|
Mohammad Bagher Sabzevari
Mohammad Bagher Sabzevari ( fa, محمدباقر سبزواری) known as Mohaghegh Sabzevari ( fa, محقق سبزواری) (born in 1608, died on 19 April 1679) was an Iranian Faqih and Shiite scholar from the 11th century AH, Shaykh al-Islām and the Imam of Friday Prayer of Isfahan. ''Mohaghegh Sabzevari'' was born in Naman village around Sabzevar and settled in Isfahan and was raised in the ''jurisprudence philosophy school of Isfahan''. He was a principled Islamic jurist, theologian and sage. He had a friendly relationship with Mullah Mohsen Fayz Kashani. In rational sciences he was one of the students of Mir Fendereski and in traditional sciences he was one of the students of ''Mullah Hassan Ali Shoushtari'' and some other great masters of the time. Life ''Mohammad Bagher Sabzevari'' was born in the village of Naman around the city of Sabzevar, Razavi Khorasan Province in 1608 and is the son of ''Mohammad Mo'men al-Sharif al-Sabzevari'' (died around 1619) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ayatollah
Ayatollah ( ; fa, آیتالله, āyatollāh) is an Title of honor, honorific title for high-ranking Twelver Shia clergy in Iran and Iraq that came into widespread usage in the 20th century. Etymology The title is originally derived from Arabic word pre-modified with the definite article and Grammatical modifier#Premodifiers and postmodifiers, post-modified with the word ''Allah'', making ( ar, آية الله). The combination has been translated to English as 'Sign of God', 'Divine Sign' or 'Reflection of God'. It is a frequently-used term in Quran, but its usage in this context is presumably a particular reference to the verse "We shall show them Our signs on the horizons and in their own selves", while it has been also used to refer to The Twelve Imams by Shias. Variants used are ( ar, آية الله في الأنعام, lit=Sign of God among mankind), ( ar, آية الله في العالمَین, lit=Sign of God in the two worlds, Dual (grammatical number), du ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mohsen Fayz Kashani
''Mul·lā'' "al-Muḥsin" "al-Fayḍ" al-Kāshānī (1598–1680; fa, ملا محسن فیض کاشانی) was an Iranian Twelver Shi'i Muslim, mystic, poet, philosopher, and muhaddith (died ''c''. 1680 ᴄᴇ). Life Mohsen Fayz Kashani was born in Kashan to a scholarly family renowned for its learning, Fayz started his education his father, Shah Morteza. His father owned a rich library which benefited Fayz. When he reached the age of twenty, he travelled to Isfahan for further study. However, after a year in Isfahan, he moved to Shiraz to study Hadith and Fiq (Jurisprudence) under Majid Bahrani, one of the leading Shi'ite scholars of his time. Bahrani died a few months later, and Fayz returned to Isfahan where he joined the circles of great scholar Shaikh Bahai and studied philosophy under Mir Damad. After performing the hajj, he stayed a short time before returning to Persia. Upon his return he found a new master, Qom Molla Sadra who taught him in different discipl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hadith
Ḥadīth ( or ; ar, حديث, , , , , , , literally "talk" or "discourse") or Athar ( ar, أثر, , literally "remnant"/"effect") refers to what the majority of Muslims believe to be a record of the words, actions, and the silent approval of the Islamic prophet Muhammad as transmitted through chains of narrators. In other words, the ḥadīth are transmitted reports attributed to what Muhammad said and did. Hadith have been called by some as "the backbone" of Islamic civilization, J.A.C. Brown, ''Misquoting Muhammad'', 2014: p.6 and for many the authority of hadith as a source for religious law and moral guidance ranks second only to that of the Quran (which Muslims hold to be the word of God revealed to Muhammad). Most Muslims believe that scriptural authority for hadith comes from the Quran, which enjoins Muslims to emulate Muhammad and obey his judgements (in verses such as , ). While the number of verses pertaining to law in the Quran is relatively few, hadith are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tabaghat Aa'lam Al-Shia
The ''Tabaghat Aa'lam Al-Shia'' ( ar, طبقات أعلام الشیعة) is a twenty-volume encyclopedia of Shia scholars from the tenth to the twentieth century, written by Aqa Bozorg Tehrani. It is divided into eleven chapters, each dedicated to a century. The name of each chapter was inspired by the number of centuries of the occultation of Mahdi The Mahdi ( ar, ٱلْمَهْدِيّ, al-Mahdī, lit=the Guided) is a messianic figure in Islamic eschatology who is believed to appear at the end of times to rid the world of evil and injustice. He is said to be a descendant of Muhammad w .... References http://www.tahoordanesh.com/page.php?pid=10562 Shia Islam Shia bibliography Books of Shia Rijal {{shia-stub en:Tabaghat Aa'lam Al-Shia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baha' Al-din Al-'Amili
Bahāʾ al‐Dīn Muḥammad ibn Ḥusayn al‐ʿĀmilī (also known as Sheikh Baha'i, fa, شیخ بهایی) (18 February 1547 – 1 September 1621) was an Iranian ArabEncyclopedia of Arabic Literature'. Taylor & Francis; 1998. . p. 85. Shia Islamic scholar, philosopher, architect, mathematician, astronomer, and poet who lived in the late 16th and early 17th centuries in Safavid Iran. He was born in Baalbek, Ottoman Syria (present-day Lebanon) but immigrated in his childhood to Safavid Iran with the rest of his family. He was one of the earliest astronomers in the Islamic world to suggest the possibility of the Earth's movement prior to the spread of the Copernican theory. He is considered one of the main co-founders of Isfahan School of Islamic Philosophy. In later years he became one of the teachers of Mulla Sadra. He wrote over 100 treatises and books in different topics, in Arabic and Persian. A number of architectural and engineering designs are attributed to him, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Islamic Manuscript, Namaz Adineh, Muhammad Baqir Al-Sabzevari- 17th Century
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God (or ''Allah'') as it was revealed to Muhammad, the main and final Islamic prophet.Peters, F. E. 2009. "Allāh." In , edited by J. L. Esposito. Oxford: Oxford University Press. . (See alsoquick reference) " e Muslims' understanding of Allāh is based...on the Qurʿān's public witness. Allāh is Unique, the Creator, Sovereign, and Judge of mankind. It is Allāh who directs the universe through his direct action on nature and who has guided human history through his prophets, Abraham, with whom he made his covenant, Moses/Moosa, Jesus/Eesa, and Muḥammad, through all of whom he founded his chosen communities, the 'Peoples of the Book.'" It is the world's second-largest religion behind Christianity, with its followers ranging between 1-1.8 billion globally, or around a quarter of the world's pop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agha Hossein Khansari
Agha Hossein Khansari ( fa, آقا حسین خوانساری), full name Hossein ibn Jamal al-Din Mohammad Khansari ( fa, حسین بن جمال الدین محمد خوانساری), known as Mohaghegh Khansari ( fa, محقق خوانساری) and also known as "''Master of all in all''" ( ar, استاد الکلّ فی الکلّ), who was nicknamed "''the disciple of mankind''" ( ar, تلمیذ البشر) because of the many masters he acquired knowledge in their presence, was one of the great Iranian jurists of ''Isfahan jurisprudential school'' (born in 1607 in Khansar, died in 1687 in Isfahan) in the 11th century AH, who was also engaged in philosophy and wisdom. He was one of the high level scholars during the reign of Sultan Suleiman of the Safavid dynasty and after the death of ''Mir Seyyed Mohammad Masoom'' in 1683, he became the Shaykh al-Islām of Isfahan. His children are ''Jamaluddin Mohammad'' known as ''Agha Jamal Khansari'' and ''Raziauddin Mohammad'' kn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Safi Of Persia
Sam Mirza ( fa, سام میرزا) (161112 May 1642), better known by his dynastic name of Shah Safi ( fa, شاه صفی), was the sixth Safavid shah (king) of Iran, ruling from 1629 to 1642. Early life Safi was given the name Sam Mirza when he was born. He was the son of Mohammad Baqer Mirza, the eldest son of Shah Abbas I, and Dilaram Khanum, a Georgian wife. In 1615, Abbas had Mohammed Baqer killed, fearing he was plotting against his life. Over the next few years, the suspicious Abbas killed or blinded his other sons, leaving his grandson Safi heir to the throne. Reign Safi was crowned on 28 January 1629 at the age of eighteen. He ruthlessly eliminated anyone he regarded as a threat to his power, executing almost all the Safavid royal princes as well as leading courtiers and generals. He paid little attention to the business of government and had no cultural or intellectual interests (he had never learned to read or write properly), preferring to spend his time dri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khalifeh Soltan
Sayyed Ala al-Din Hoseyn ( fa, سید علاء الدین حسین) (c.1592 5March 1654), better known as Khalifeh Soltan (), and also known as Soltan al-Ulama (), was an Iranian statesman and cleric, who served as the grand vizier of the Safavid king ('' shah'') Abbas I (r. 1588–1629), the latter's grandson Safi (r. 1629–1642), and Abbas II (r. 1642–1666). A member of a prominent Sayyid family with origins in the royal Marashi family of Mazandaran, Khalifeh Soltan was a well-educated man of letters, who played an important role in the Iranian clergy affairs, and also later in the Safavid administration, when he was appointed as grand vizier in 1623/4. He was, however, in 1632, disgraced and exiled by the ruthless newly-crowned shah Safi. Later, in 1645, Khalifeh Soltan was re-appointed as grand vizier by the latter's son and successor, Abbas II, whom he became a close companion of, and gained considerable influence. Khalifeh Soltan later died in 5 March 1654 in his an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molla Abdollah School
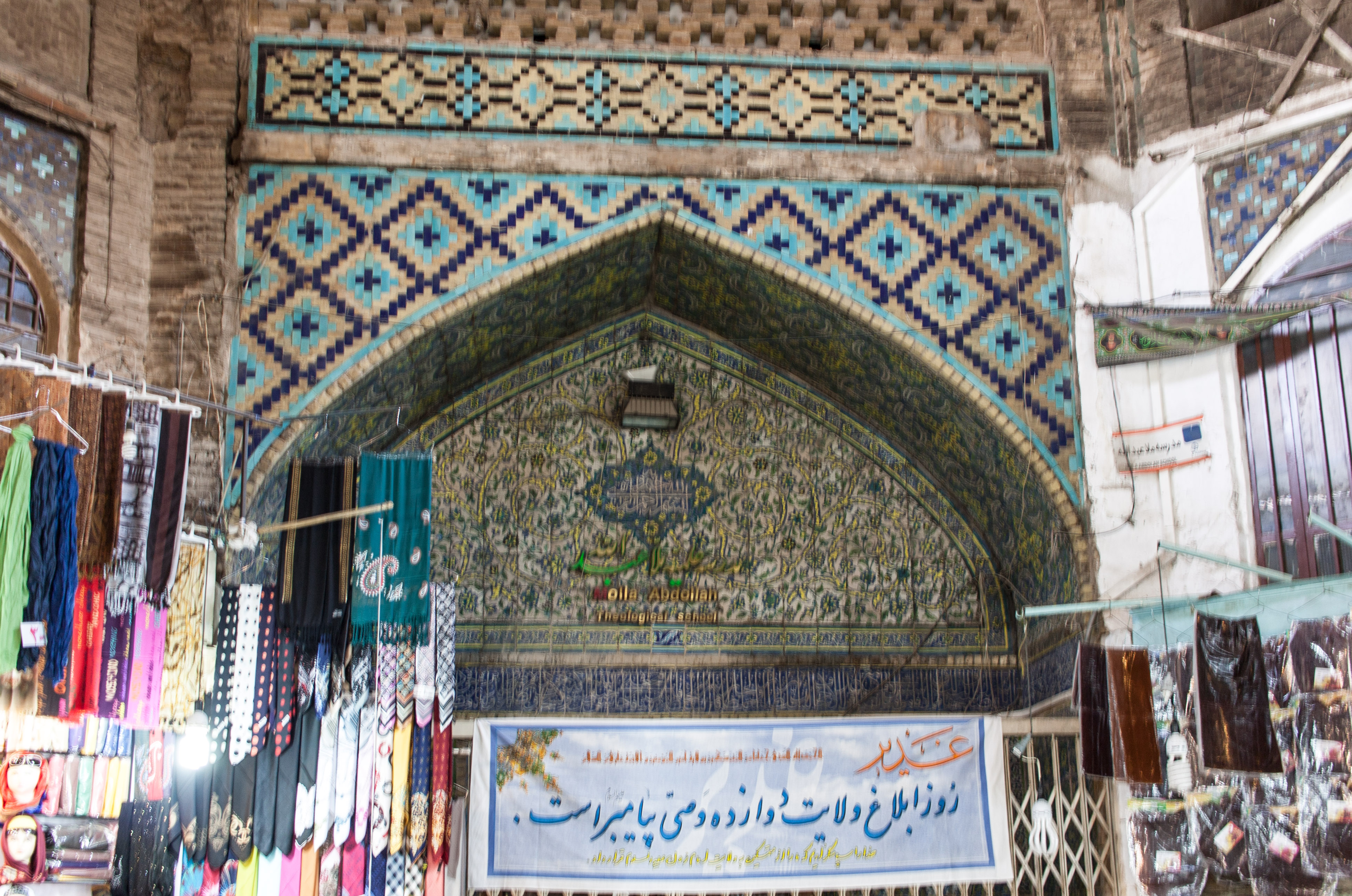 Molla Abdollah School is located in the bazaar of Isfahan, Iran, and was a premises for prayer and theological studies by clergy.
Schools in Isfahan
{{Iran-school-stub ...
Molla Abdollah School is located in the bazaar of Isfahan, Iran, and was a premises for prayer and theological studies by clergy.
Schools in Isfahan
{{Iran-school-stub ...
[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shah Mosque (Isfahan)
The Shah Mosque ( fa, مسجد شاه) is a mosque located in Isfahan, Iran. It is located on the south side of Naghsh-e Jahan Square. It was built during the Safavid dynasty under the order of Shah Abbas I of Persia. It is regarded as one of the masterpieces of Persian architecture in the Islamic era. The Royal Mosque is registered, along with the Naghsh-e Jahan Square, as a UNESCO World Heritage Site. Its construction began in 1611, and its splendour is mainly due to the beauty of its seven-colour mosaic tiles and calligraphic inscriptions. The mosque is depicted on the reverse of the Iranian 20,000 rials banknote. It was found damaged in 2022. History In 1598, when Shah Abbas decided to move the capital of his Persian empire from the northwestern city of Qazvin to the central city of Isfahan, he initiated what would become one of the greatest programmes in Persian history; the complete remaking of this ancient city. By choosing the central city of Isfahan, fertiliz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abbas II Of Persia
Abbas II (; born Soltan Mohammad Mirza; 30 August 1632 – 26 October 1666) was the seventh Shah of Safavid Iran, ruling from 1642 to 1666. As the eldest son of Safi and his Circassian wife, Anna Khanum, he inherited the throne when he was nine, and had to rely on a regency led by Saru Taqi, the erstwhile grand vizier of his father, to govern in his place. During the regency, Abbas received formal kingly education that until then, he had been denied. In 1645, at age fifteen, he was able to remove Saru Taqi from power, and after purging the bureaucracy ranks, asserted his authority over his court and began his absolute rule. Abbas II's reign was marked by peacefulness and progression. He intentionally avoided a war with the Ottoman Empire, and his relations with the Uzbeks in the east were friendly. He enhanced his reputation as a military commander by leading his army during the war with the Mughal Empire, and successfully recovering the city of Kandahar. On his behest, Ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)