|
Mueang Chaliang
Chaliang (, ) or Sawankhalok, later known as Si Satchanalai, was a political entity in the upper Chao Phraya Valley in central Thailand. It was founded in the early 600s by uniting four regional chiefdoms, with Haritvanlee or Chaliang () as the center, and became part of the Dvaravati's Lavo. In 1001, Chaliang was referred to as an independent kingdom ''Chéng Liáng'' in the Chinese text Song Shi. The term ''San-lo'' () mentioned in Lingwai Daida in 1178 plausibly referred to Chaliang's new center, Sawankhalok. After Haripuñjaya and Suphannabhum reclaimed Lavo from Angkor in 1052, Lavo's king, Phra Narai, moved the capital to Ayodhya in the 1080s and left the throne at Lavapura. The Mon- Tai dynasty of Chaliang took over and moved the seat southward to Lavo's former capital Lavapura; Chaliang then again became Lavapura's northern fortress. However, this dynasty later lost Lavapura to Angkor following the Angkorian influence-expanding campaign to the Menam Valley in 11 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Si Satchanalai Historical Park
The Si Satchanalai Historical Park () is a historical park in Si Satchanalai district, Sukhothai Province, northern Thailand. The park covers the ruins of Si Satchanalai and Chaliang. Si Satchanalai, which literally means "City of good people", was founded in 1250 as the second center of the Sukhothai Kingdom and as a residence of the crown prince in the 13th and 14th centuries. The city was rectangular in shape. In the 16th century, a 5-metre high wall with an upstream moat was built to fend off the growing Burmese attacks. The location of the town was facilitated by two neighboring dominant hills. The park is maintained by the Fine Arts Department of Thailand with help from UNESCO, which has declared it a World Heritage Site together with the associated historic parks in Kamphaengphet and Sukhothai. Similar to Sukhothai Historical Park, Si Satchanalai Historical Park attracts thousands of visitors each year, who marvel at the ancient Buddha figures, palace buildings and ruin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
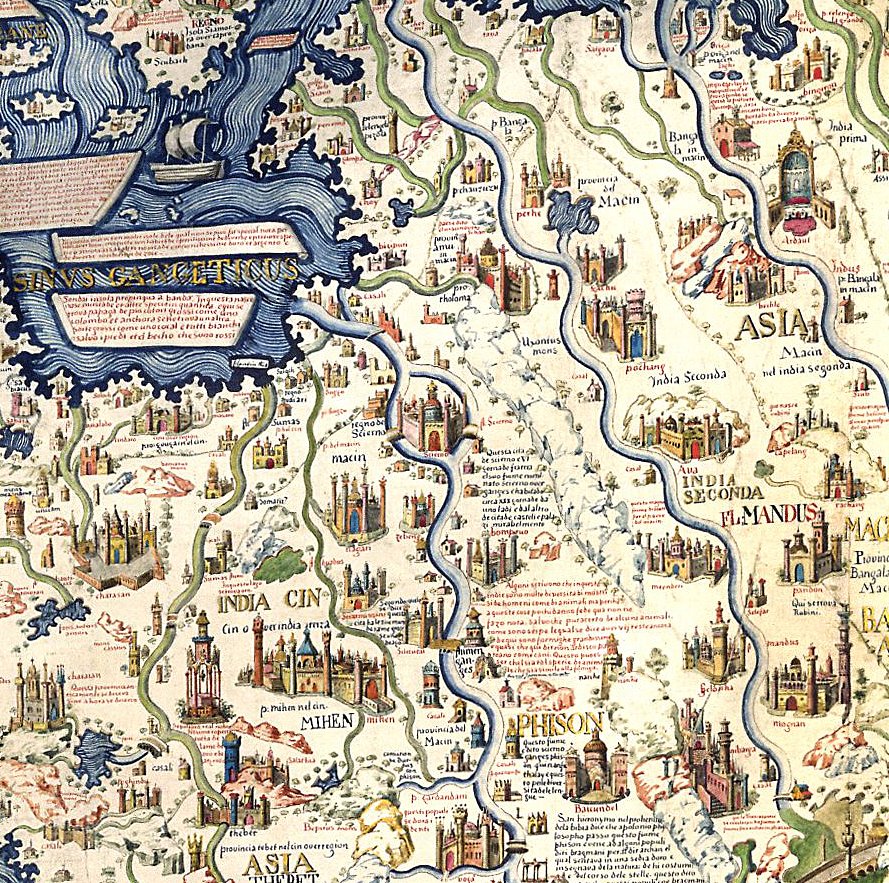
Dvaravati
Dvaravati () was a medieval Mon political principality from the 6th century to the 11th century, located in the region now known as central Thailand, and was speculated to be a succeeding state of Lang-chia or Lang-ya-hsiu (). It was described by Chinese pilgrims in the middle of the 7th century as a Buddhist kingdom named ''To-lo-po-ti'' situated to the west of Isanapura (Cambodia), to the east of Sri Ksetra (Burma), and adjoined Pan Pan in the South. Its northern border met ''Jiā Luó Shě Fú'' (), which was speculated to be either ''Kalasapura'', situated along the coast of the Bay of Bengal somewhere between Tavoy and Rangoon, or Canasapura in modern northeast Thailand. Dvaravati sent the first embassy to the Chinese court around 605–616, and then in 756. Text: Dvaravati also refers to a culture, an art style, and a disparate conglomeration of principalities of Mon people. The Mon migrants as maritime traders might have brought the Dvaravati Civilization to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Language
English is a West Germanic language that developed in early medieval England and has since become a English as a lingua franca, global lingua franca. The namesake of the language is the Angles (tribe), Angles, one of the Germanic peoples that Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain, migrated to Britain after its End of Roman rule in Britain, Roman occupiers left. English is the list of languages by total number of speakers, most spoken language in the world, primarily due to the global influences of the former British Empire (succeeded by the Commonwealth of Nations) and the United States. English is the list of languages by number of native speakers, third-most spoken native language, after Mandarin Chinese and Spanish language, Spanish; it is also the most widely learned second language in the world, with more second-language speakers than native speakers. English is either the official language or one of the official languages in list of countries and territories where English ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nam Ou
The Nam Ou (Lao language, Laotian: ນ້ຳອູ , Literal translation, literally: "rice bowl river") is one of the most important rivers of Laos. It runs 448 km from Phongsaly Province to Luang Prabang Province. The river rises in Muang Ou Nua near the Lao-Chinese border, and traverses the northern Laos mountains and gorges until meeting the Mekong River in Ban Pak Ou. Along with the Mekong, the Nam Ou is the only natural channel suitable for large-draft ship transport, boat transportation. The Nam Ou is one of the 12 principal tributaries of the Mekong River. The river has a total area of nearly 26,000 km2. Near its confluence with the Mekong are the Pak Ou Caves, famous for their Buddharupa, Buddha statues. The river is also surrounded by limestone karts, forests, and valleys. The river supports Lao rice cultivation. The Nam Ou placed in the top 80th percentile for river health according to the Mekong River Commission's aquatic health index. Ecology The Nam O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muang Sua
Muang Sua (, ) was the name of Luang Phrabang following its conquest in 698 by a Tai peoples, Tai/Lao prince, Khun Lo, who seized his opportunity when the king of Kingdom of Nanzhao, Nanzhao was engaged elsewhere. Khun Lo had been awarded the town by his father, Khun Borom, who is associated with the Lao people, Lao legend of the creation of the world, which the Lao share with the Shan people, Shan and other peoples of the region. Khun Lo established a dynasty whose fifteen rulers reigned over an independent Muang Sua for the better part of a century. History Muang Sua, nowadays known as Luang Prabang, was named in 698 following its conquest, by the Lao prince Khun Lo, who awarded the town to his father Khun Borom, the legendary progenitor of the Lao race and it is the first laos kingdom. In the second half of the eighth century, Nanzhao intervened frequently in the affairs of the principalities of the middle Mekong Valley, resulting in the occupation of Muang Sua in 709. Nanzha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xiān
Xiān ( zh, 暹) or Siam () was a confederation of maritime-oriented port polities along the present Bay of Bangkok, including Ayutthaya Kingdom#Pre-Ayutthaya cities, Ayodhya, Suphannabhum, and Phip Phli Kingdom, Phip Phli, as well as Nakhon Si Thammarat Kingdom, Nakhon Si Thammarat (Ligor), which became Siam in the late 13th century. Previous studies suggested that ''Xiān'' in Chinese dynasty records only referred to Sukhothai Kingdom, Sukhothai, but this presupposition has recently been rebutted. Xiān was formed from city-states on the west Chao Phraya River, Chao Phraya plain after the decline of Dvaravati in the 11th century. In 1178, the region was mentioned in the term ''San-lo '', as recorded in the Chinese Lingwai Daida, in which Thai scholars suggest it was plausibly referred to Mueang Chaliang, Chaliang's new center, Si Satchanalai Historical Park, Sawankhalok. Xiān or Siam, which was also recorded as Suphannabhum, Suphan Buri and Nakhon Si Thammarat Kingdom, Nakho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Intermarriage
Royal intermarriage is the practice of members of ruling dynasties marrying into other reigning families. It was more commonly done in the past as part of strategic diplomacy for national interest. Although sometimes enforced by legal requirement on persons of royal birth, more often it has been a matter of political policy or tradition in monarchies. In Europe, the practice was most prevalent from the medieval era until the outbreak of World War I, but evidence of intermarriage between royal dynasties in other parts of the world can be found as far back as the Bronze Age. Monarchs were often in pursuit of national and international aggrandisement on behalf of themselves and their dynasties, thus bonds of kinship tended to promote or restrain aggression.Bucholz, p.228 Marriage between dynasties could serve to initiate, reinforce or guarantee peace between nations. Alternatively, kinship by marriage could secure an alliance between two dynasties which sought to reduce the sense ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lopburi
Lopburi (, , ) is the capital city of Lopburi Province in Thailand. It is about northeast of Bangkok. It has a population of 58,000. The town ('' thesaban mueang'') covers the whole ''tambon'' Tha Hin and parts of Thale Chup Son of Mueang Lopburi District, a total area of 6.85 km2. History Chronology The city has a history dating back to the Dvaravati period more than 1,000 years ago.Higham, C., 2014, ''Early Mainland south-east Asia'', Bangkok: River Books Co., Ltd., According to the ''Northern Chronicles,'' Lavo was founded by Phraya Kalavarnadishraj, who came from Takkasila in 648 CE. According to Thai records, Phraya Kakabatr from Takkasila (it is assumed that the city was Tak or Nakhon Chai Si) set the new era, Chula Sakarat in 638 CE, which was the era used by the Siamese and the Burmese until the 19th century. His son, Phraya Kalavarnadishraj founded the city a decade later. Lopburi, or Lavapura as it then was, was under the rule of the rising Angk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mon People
The Mon (; Thai Mon: ဂကူမည်; , ; , ) are an ethnic group who inhabit Lower Myanmar's Mon State, Kayin State, Kayah State, Tanintharyi Region, Bago Region, the Irrawaddy Delta, and several areas in Thailand (mostly in Pathum Thani province, Phra Pradaeng and Nong Ya Plong). The native language is Mon, which belongs to the Monic branch of the Austroasiatic language family and shares a common origin with the Nyah Kur language, which is spoken by the people of the same name that live in Northeastern Thailand. A number of languages in Mainland Southeast Asia are influenced by the Mon language, which is also in turn influenced by those languages. The Mon were one of the earliest to reside in Southeast Asia, and were responsible for the spread of Theravada Buddhism in Mainland Southeast Asia. The civilizations founded by the Mon were some of the earliest in Thailand as well as Myanmar and Laos. The Mon are regarded as a large exporter of Southeast Asian cultur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phra Nakhon Si Ayutthaya (city)
Phra Nakhon Si Ayutthaya (, ), or locally and simply Ayutthaya is the capital of Phra Nakhon Si Ayutthaya province of Thailand. Ayutthaya was the capital of the Ayutthaya Kingdom. Located on an island at the confluence of the Chao Phraya River, Chao Phraya and Pa Sak River, Pa Sak rivers, Ayutthaya is the birthplace of the founder of Bangkok, Rama I, King Rama I. The ruins of the old city are preserved in the Ayutthaya Historical Park. Etymology The name ''Ayutthaya'' is derived from Sanskrit अयोध्य - Ayodhya (Ramayana), Ayodhya and is from the Thai national epic ''Ramakien''; (from Khmer language, Khmer: ''preah'' ព្រះ ) is a prefix for a noun concerning a royal person, and (from Pali: ''nagara'') designates an important or capital city. History Prior to Ayutthaya's traditional founding date, archaeological and written evidence has revealed that Ayutthaya may have existed as early as the late 13th century as a water-borne port town. Further evidence o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
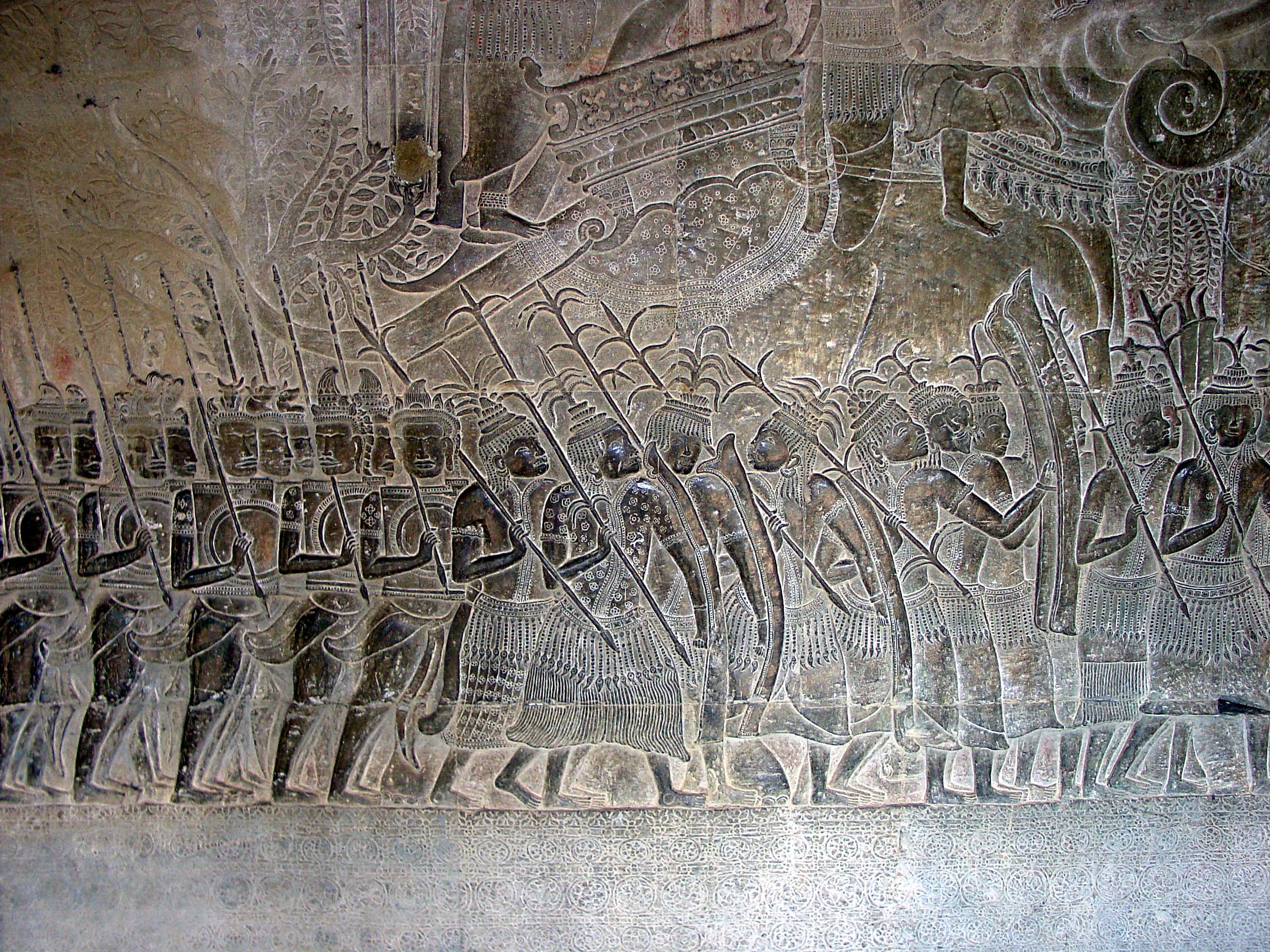
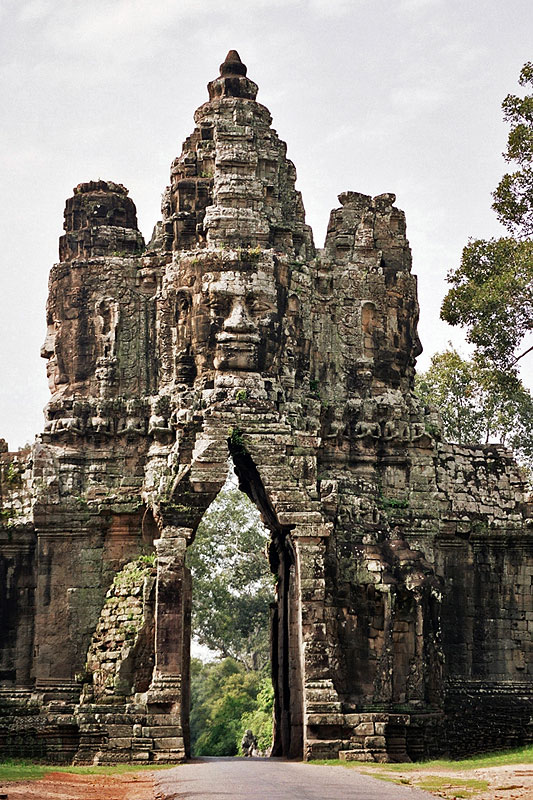
Angkor
Angkor ( , 'capital city'), also known as Yasodharapura (; ),Headly, Robert K.; Chhor, Kylin; Lim, Lam Kheng; Kheang, Lim Hak; Chun, Chen. 1977. ''Cambodian-English Dictionary''. Bureau of Special Research in Modern Languages. The Catholic University of America Press. Washington, D.C. Chuon Nath Khmer Dictionary (1966, Buddhist Institute, Phnom Penh). was the capital city of the Khmer Empire, located in present-day Cambodia. The city and empire flourished from approximately the 9th to the 15th centuries. The city houses the Angkor Wat, one of Cambodia's most popular tourist attractions. The name ''Angkor'' is derived from ''nokor'' (), a Khmer language, Khmer word meaning "kingdom" which in turn derived from Sanskrit ''nagara'' (), meaning "city". The Angkorian period began in AD 802, when the Khmer people, Khmer Hinduism, Hindu monarch Jayavarman II declared himself a "universal monarch" and "Devaraja, god-king", and lasted until the late 14th century, first falling under Ayut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suphannabhum
Suphannabhum or Suvarnabhumi; later known as Suphan Buri () was a Siamese city-state, that emerged in the early "Siam proper" which stretched from present-day west central Thailand to the north of the Kra Isthmus, with key historical sites at Mueang Uthong, Uthong, Nakhon Pathom, Suphan Buri, and . The kingdom is referred to as ''Xiān'' in the Chinese records since 1349, but according to the archaeological evidence in Suphan Buri, it was speculated to have emerged around the mid-12th century. However, a calculation made by Borihan Thepthani based on the information provided in the says that the city of Suphan Buri was founded in 877 and became a free city-state after Nakhon Pathom of Kamalanka fell to Phetchaburi in 913. Suphannabhum became the center of ''Xiān'', succeeding Phip Phli, no later than 1349, when ''Xiān'' was defeated by ''Luó hú'' (Lavo Kingdom, Lavo) and the tribute sent to China under the name of ''Xiānluó hú'' (Siam-Lavo or Ayutthaya Kingdom) was led by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |