was a British paleontologist who, in 1986 alongside Alan Charig, described the dinosaur '' Baryonyx''. Early life Milner was born Angela Girven in Gosforth, daughter of Cyril and Lucia Girven. Her father was the county engineer for Northumberland. She attended Church High school. She initially planned to focus on microbiology for her university degree, but inspiring lectures from Alec Panchen made her change to palaeontology. She gained a BSc in zoology at Newcastle University and stayed there in 1969 to take a PhD in palaeontology supervised by Panchen focusing on the nectrideans, a group of Paleozoic tetrapods. Career Milner was first employed at the Natural History Museum in London in 1976. Her unusual career path led her to reach a management as well as scientific role, finally being promoted to Assistant Keeper of Palaeontology as well as being a senior scientist. She was Head of the Fossil Vertebrates D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Terrestrisuchus
''Terrestrisuchus'' is an extinct genus of very small early crocodylomorph that was about long. Fossils have been found in Wales and Southern England and date from near the very end of the Late Triassic during the Rhaetian, and it is known by type and only known species ''T. gracilis''. ''Terrestrisuchus'' was a long-legged, active predator that lived entirely on land, unlike modern crocodilians. It inhabited a chain of tropical, low-lying islands that made up southern Britain, along with similarly small-sized dinosaurs and abundant rhynchocephalians. Numerous fossils of ''Terrestrisuchus'' are known from fissures in limestone karst which made up the islands it lived on, which formed caverns and sinkholes that preserved the remains of ''Terrestrisuchus'' and other island-living reptiles. Description ''Terrestrisuchus'' was a small, slender crocodylomorph with very long legs, quite unlike modern crocodilians. It was initially estimated to have been between long, although this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aenigmaspina
''Aenigmaspina'' (from Latin ''aenigma'' and ''spina'', meaning "enigmatic spine") is an extinct genus of enigmatic pseudosuchian (=crurotarsan) archosaur from the Late Triassic of the United Kingdom. Its fossils are known from the Pant-y-ffynnon Quarry in South Wales, of which its type and only known species is named after, ''A. pantyffynnonensis''. ''Aenigmaspina'' is characterised by the unusual spines on its vertebrae, which are broad and flat on top with a unique 'Y' shape. Although parts of its skeleton is relatively well known, the affinities of ''Aenigmaspina'' to other pseudosuchians are unclear, although it is possibly related to families Ornithosuchidae, Erpetosuchidae or Gracilisuchidae. Description ''Aenigmaspina'' was a small (<1 m long) archosaur with a slender skeleton and build. It is mostly known from the front half of its body, including its |
Coelophysis
''Coelophysis'' ( traditionally; or , as heard more commonly in recent decades) is an extinct genus of coelophysid theropod dinosaur that lived approximately 228 to 201.3 million years ago during the latter part of the Triassic Period from the Carnian and Rhaetian faunal stages in what is now the southwestern United States. '' Megapnosaurus'' was once considered a species within this genus,Weishampel, David B; et al. (2004). "Dinosaur distribution (Early Jurassic, Africa)." In: Weishampel, David B.; Dodson, Peter; and Osmólska, Halszka (eds.): The Dinosauria, 2nd, Berkeley: University of California Press. Pp. 535–536. but this interpretation has been challenged since 2017 and the genus ''Megapnosaurus'' is now considered valid. ''Coelophysis'' was a small, slenderly-built, ground-dwelling, bipedal carnivore that could grow up to long. It is one of the earliest known dinosaur genera. Scattered material representing similar animals has been found worldwide in some Lat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coelophysoid
Coelophysoidea were common dinosaurs of the Late Triassic and Early Jurassic periods. They were widespread geographically, probably living on all continents. Coelophysoids were all slender, carnivorous forms with a superficial similarity to the coelurosaurs, with which they were formerly classified, and some species had delicate cranial crests. Sizes range from about 1 to 6 m in length. It is unknown what kind of external covering coelophysoids had, and various artists have portrayed them as either scaly or feathered. Some species may have lived in packs, as inferred from sites where numerous individuals have been found together. Examples of coelophysoids include ''Coelophysis'', ''Procompsognathus'' and ''Liliensternus''. Most dinosaurs formerly referred to as being in the dubious taxon "Podokesauridae" are now classified as coelophysoids. Classification Despite their very early occurrence in the fossil record, coelophysoids have a number of derived features that separate th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thecodontosaurus
''Thecodontosaurus'' ("socket-tooth lizard") is a genus of herbivorous basal sauropodomorph dinosaur that lived during the late Triassic period (Rhaetian age). Its remains are known mostly from Triassic "fissure fillings" in South England. ''Thecodontosaurus'' was a small bipedal animal, about 2 m (6.5 ft) long. It is one of the first dinosaurs to be discovered and is one of the oldest that existed. Many species have been named in the genus, but only the type species ''Thecodontosaurus antiquus'' is seen as valid today. Discovery and naming ''Thecodontosaurus antiquus'' In the autumn of 1834, surgeon Henry Riley (1797–1848) and the curator of the Bristol Institution, Samuel Stutchbury, began to excavate "saurian remains" at the quarry of Durdham Down, at Clifton, presently a part of Bristol, which is part of the Magnesian Conglomerate. In 1834 and 1835, they briefly reported on the finds. They provided their initial description in 1836, naming a new genus: ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhynchocephalia
Rhynchocephalia (; ) is an order of lizard-like reptiles that includes only one living species, the tuatara (''Sphenodon punctatus'') of New Zealand. Despite its current lack of diversity, during the Mesozoic rhynchocephalians were a diverse group including a wide array of morphologically distinct forms. The oldest record of the group is dated to the Middle Triassic around 238 to 240 million years ago, and they had achieved a worldwide distribution by the Early Jurassic. Most rhynchocephalians belong to the group Sphenodontia ('wedge-teeth'). Their closest living relatives are lizards and snakes in the order Squamata, with the two orders being grouped together in the superorder Lepidosauria. Many of the niches occupied by lizards today were held by sphenodontians during the Triassic and Jurassic, although lizard diversity began to overtake sphenodontian diversity in the Cretaceous, and they had disappeared almost entirely by the beginning of the Cenozoic. While the modern tuat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
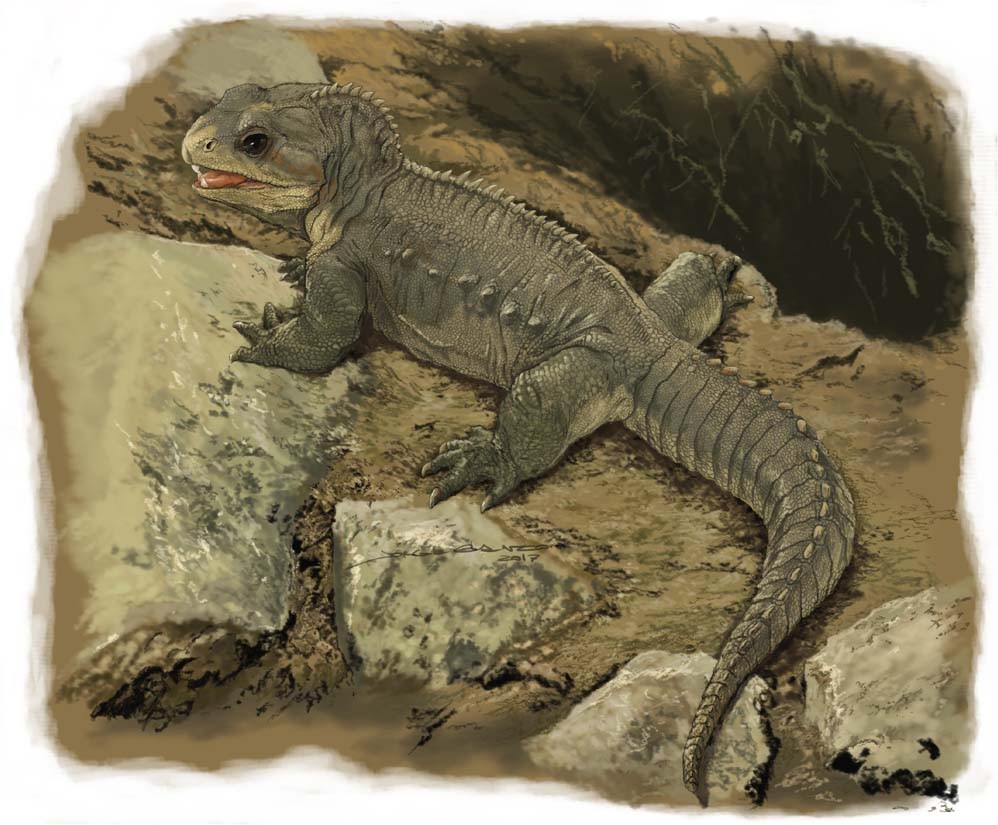
Clevosaurus
''Clevosaurus'' (meaning "Gloucester lizard") is an extinct genus of rhynchocephalian reptile from the Late Triassic and the Early Jurassic periods. Species of ''Clevosaurus'' were widespread across Pangaea, and have been found on all continents except Australia and Antarctica. Five species of ''Clevosaurus'' have been found in ancient fissure fill deposits in south-west England and Wales, alongside other sphenodontians, early mammals and dinosaurs. In regards to its Pangaean distribution, ''C. hadroprodon'' is the oldest record of a sphenodontian from Gondwana, though its affinity to ''Clevosaurus'' has been questioned. History of discovery The first species of ''Clevosaurus'' to be described was ''C. hudsoni'', which was described by William Elgin Swinton in 1939 from a fissure fill deposit in Cromhall Quarry ( Magnesian Conglomerate Formation) in the county of Gloucestershire, England, with the name of the county lending its name to the genus. Description ''Clevosaurus' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




_601758.jpg)
