|
Pachysentis Procumbens
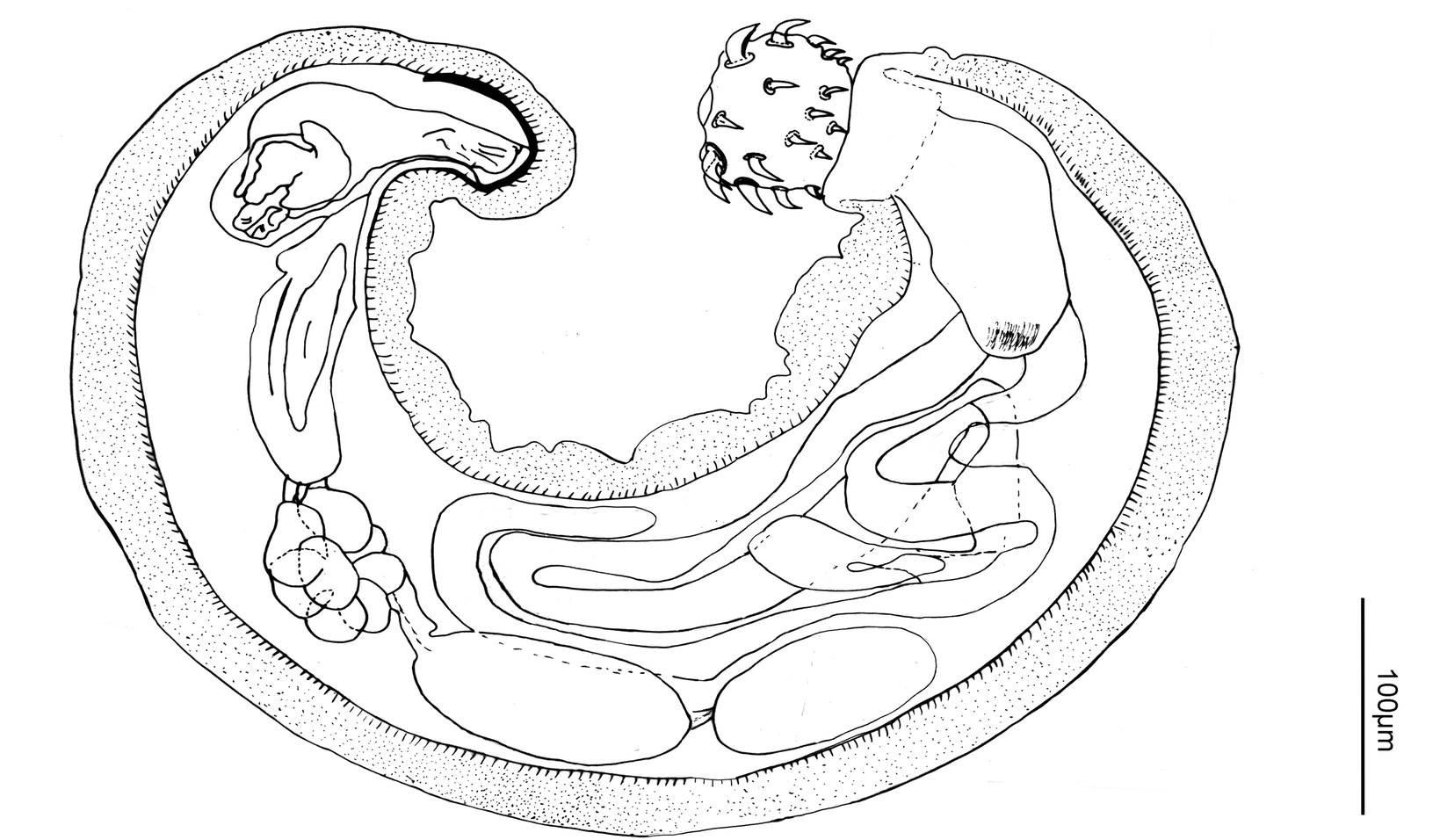
''Pachysentis'' is a genus in Acanthocephala (thorny-headed worms, also known as spiny-headed worms) that parasitize primates and carnivorans. They are distributed across Africa, the Middle East, and the Americas. ''Pachysentis'' species attach themselves to the inner lining of the gastrointestinal tract of their hosts using their hook-covered proboscis. Their life cycle includes an egg stage found in host feces, a cystacanth (larval) stage in an intermediate host such as the Egyptian cobra, and an adult stage where cystacanths mature in the intestines of the host. This genus appears identical to the closely related '' Oncicola'' apart from a greater number of hooks on the proboscis. There are eleven species assigned to this genus, although ''P. septemserialis'' is of uncertain taxonomic status. The female worms range from long and wide in ''P. lauroi'' to long and wide in ''P. dollfusi''. Virtually all of the length is the trunk, with a short proboscis. There is pronounced ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proboscis
A proboscis () is an elongated appendage from the head of an animal, either a vertebrate or an invertebrate. In invertebrates, the term usually refers to tubular arthropod mouthparts, mouthparts used for feeding and sucking. In vertebrates, a proboscis is an elongated nose or snout. Etymology First attested in English in 1609 from Latin , the latinisation (literature), latinisation of the Ancient Greek (), which comes from () 'forth, forward, before' + (), 'to feed, to nourish'. The plural as derived from the Greek is , but in English the plural form ''proboscises'' occurs frequently. Invertebrates The most common usage is to refer to the tubular feeding and sucking organ of certain invertebrates such as insects (e.g., Insect mouthparts#Proboscis, moths, butterflies, and mosquitoes), worms (including Acanthocephala, Nemertea, proboscis worms) and gastropod molluscs. Acanthocephala The Acanthocephala, the thorny-headed worms or spiny-headed worms, are characterized by the pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
28S Ribosomal RNA
28S ribosomal RNA is the structural ribosomal RNA (rRNA) for the large subunit (LSU) of eukaryotic cytoplasmic ribosomes, and thus one of the basic components of all eukaryotic cells. It has a size of 25S in plants and 28S in mammals, hence the alias of 25S–28S rRNA. Combined with 5.8S rRNA to the 5' side, it is the eukaryotic nuclear homologue of the prokaryotic 23S and mitochondrial 16S ribosomal RNAs. Use in phylogeny The genes coding for 28S rRNA are referred to as 28S rDNA. The comparison of the sequences from these genes are sometimes used in molecular analysis to construct phylogenetic trees, for example in protists, fungi, insects, arachnids, tardigrades, and vertebrates. Structure The 28S rRNA is typically 4000–5000 nt long. Some eukaryotes cleave 28S rRNA into two parts before assembling both into the ribosome, a phenomenon termed the "hidden break". Databases Several databases provide alignments and annotations of LSU rRNA sequences for compar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Göttingen
Göttingen (, ; ; ) is a college town, university city in Lower Saxony, central Germany, the Capital (political), capital of Göttingen (district), the eponymous district. The River Leine runs through it. According to the 2022 German census, the population of Göttingen was 124,548. Overview The origins of Göttingen lay in a village called ''Gutingi, ''first mentioned in a document in 953 AD. The city was founded northwest of this village, between 1150 and 1200 AD, and adopted its name. In Middle Ages, medieval times the city was a member of the Hanseatic League and hence a wealthy town. Today, Göttingen is famous for its old university (''Georgia Augusta'', or University of Göttingen, "Georg-August-Universität"), which was founded in 1734 (first classes in 1737) and became the most visited university of Europe. In 1837, seven professors protested against the absolute sovereignty of the House of Hanover, kings of Kingdom of Hanover, Hanover; they lost their positions, but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cement Gland
Cement glands are small organs found in Acanthocephala that are used to temporarily close the posterior end of the female after copulation. Cement glands are also mucus-secreting organs that can attach embryos or larvae to a solid substrate. These can be found in frogs such as those in the genus ''Xenopus ''Xenopus'' () (Gk., ξενος, ''xenos'' = strange, πους, ''pous'' = foot, commonly known as the clawed frog) is a genus of highly aquatic frogs native to sub-Saharan Africa. Twenty species are currently described with ...'', fish such as the Mexican tetra, and crustaceans. References Animal anatomy {{Animal-anatomy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gigantorhynchus Echinodiscus
''Gigantorhynchus'' is a genus of Acanthocephala (thorny-headed worms, also known as spiny-headed worms) that parasitize marsupials, anteaters, and possibly baboons by attaching themselves to the intestines using their hook-covered proboscis. Their life cycle includes an egg stage found in host feces, a cystacanth (larval) stage in an intermediate host such as termites, and an adult stage where cystacanths mature in the intestines of the host. This genus is characterized by a cylindrical proboscis with a crown of robust hooks at the apex followed by numerous small hooks on the rest of the proboscis, a long body with pseudosegmentation, filiform lemnisci, and ellipsoid testes. The largest known specimen is the female ''G. ortizi'' with a length of around and a width of . Genetic analysis on one species of ''Gigantorhynchus'' places it with the related genus ''Mediorhynchus'' in the family Gigantorhynchidae. Six species in this genus are distributed across Central and South ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mediorhynchus
''Mediorhynchus'' is a genus of small parasitic spiny-headed (or thorny-headed) worms. Phylogenetic analysis has been conducted on two known species of ''Mediorhynchus'' and confirmed the placement along with the related genus Gigantorhynchus in the family Gigantorhynchida. The distinguishing features of this order among archiacanthocephalans is a divided proboscis (specifically, the presence of a "teloboscis" which is the posterior third of a proboscis). This genus contains fifty-eight species that are distributed globally. These worms exclusively parasitize birds by attaching themselves around the cloaca using their hook-covered proboscis. The bird hosts are of different orders. Taxonomy ''Mediorhynchus'' is monophyletic based on phylogenetic analysis. Description Species can be identified primarily morphologically by the arrangement of hooks of the proboscis. The presence of a divided proboscis (specifically, the presence of a "teloboscis" which is the posterior third of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gigantorhynchida
Gigantorhynchida is an order containing a single family, Gigantorhynchidae of Acanthocephala (thorny-headed worms, also known as spiny-headed worms) that parasitize vertebrates by attaching themselves to the intestinal wall of their host. There are over 60 species classified into three genera in Gigantorhynchida '' Gigantorhynchus'', '' Intraproboscis'', and '' Mediorhynchus''. Taxonomy Phylogenetically, the family Gigantorhynchidae is sister to the family Moniliformidae, represented by sequences of ''Moniliformis Moniliformis'' that form a supported monophyletic group. The group formed by Gigantorhynchidae and Moniliformidae suggest it to be a sister to the group formed by sequences of ''Macracanthorhynchus ingens'' and ''Oncicola venezuelensis'' A new taxonomic analysis has been performed. Genera Gigantorhynchida contains three genera. Gigantorhynchus The genus ''Gigantorhynchus'' contains six species with ''G. echinodiscus'' as the type species. It was described by Hama ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moniliformidae
Moniliformidae is a family of parasitic spiny-headed (or thorny-headed) worms. It is the only family in the Moniliformida order and contains three genera: ''Australiformis'' containing a single species, ''Moniliformis'' containing eighteen species and ''Promoniliformis'' containing a single species. Genetic analysis have determined that the clade is monophyletic despite being distributed globally. These worms primarily parasitize mammals, including humans in the case of ''Moniliformis moniliformis'', and occasionally birds by attaching themselves into the intestinal wall using their hook-covered proboscis. The intermediate hosts are mostly cockroaches. The distinguishing features of this order among archiacanthocephalans is the presence of a cylindrical proboscis with long rows of hooks with posteriorly directed roots and proboscis retractor muscles that pierce both the posterior and ventral end or just posterior end of the receptacle. Infestation with Monoliformida species can c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |