|
Mayamata
Mamuni Mayan () is an ancient sage referenced in Tamil literature. He is featured in works of Sangam literature such as the Cilappatikaram, Manimekalai, and Civaka Cintamani, identified with the asura Mayasura of the Hindu epic Mahabharata. Mayan is regarded to be the founder of the Vastu Shastra. In Tamil tradition, Mayan is known as the progenitor of the original Veda, called Pranava Veda, and is credited with the authorship of the Mayamata Vastu Shastra as well as the ''Aintiram'' ('' Aindra'', a school of grammar connected with the Tolkappiyam). He is also credited with the authorship of the Surya Siddhanta.Translation of the Surya Siddhanta into English, by Bhāskarācārya, Bapu Deva Sastri, Lancelot Wilkinson, , , http://www.wilbourhall.org/pdfs/suryaEnglish.pdf See also *Mayasura *Kubera *Vishvakarma Vishvakarma or Vishvakarman (, ) is a craftsman deity and the divine architect of the devas in contemporary Hinduism. In the early texts, the craftsman deity was know ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vastu Shastra
Originating in ancient India, ''Vastu Shastra'' (, ' – literally "science of architecture") is a traditional Hindu system of architecture based on ancient texts that describe principles of design, layout, measurements, ground preparation, space arrangement, and spatial geometry. The designs aim to integrate architecture with nature, the relative functions of various parts of the structure, and ancient beliefs utilising geometric patterns ( yantra), symmetry, and directional alignments. Vastu Shastra are the textual part of ''Vastu Vidya'' – the broader knowledge about architecture and design theories from ancient India. Vastu Vidya is a collection of ideas and concepts, with or without the support of layout diagrams, that are not rigid. Rather, these ideas and concepts are models for the organisation of space and form within a building or collection of buildings, based on their functions in relation to each other, their usage and the overall fabric of the Vastu. Ancient ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
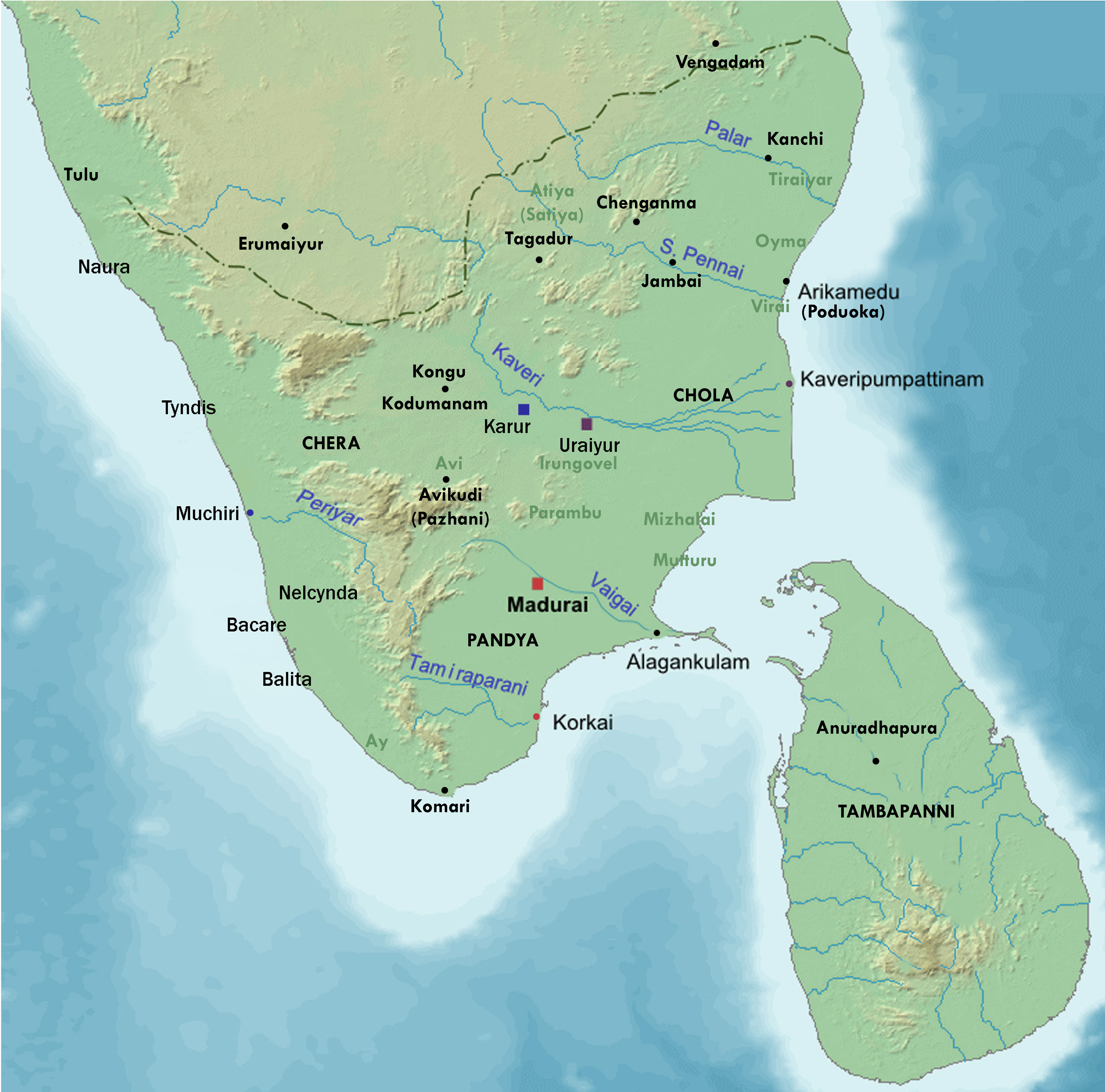
Tamil Literature
Tamil literature includes a collection of literary works that have come from a tradition spanning more than two thousand years. The oldest extant works show signs of maturity indicating an even longer period of evolution. Contributors to the Tamil literature are mainly from Tamil people from south India, including the land now comprising Tamil Nadu, Kerala, Sri Lankan Tamil people, Eelam Tamils from Sri Lanka, as well as the Tamil diaspora. The history of Tamil literature follows the history of Tamil Nadu, closely following the social, economical, political and cultural trends of various periods. The early Sangam literature, dated before 300 BCE, contain anthologies of various poets dealing with many aspects of life, including love, war, social values and religion.Akananuru (1, 15, 31, 55, 61, 65, 91, 97, 101, 115, 127, 187, 197, 201, 211, 233, 251, 265, 281, 311, 325, 331, 347, 349, 359, 393, 281, 295), Kurunthogai (11), and Natrinai (14, 75) are dated before 300 BCE. This was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sangam Literature
The Sangam literature (Tamil language, Tamil: சங்க இலக்கியம், ''caṅka ilakkiyam''), historically known as 'the poetry of the noble ones' (Tamil language, Tamil: சான்றோர் செய்யுள், ''Cāṉṟōr ceyyuḷ''), connotes the early classical Tamil literature and is the earliest known literature of South India. The Tamil tradition links it to Legendary Tamil Sangams, legendary literary gatherings around Madurai in the ancient Pandya dynasty, Pandya kingdom. It is generally accepted by most scholars that the historical Sangam literature era, also known as the Sangam period, spanned from 100 BCE to 250 CE, on the basis of linguistic, epigraphic, archaeological, numismatic and historical data; though some scholars give a broader range of 300 BCE to 300 CE. The Eighteen Greater Texts (Patiṉeṇmēlkaṇakku), along with the Tamil grammar work Tolkāppiyam, Tolkappiyam, are collectively considered as Sangam literature. These tex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silappathikaram
''Cilappatikāram'' ( IPA: ʧiləppət̪ikɑːrəm, ''lit.'' "the Tale of an Anklet"), also referred to as ''Silappathikaram'' or ''Silappatikaram'', is the earliest Tamil epic. It is a poem of 5,730 lines in almost entirely ''akaval'' (''aciriyam'') meter. The epic is a tragic love story of an ordinary couple, Kaṇṇaki and her husband Kōvalaṉ. The ''Cilappatikāram'' has more ancient roots in the Tamil bardic tradition, as Kannaki and other characters of the story are mentioned or alluded to in the Sangam literature such as in the '' Natṟiṇai'' and later texts such as the ''Kovalam Katai''. It is attributed to a prince-turned-jain-monk Iḷaṅkō Aṭikaḷ, and was probably composed in the 5th century CE (although estimates range from 2nd to 6th century CE). The ''Cilappatikāram'' is an ancient literary masterpiece. It is to the Tamil culture what the ''Iliad'' is to the Greek culture, states R. Parthasarathy. It blends the themes, mythologies and theological v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manimekalai
''Maṇimēkalai'' (, ), also spelled ''Manimekhalai'' or ''Manimekalai'', is a Tamil Buddhist epic composed by Kulavāṇikaṉ Seethalai Sataṉar probably somewhere between the 2nd century to the 6th century. It is an "anti-love story", a sequel to the "love story" in the earliest Tamil epic '' Cilappatikaram'', with some characters from it and their next generation. The epic consists of 4,861 lines in ''akaval'' meter, arranged in 30 cantos. The title ''Manimekalai'' is also the name of the daughter of Kovalan and Madhavi, who follows in her mother's footsteps as a dancer and a Buddhist nun. The epic tells her story. Her physical beauty and artistic achievements seduces the Chola prince Udayakumara. He pursues her. She, a nun of Mahayana Buddhism persuasion, feels a commitment to free herself from human ties. She rejects his advances, yet finds herself drawn to him. She hides, prays and seeks the help of her mother, her Buddhist teacher Aravana Adikal and angels. They ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asura
Asuras () are a class of beings in Indian religions, and later Persian and Turkic mythology. They are described as power-seeking beings related to the more benevolent Devas (also known as Suras) in Hinduism. In its Buddhist context, the word is translated as "titan" or " antigod". According to Hindu texts, the asuras are in constant fear of the devas. Asuras are described in Indian texts as powerful superhuman demigods with good or bad qualities. In early Vedic literature, the good Asuras are called '' Adityas'' and are led by Varuna, while the malevolent ones are called '' Danavas'' and are led by Vritra. In the earliest layer of Vedic texts, Agni, Indra and other gods are also called Asuras, in the sense of their being "lords" of their respective domains, knowledge and abilities. In later Vedic and post-Vedic texts, the benevolent gods are called ''Devas'', while malevolent Asuras compete against these Devas and are considered "enem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
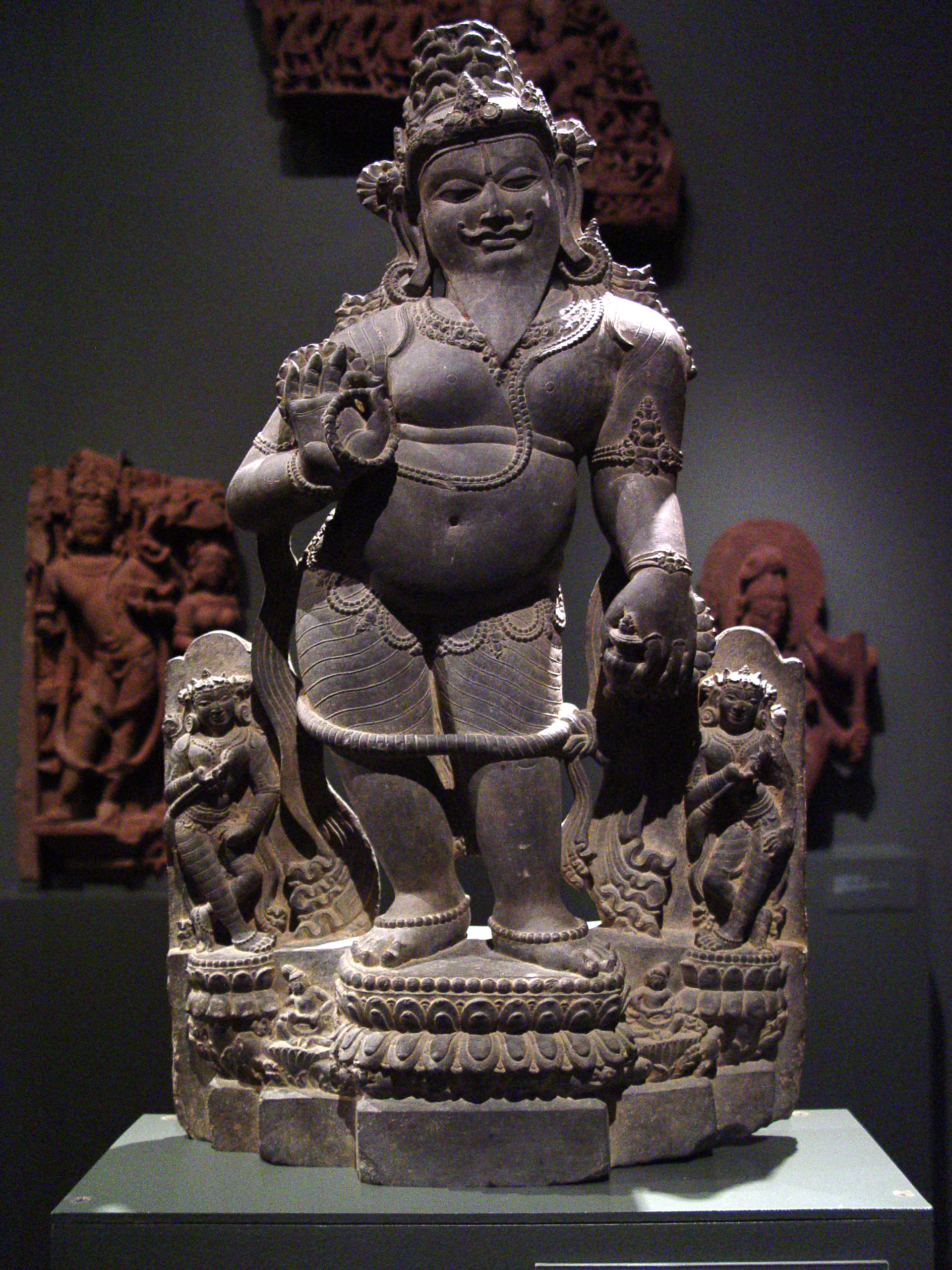
Mayasura
Maya () or Mayāsura () is a figure in Hindu history, described as the king of the Danavas, a race of beings descending from Kashyapa and his wife Danu. He is known for his architectural expertise, credited with creating the Mayasabha (Hall of Illusions) for the Pandavas and Tripura (Three cities) for the sons of Tarakasura. In the ''Ramayana'', he is mentioned as the father-in-law of Ravana. He is presented as an architect of Maya (the illusory material reality). In the Surya Siddhanta 1.02, Mayāsura is described as a Daitya who received divine astronomical knowledge from the Sun God sometime around the end of Satya Yuga. In the ''Mahabharata'' Mayasura is mentioned to be a son of the sage Kashyapa and his wife Danu. Mayasura had befriended a Nāga named Takshaka and lived with him in the area of Khandavaprastha along with his family and friends, but when the Pandavas came there after the partition of Hastinapura, Arjuna burnt the entire forest, forcing Takshaka to flee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hinduism
Hinduism () is an Hypernymy and hyponymy, umbrella term for a range of Indian religions, Indian List of religions and spiritual traditions#Indian religions, religious and spiritual traditions (Sampradaya, ''sampradaya''s) that are unified by adherence to the concept of ''dharma'', a Ṛta, cosmic order maintained by its followers through rituals and righteous living, as expounded in the Vedas. The word ''Hindu'' is an exonym, and while Hinduism has been called the oldest religion in the world, it has also been described by the modern term ''Sanātana Dharma'' () emphasizing its eternal nature. ''Vaidika Dharma'' () and ''Arya dharma'' are historical endonyms for Hinduism. Hinduism entails diverse systems of thought, marked by a range of shared Glossary of Hinduism terms, concepts that discuss God in Hinduism, theology, Hindu mythology, mythology, among other topics in Hindu texts, textual sources. Hindu texts have been classified into Śruti () and Smṛti (). The major Hin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mahabharata
The ''Mahābhārata'' ( ; , , ) is one of the two major Sanskrit Indian epic poetry, epics of ancient India revered as Smriti texts in Hinduism, the other being the ''Ramayana, Rāmāyaṇa''. It narrates the events and aftermath of the Kurukshetra War, a war of succession between two groups of princely cousins, the Kauravas and the Pandava, Pāṇḍavas. It also contains Hindu philosophy, philosophical and devotional material, such as a discussion of the four "goals of life" or ''puruṣārtha'' (12.161). Among the principal works and stories in the ''Mahābhārata'' are the ''Bhagavad Gita'', the story of Damayanti, the story of Shakuntala, the story of Pururava and Urvashi, the story of Savitri and Satyavan, the story of Kacha (sage), Kacha and Devayani, the story of Rishyasringa and an Ramopakhyana, abbreviated version of the ''Rāmāyaṇa'', often considered as works in their own right. Traditionally, the authorship of the ''Mahābhārata'' is attributed to Vyasa, Vy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aindra
The Aindra (of Indra) school of Sanskrit grammar is one of the eleven schools of Sanskrit grammar mentioned in Pāṇini's '' Ashtadhyayi''. It is named after Indra as a reference to Lord Indra, the king of deities in Hindu mythology. Arthur Coke Burnell, a renowned orientologist, in his 1875 book, ''"On the Aindra school of Sanskrit grammars",'' describes this school. Burnell believed that most non-Pāṇinian systems of Sanskrit grammar were traceable to this school of grammar, believed to be the oldest and reputed to be founded by Indra himself. Aindra, Katantra schools and the Tolkappiyam Burnell's search for the Aindra school took him to Southern India where he came across the Tamil grammatical work '' Tolkappiyam''. A preface of this work, written during the twelfth century CE by Ilampuranar describes the work as ''aindiram nirainda Tolkappiyam'' ncorrect quote/sup>('comprising Aindra'). Burnell posits that this is an allusion to the pre-Pāṇinian Aindra school of grammar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tolkāppiyam
''Tolkāppiyam'', also romanised as ''Tholkaappiyam'' ( , ''lit.'' "ancient poem"), is the oldest extant Tamil grammar text and the oldest extant long work of Tamil literature. It is the earliest Tamil text mentioning Gods, perhaps linked to Tamil deities. There is no firm evidence to assign the authorship of this treatise to any one author. There is a tradition of belief that it was written by a single author named Tolkappiyar, a disciple of Tamil sage Agathiyar. The surviving manuscripts of the ''Tolkappiyam'' consists of three books (), each with nine chapters (), with a cumulative total of 1,610 (483+463+664) '' sutras'' in the meter. It is a comprehensive text on grammar, and includes ''sutras'' on orthography, phonology, etymology, morphology, semantics, prosody, sentence structure and the significance of context in language. Mayyon as (Vishnu), Seyyon as ( Kanda), Vendhan as (Indra), Varuna as ( Varuna) and Kotṟavai as (Devi or Bagavathi) are the gods mention ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |